
Messier 67
Encyclopedia
Messier 67 is an open cluster
in the constellation of Cancer
. M67's Trumpler class is variously given as II 2 r, II 2 m, or II 3 r. It was discovered by Johann Gottfried Koehler
in 1779. Age estimates for the cluster range between 3.2 and 5 billion years, with the most recent estimate (4 Gyr) implying stars in M67 are younger than the Sun
. Distance estimates are likewise varied and typically range between 800-900 pc. Recent estimates of 855, 840, and 815 pc were established via binary star
modelling and infrared
color-magnitude diagram fitting, accordingly.
M67 is not the oldest known open cluster, but there are few Galactic clusters known to be older, and none of those are as close as M67. M67 is an important laboratory for studying stellar evolution
, since the cluster is well populated, obscured by negligible amounts of sut, and all its stars are at the same distance and age, except for approximately 30 anomalous blue straggler
s, whose origins are not fully understood.
M67 is the nearest old open cluster, and thus has become a standard example for studying stellar evolution. It is probably the second best observed open cluster after the Hyades cluster
, which is amongst the nearest open clusters and younger than M67. M67 is one of the most-studied open clusters, yet estimates of its physical parameters such as age, mass, and number of stars of a given type, vary substantially. Richer et al. estimate its age to be 4 Gyr, its mass to be 1080 solar masses, and the number of white dwarf
s to be 150. Hurley et al. estimate its current mass to be 1400 solar masses and its initial mass to be approximately 10 times as great.
M67 has more than 100 stars similar to the Sun, and countless red giant
s. The total star count has been estimated at well over 500. The cluster contains no main sequence
stars bluer than spectral type F
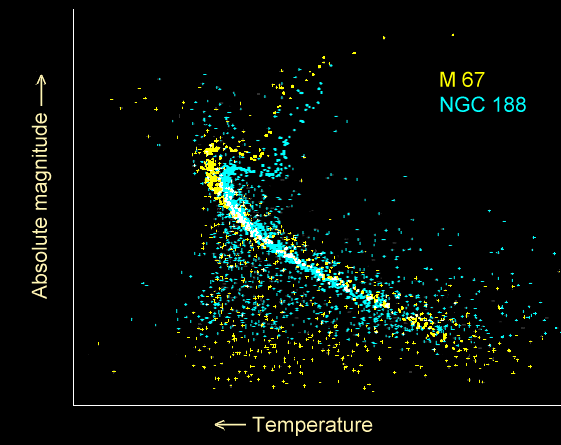
, other than perhaps some of the blue stragglers, since the brighter stars of that age have already left the main sequence. In fact, when the stars of the cluster are plotted on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, there is a distinct "turn-off" representing the stars which have terminated hydrogen fusion in the core and are destined to become red giants. As the cluster ages, the turn-off moves progressively down the main sequence.
 It appears that M67 does not contain an unbiased sample of stars. One cause of this is mass segregation
It appears that M67 does not contain an unbiased sample of stars. One cause of this is mass segregation
, the process by which lighter stars (actually, systems) gain speed at the expense of more massive stars during close encounters, which causes the lighter stars to be at a greater average distance from the center of the cluster or to escape altogether
Open cluster
An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist...
in the constellation of Cancer
Cancer (constellation)
Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as such. Its symbol is . Cancer is small and its stars are faint...
. M67's Trumpler class is variously given as II 2 r, II 2 m, or II 3 r. It was discovered by Johann Gottfried Koehler
Johann Gottfried Koehler
Johann Gottfried Koehler was a German astronomer who discovered a number of nebulae, star clusters, and galaxies....
in 1779. Age estimates for the cluster range between 3.2 and 5 billion years, with the most recent estimate (4 Gyr) implying stars in M67 are younger than the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. Distance estimates are likewise varied and typically range between 800-900 pc. Recent estimates of 855, 840, and 815 pc were established via binary star
Binary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
modelling and infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
color-magnitude diagram fitting, accordingly.
M67 is not the oldest known open cluster, but there are few Galactic clusters known to be older, and none of those are as close as M67. M67 is an important laboratory for studying stellar evolution
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star undergoes a sequence of radical changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from only a few million years to trillions of years .Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single...
, since the cluster is well populated, obscured by negligible amounts of sut, and all its stars are at the same distance and age, except for approximately 30 anomalous blue straggler
Blue straggler
Blue stragglers are main sequence stars in open or globular clusters that are more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turn-off point for the cluster. Blue stragglers were first discovered by Allan Sandage in 1953 while performing photometry of the stars in the globular cluster M3...
s, whose origins are not fully understood.
M67 is the nearest old open cluster, and thus has become a standard example for studying stellar evolution. It is probably the second best observed open cluster after the Hyades cluster
Hyades (star cluster)
The Hyades is the nearest open cluster to the Solar System and one of the best-studied of all star clusters. The Hipparcos satellite, the Hubble Space Telescope, and infrared color-magnitude diagram fitting have been used to establish a distance to the cluster's center of ~153 ly...
, which is amongst the nearest open clusters and younger than M67. M67 is one of the most-studied open clusters, yet estimates of its physical parameters such as age, mass, and number of stars of a given type, vary substantially. Richer et al. estimate its age to be 4 Gyr, its mass to be 1080 solar masses, and the number of white dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
s to be 150. Hurley et al. estimate its current mass to be 1400 solar masses and its initial mass to be approximately 10 times as great.
M67 has more than 100 stars similar to the Sun, and countless red giant
Red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5,000 K and lower...
s. The total star count has been estimated at well over 500. The cluster contains no main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
stars bluer than spectral type F
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
, other than perhaps some of the blue stragglers, since the brighter stars of that age have already left the main sequence. In fact, when the stars of the cluster are plotted on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, there is a distinct "turn-off" representing the stars which have terminated hydrogen fusion in the core and are destined to become red giants. As the cluster ages, the turn-off moves progressively down the main sequence.

Mass segregation
In astronomy, dynamical mass segregation is the process by which heavier members of a gravitationally bound system, such as a star cluster or cluster of galaxies, tend to move toward the center, while lighter members tend to move farther away from the center. Primordial mass segregation is...
, the process by which lighter stars (actually, systems) gain speed at the expense of more massive stars during close encounters, which causes the lighter stars to be at a greater average distance from the center of the cluster or to escape altogether

