
Mesosaurus
Encyclopedia
Mesosaurus is an extinct genus
of reptile
from the Early Permian of southern Africa
and South America
. Along with the genus Stereosternum
, it is a member of the family
Mesosauridae and the order
Mesosauria. Mesosaurus was one of the first marine reptile
s, and had many adaptations to a fully aquatic lifestyle. It is usually considered to have been anapsid
, although Friedrich von Huene
considered that it was synapsid
, and this hypothesis has been revived recently.
The bones of the postcranial skeleton are thick, having undergone pachyostosis
. Mesosaurus is unusual among reptiles in that it possesses a cleithrum
. A cleithrum is a type of dermal bone
that overlies the scapula
, and is usually found in more primitive bony fish and tetrapods. The head of the interclavicle
of Mesosaurus is triangular, unlike those of other early reptiles, which are diamond-shaped.
 Mesosaurus was one of the first reptiles to return to the water
Mesosaurus was one of the first reptiles to return to the water
after early tetrapod
s came to land in the Late Devonian or later in the Paleozoic. It was around 1 metres (3.3 ft) in length, with webbed feet, a streamlined body, and a long tail that may have supported a fin. It probably propelled itself through the water with its long hind legs and flexible tail. Its body was also flexible and could easily move sideways, but it had heavily thickened rib
s, which would have prevented it from twisting its body.
Mesosaurus had a small skull
with long jaw
s. The nostril
s were located at the top, allowing the creature to breathe with only the upper side of its head breaking the surface, in a similar manner to a modern crocodile
. The teeth were originally thought to have been straining devices for the filter feeding of plankton
ic organisms. However, this idea was based on the assumption that the teeth of Mesosaurus were numerous and close together in the jaws. Newly examined remains of Mesosaurus show that it had fewer teeth, and that the dentition was suitable for catching small nekton
ic prey such as crustaceans.
 The pachyostosis seen in the bones of Mesosaurus may have enabled it to reach neutral buoyancy
The pachyostosis seen in the bones of Mesosaurus may have enabled it to reach neutral buoyancy
in the upper few meters of the water column. The additional weight may have stabilized the animal at the water's surface. Alternatively, it could have given Mesosaurus greater momentum when gliding underwater. While many features suggest a wholly aquatic lifestyle, Mesosaurus may have been able to move onto land for short periods of time. The elbows and ankles had restricted movement, making walking impossible. It is more likely that if Mesosaurus moved onto land, it would push itself forward in a similar way to living female sea turtle
s when nesting on beaches.
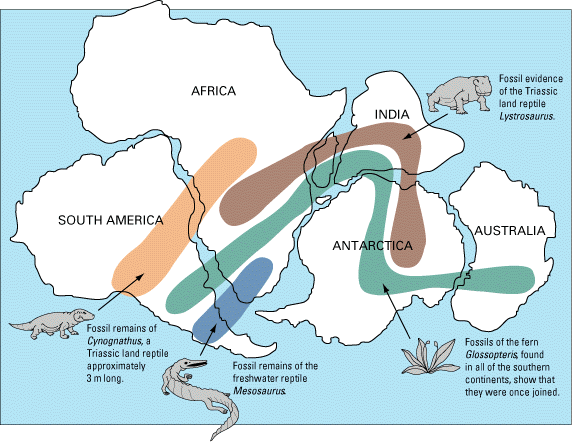 Mesosaurus was significant in providing evidence for the theory
Mesosaurus was significant in providing evidence for the theory
of continental drift
, because its remains were found in southern Africa and eastern South America, two far away places. As Mesosaurus was a coastal animal, and therefore could not have crossed the Atlantic Ocean
, this distribution indicated that the two continents used to be joined together.
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of reptile
Reptile
Reptiles are members of a class of air-breathing, ectothermic vertebrates which are characterized by laying shelled eggs , and having skin covered in scales and/or scutes. They are tetrapods, either having four limbs or being descended from four-limbed ancestors...
from the Early Permian of southern Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
. Along with the genus Stereosternum
Stereosternum
Stereosternum is a genus of mesosaurid marine reptile from the Early Permian of Brazil.-References:Cope, E.D. 1886. A contribution to the vertebrate paleontology of Brazil. Stereosternum tumidum, gen. et sp. nov. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 23:1-21.-External links:*...
, it is a member of the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Mesosauridae and the order
Order (biology)
In scientific classification used in biology, the order is# a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, family, genus, and species, with order fitting in between class and family...
Mesosauria. Mesosaurus was one of the first marine reptile
Marine reptile
Marine reptiles are reptiles which have become secondarily adapted for an aquatic or semi-aquatic life in a marine environment.The earliest marine reptiles arose in the Permian period during the Paleozoic era...
s, and had many adaptations to a fully aquatic lifestyle. It is usually considered to have been anapsid
Anapsid
An anapsid is an amniote whose skull does not have openings near the temples.While "anapsid reptiles" or "anapsida" are traditionally spoken of as if they were a monophyletic group, it has been suggested that several groups of reptiles that had anapsid skulls may be only distantly related...
, although Friedrich von Huene
Friedrich von Huene
Friedrich von Huene was a German paleontologist who named more dinosaurs in the early 20th century than anyone else in Europe.-Biography:...
considered that it was synapsid
Synapsid
Synapsids are a group of animals that includes mammals and everything more closely related to mammals than to other living amniotes. They are easily separated from other amniotes by having an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye, leaving a bony arch beneath each, accounting for their name...
, and this hypothesis has been revived recently.
Description
Mesosaurus had a long skull that was larger than that of Stereosternum and had longer teeth. The teeth are angled outwards, especially those at the tips of the jaws.The bones of the postcranial skeleton are thick, having undergone pachyostosis
Pachyostosis
Pachyostosis is a condition in vertebrate animals in which the bones experience a thickening, resulting in unusually solid bone structure with little to no marrow. It occurs in both terrestrial and aquatic vertebrates, such as manatees and dugongs, plesiosaurs, and members of the Dinocephalia...
. Mesosaurus is unusual among reptiles in that it possesses a cleithrum
Cleithrum
The cleithrum is a membrane bone which first appears as part of the skeleton in primitive bony fish, where it runs vertically along the scapula. Its name is derived from Greek κλειθρον = "key ", by analogy with "clavicle" from Latin clavicula = "little key".In modern fishes, the cleithrum is a...
. A cleithrum is a type of dermal bone
Dermal bone
A dermal bone - bony structures derived from intramembranous ossification that form components of the vertebrate skeleton including the skull, jaws, gills, fins and exoskeleton. In contrast to endochondral bone, dermal bone does not form from cartilage first and then calcify...
that overlies the scapula
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula , omo, or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle ....
, and is usually found in more primitive bony fish and tetrapods. The head of the interclavicle
Interclavicle
An interclavicle is a bone which, in most tetrapods, is located between the clavicles. Therian mammals are the only tetrapods which never have an interclavicle, although some members of other groups also lack one. Monotremes, although part of the mammalian class, do have interclavicles...
of Mesosaurus is triangular, unlike those of other early reptiles, which are diamond-shaped.
Palaeobiology

Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
after early tetrapod
Tetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
s came to land in the Late Devonian or later in the Paleozoic. It was around 1 metres (3.3 ft) in length, with webbed feet, a streamlined body, and a long tail that may have supported a fin. It probably propelled itself through the water with its long hind legs and flexible tail. Its body was also flexible and could easily move sideways, but it had heavily thickened rib
Rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage. In most vertebrates, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other internal organs of the thorax...
s, which would have prevented it from twisting its body.
Mesosaurus had a small skull
Skull
The skull is a bony structure in the head of many animals that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. A skull without a mandible is only a cranium. Animals that have skulls are called craniates...
with long jaw
Jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
s. The nostril
Nostril
A nostril is one of the two channels of the nose, from the point where they bifurcate to the external opening. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates, whose function is to warm air on inhalation and remove moisture on exhalation...
s were located at the top, allowing the creature to breathe with only the upper side of its head breaking the surface, in a similar manner to a modern crocodile
Crocodile
A crocodile is any species belonging to the family Crocodylidae . The term can also be used more loosely to include all extant members of the order Crocodilia: i.e...
. The teeth were originally thought to have been straining devices for the filter feeding of plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
ic organisms. However, this idea was based on the assumption that the teeth of Mesosaurus were numerous and close together in the jaws. Newly examined remains of Mesosaurus show that it had fewer teeth, and that the dentition was suitable for catching small nekton
Nekton
Nekton refers to the aggregate of actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water able to move independently of water currents....
ic prey such as crustaceans.

Neutral buoyancy
Neutral buoyancy is a condition in which a physical body's mass equals the mass it displaces in a surrounding medium. This offsets the force of gravity that would otherwise cause the object to sink...
in the upper few meters of the water column. The additional weight may have stabilized the animal at the water's surface. Alternatively, it could have given Mesosaurus greater momentum when gliding underwater. While many features suggest a wholly aquatic lifestyle, Mesosaurus may have been able to move onto land for short periods of time. The elbows and ankles had restricted movement, making walking impossible. It is more likely that if Mesosaurus moved onto land, it would push itself forward in a similar way to living female sea turtle
Sea turtle
Sea turtles are marine reptiles that inhabit all of the world's oceans except the Arctic.-Distribution:...
s when nesting on beaches.
Distribution

Theory
The English word theory was derived from a technical term in Ancient Greek philosophy. The word theoria, , meant "a looking at, viewing, beholding", and referring to contemplation or speculation, as opposed to action...
of continental drift
Continental drift
Continental drift is the movement of the Earth's continents relative to each other. The hypothesis that continents 'drift' was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596 and was fully developed by Alfred Wegener in 1912...
, because its remains were found in southern Africa and eastern South America, two far away places. As Mesosaurus was a coastal animal, and therefore could not have crossed the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, this distribution indicated that the two continents used to be joined together.

