
Melbourne cable tramway system
Encyclopedia
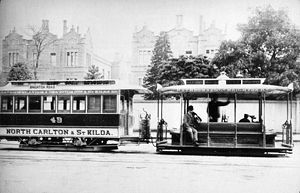
Cable car (railway)
A cable car or cable railway is a mass transit system using rail cars that are hauled by a continuously moving cable running at a constant speed. Individual cars stop and start by releasing and gripping this cable as required...
public transportation
Public transport
Public transport is a shared passenger transportation service which is available for use by the general public, as distinct from modes such as taxicab, car pooling or hired buses which are not shared by strangers without private arrangement.Public transport modes include buses, trolleybuses, trams...
system operated from 1885 to 1940 in Melbourne
Melbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
, Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
.
The system grew to about 75 kilometres (46.6 mi) of double track (103.2 route km or 64.12 route miles) and 1200 cars and trailers, on 17 radiating routes from the centre of Melbourne to neighbouring suburbs. It was one of the largest cable car systems in the world, comparable with the San Francisco
San Francisco cable car system
The San Francisco cable car system is the world's last permanently operational manually operated cable car system, in the US sense of a tramway whose cars are pulled along by cables embedded in the street. It is an icon of San Francisco, California...
and Chicago
Chicago City Railway
The Chicago City Railway was a cable car system, designed by William Eppelsheimer and opened in Chicago in 1882.This system was to become, for a while, the largest and most profitable cable car system in the world. Counter to some people's expectations, the cable cars did not suffer much from the...
cable car networks. George Smith Duncan
George Smith Duncan
George Smith Duncan was a tramway and mining engineer best known for his work on cable trams, and for his work in the gold mining industry.Duncan was born in the New Zealand city of Dunedin in 1852, the son of recent Scottish immigrants...
was appointed as consulting engineer (and subsequently engineer) for the development of the tramway network. The network in Melbourne was built by local Tramway trusts composed of local councils and municipalities, and was operated by the Melbourne Tramway and Omnibus Company from 1885 to 1916 (with the exception of the Northcote tramway, which was privately built and operated), after which the service was transferred to the Victorian Government, and passed to the Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board on 1 November 1919 (the Northcote tramway was transferred to the Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board on 20 February 1920).
Although the first electric tram was introduced in 1885 at Doncaster and ran for 11 years, the electric tram network did not seriously commence until 1906 when the Victorian Railways
Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways operated railways in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations...
built an "Electric Street Railway" from St Kilda railway station to Brighton, and the North Melbourne Electric Tramway and Lighting Company (NMETL) built a feeder line from the terminus of the cable system out towards Essendon. From 1924 the cable tram lines were progressively converted to electric trams with the last Melbourne cable tram operating on 26 October 1940.
Spencer Street - Richmond tramway
Line opened on 11 November 1885. The trams operated along Spencer from Bourke Street to Flinders Street, Flinders Street to Wellington Parade, Bridge Road to Hawthorn BridgeHawthorn Bridge
Hawthorn Bridge crosses the Yarra River five kilometres east of Melbourne connecting Bridge Road and Burwood Road. It was designed by Francis Bell and is the oldest extant bridge over the Yarra River....
. The powerhouse was located on Bridge Road, at Hoddle Street, and has since been demolished for a left turn lane. The remains of the Richmond Cable Tram depot now form part of the Amora Hotel, near Hawthorn Bridge. The trams were double-ended dummy and trailer operated by a single-jaw side grip on a 4' 8½" gauge tram line.
North Fitzroy tramway
Line opened on 2 October 1886 with the powerhouse located on the north east corner of Victoria Parade and Brunswick Street.Victoria Bridge tramway
Line opened on 22 November 1886 with the powerhouse located on the north east corner of Victoria Parade and Brunswick Street.Clifton Hill tramway
Line opened on 10 August 1887 with the powerhouse located on the south east corner of Nicholson Street and Gertrude Street.Nicholson Street tramway
Line opened on 30 August 1887 with the powerhouse located on the south east corner of Nicholson Street and Gertrude Street.Brunswick tramway
Line opened on 1 October 1887 with the powerhouse located on the north west corner of Brunswick Road and Black Street.Johnston Street Bridge (Carlton) tramway
Line opened on 21 December 1887 with the powerhouse located on the north side of Johnston Street, near Brunswick Street.Brighton Road tramway
Line opened on 11 October 1888 with the powerhouse located on the south east corner of St. Kilda Road and Bromby Street.Prahran tramway
Line opened on 26 October 1888 with the powerhouse located on the north west corner of Toorak Road and Chapel Street.North Carlton tramway
Line opened on 9 February 1889 with the powerhouse located at the south west corner of: Rathdowne Street and Park Street.Toorak tramway
Line opened on 15 February 1889 with the powerhouse located on the north west corner of Toorak Road and Chapel Street.North Melbourne tramway
Line opened on 3 March 1890 with the powerhouse located at the south west corner of Queensberry Street and Abbotsford Street.West Melbourne tramway
Line opened on 18 April 1890 with the powerhouse located at the south west corner of Queensberry Street and Abbotsford Street.South Melbourne tramway
Line opened on 17 June 1890 with the powerhouse located on the south side of City Road, near Cecil Street.Port Melbourne tramway
Line opened on 20 June 1890 with the powerhouse located on the south side of City Road, near Cecil Street.Windsor to St. Kilda Esplanade tramway
Line opened on 17 October 1891 with the powerhouse located on the north side of Wellington Street, near Marlton Crescent. This was the first major line to close on 29 August 1925.Northcote tramway
Line opened on 18 February 1890 and was originally operated as an independent line, with the powerhouse located on the north east corner of High Street and Martin Street. This was Melbourne's only privately built and operated cable tramway. The powerhouse building is occupied in 2005 by an automobile service and repair business.External links
Further reading
The Melbourne Cable Trams Matthews, H.H. Australian Railway Historical Society BulletinAustralian Railway History
Australian Railway History , is the premier magazine covering railway history in Australia...
, January 1941

