
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1
Encyclopedia
The glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, also known as GRM1, is a human gene
which encodes the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) protein.
in the central nervous system and activates both ionotropic
and metabotropic
glutamate receptor
s. Glutamatergic neurotransmission is involved in most aspects of normal brain function and can be perturbed in many neuropathologic conditions. The metabotropic glutamate receptors are a family of G protein-coupled receptor
s, that have been divided into 3 groups on the basis of sequence homology, putative signal transduction mechanisms, and pharmacologic properties. Group I includes GRM1 and GRM5
and these receptors have been shown to activate phospholipase C. Group II includes GRM2
and GRM3
while Group III includes GRM4
, GRM6
, GRM7
and GRM8
. Group II and III receptors are linked to the inhibition of the cyclic AMP cascade but differ in their agonist selectivities. Alternative splice
variants of the GRM1 gene have been described but their full-length nature has not been determined.
mediated gene targeting those mice became deficient in mGlu receptor 1 protein. The mice did not show any basic anatomical changes in the brain but had impaired cerebellar long-term depression
and hippocampal long-term potentiation
. In addition they had impaired motor functions, characterized by impaired balance. In the Morris watermaze test, an assay for learning abilities, those mice needed significantly more time to successfully complete the task.
susceptibility.
s exist on the mGluR1. A respectable number of potent and specific allosteric ligands – predominantly antagonists/inhibitors – has been developed in recent years, although no orthosteric subtype-selective ligands have yet been discovered (2008).
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
which encodes the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) protein.
Function
L-glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitterNeurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
in the central nervous system and activates both ionotropic
Ligand-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channels are one type of ionotropic receptor or channel-linked receptor. They are a group of transmembrane ion channels that are opened or closed in response to the binding of a chemical messenger , such as a neurotransmitter.The binding site of endogenous ligands on LGICs...
and metabotropic
Metabotropic glutamate receptor
The metabotropic glutamate receptors, or mGluRs, are a type of glutamate receptor that are active through an indirect metabotropic process. They are members of the group C family of G-protein-coupled receptors, or GPCRs...
glutamate receptor
Glutamate receptor
Glutamate receptors are synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal cells. Glutamate is one of the 20 amino acids used to assemble proteins and as a result is abundant in many areas of the body, but it also functions as a neurotransmitter and is particularly abundant in the...
s. Glutamatergic neurotransmission is involved in most aspects of normal brain function and can be perturbed in many neuropathologic conditions. The metabotropic glutamate receptors are a family of G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors , also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein-linked receptors , comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal...
s, that have been divided into 3 groups on the basis of sequence homology, putative signal transduction mechanisms, and pharmacologic properties. Group I includes GRM1 and GRM5
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM5 gene.- Function :The amino acid L-glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and activates both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors...
and these receptors have been shown to activate phospholipase C. Group II includes GRM2
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM2 gene.-PAMs:The development of subtype-2-selective positive allosteric modulators experienced steady advance in recent years...
and GRM3
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM3 gene.-Ligands:Though truly mGluR3 selective agents still await their discovery, mixed mGluR2/3 ligands with selectivity over other mGluR-subtypes are known...
while Group III includes GRM4
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 4
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM4 gene.Together with GRM6, GRM7 and GRM8 it belongs to group III of the metabotropic glutamate receptor family. Group III receptors are linked to the inhibition of the cyclic AMP cascade.Activation of GRM4 has...
, GRM6
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 6
Glutamate receptor, metabotropic 6, also known as GRM6, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GRM6 gene.- Function :L-glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and activates both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors...
, GRM7
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 7
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM7 gene.-Agonists:*AMN082: allosteric agonist; induces rapid internalization; non-glutamatergic binding component-Interactions:...
and GRM8
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 8
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM8 gene.-Further reading:...
. Group II and III receptors are linked to the inhibition of the cyclic AMP cascade but differ in their agonist selectivities. Alternative splice
Alternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a process by which the exons of the RNA produced by transcription of a gene are reconnected in multiple ways during RNA splicing...
variants of the GRM1 gene have been described but their full-length nature has not been determined.
Studies with knockout mice
Mice lacking functional glutamate receptor 1 were reported in 1994. By homologous recombinationHomologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks...
mediated gene targeting those mice became deficient in mGlu receptor 1 protein. The mice did not show any basic anatomical changes in the brain but had impaired cerebellar long-term depression
Long-term depression
Long-term depression , in neurophysiology, is an activity-dependent reduction in the efficacy of neuronal synapses lasting hours or longer. LTD occurs in many areas of the CNS with varying mechanisms depending upon brain region and developmental progress...
and hippocampal long-term potentiation
Long-term potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation is a long-lasting enhancement in signal transmission between two neurons that results from stimulating them synchronously. It is one of several phenomena underlying synaptic plasticity, the ability of chemical synapses to change their strength...
. In addition they had impaired motor functions, characterized by impaired balance. In the Morris watermaze test, an assay for learning abilities, those mice needed significantly more time to successfully complete the task.
Clinical significance
Mutations in the GRM1 gene may contribute to melanomaMelanoma
Melanoma is a malignant tumor of melanocytes. Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin. They predominantly occur in skin, but are also found in other parts of the body, including the bowel and the eye...
susceptibility.
Ligands
In addition to the orthosteric site (the site where the endogenous ligand glutamate binds) at least two distinct allosteric binding siteBinding site
In biochemistry, a binding site is a region on a protein, DNA, or RNA to which specific other molecules and ions—in this context collectively called ligands—form a chemical bond...
s exist on the mGluR1. A respectable number of potent and specific allosteric ligands – predominantly antagonists/inhibitors – has been developed in recent years, although no orthosteric subtype-selective ligands have yet been discovered (2008).
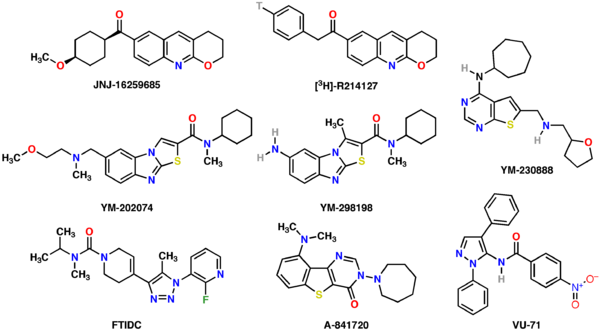
- JNJ-16259685: highly potent, selective non-competitive antagonist
- R-214,127 and [3HRadioligandA radioligand is a radioactive biochemical substance that is used for diagnosis or for research-oriented study of the receptor systems of the body....
]-analog: high-affinity, selective allosteric inhibitor - YM-202,074: high-affinity, selective allosteric antagonist
- YM-230,888: high-affinity, selective allosteric antagonist
- YM-298,198 and [3H]-analog: selective non-competitive antagonist
- FTIDC: highly potent and selective allosteric antagonist/inverse agonist
- A-841,720: potent non-competitive antagonist; minor hmGluR5 binding
- VU-71: potentiator
- Fluorinated 9H-xanthene-9-carboxylic acid oxazol-2-yl-amides: orally available PAMs


