Metering pump
Encyclopedia
A metering pump is a pump
used to pump liquid
s at adjustable flow rates which are precise
when averaged over time. Delivery of fluids in precise adjustable flow rates is sometimes called metering. The term "metering pump" is based on the application or use rather than the exact kind of pump used, although a couple types of pumps are far more suitable than most other types of pumps.
Although metering pumps can pump water
, they are often used to pump chemicals, solution
s, or other liquids. Many metering pumps are rated to be able to pump into a high discharge pressure
. They are typically made to meter at flow rates which are practically constant (when averaged over time) within a wide range of discharge (outlet) pressure. Manufacturers provide each of their models of metering pumps with a maximum discharge pressure rating against which each model is guaranteed to be able to pump against. An engineer, designer, or user should ensure that the pressure and temperature
ratings and wetted pump materials are compatible for the application and the type of liquid being pumped.
Most metering pumps have a pump head and a motor. The liquid being pumped goes through the pump head, entering through an inlet line and leaving through an outlet line. The motor is commonly an electric motor
which drives the pump head.
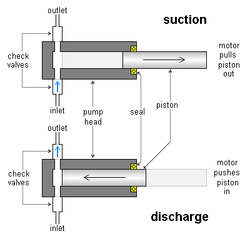
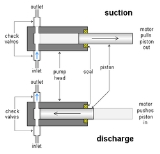
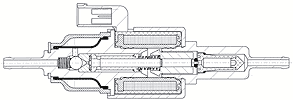 Many metering pumps are piston-driven. Piston pumps are positive displacement pumps which can be designed to pump at practically constant flow rates (averaged over time) against a wide range of discharge pressure, including high discharge pressures of thousands of psi
Many metering pumps are piston-driven. Piston pumps are positive displacement pumps which can be designed to pump at practically constant flow rates (averaged over time) against a wide range of discharge pressure, including high discharge pressures of thousands of psi
.
Piston-driven metering pumps commonly work as follows: There is a piston
(sometimes called plunger), typically cylindrical, which can go in and out of a correspondingly shaped chamber in the pump head. The inlet and outlet lines are joined to the piston chamber. There are two check valve
s, often ball check valves, attached to the pump head, one at the inlet line and the other at the outlet line. The inlet valve allows flow from the inlet line to the piston chamber, but not in the reverse direction. The outlet valve allows flow from the chamber to the outlet line, but not in reverse. The motor repeatedly moves the piston into and out of the piston chamber, causing the volume of the chamber to repeatedly become smaller and larger. When the piston moves out, a vacuum is created. Low pressure in the chamber causes liquid to enter and fill the chamber through the inlet check valve, but higher pressure at the outlet causes the outlet valve to shut. Then when the piston moves in, it pressurizes the liquid in the chamber. High pressure in the chamber causes the inlet valve to shut and forces the outlet valve to open, forcing liquid out at the outlet. These alternating suction
and discharge strokes are repeated over and over to meter the liquid. In back of the chamber, there is packing around the piston or a doughnut-shaped seal with a toroid-shaped sphincter-like spring inside compressing the seal around the piston. This holds the fluid pressure when the piston slides in and out and makes the pump leak-tight. The packing or seals can wear out after prolonged use and can be replaced. The metering rate can be adjusted by varying the strokelength by which the piston moves back and forth or varying the speed of the piston motion.
A single-piston pump delivers liquid to the outlet only during the discharge stroke. If the piston's suction and discharge strokes occur at the same speed and liquid is metered out half the time the pump is working, then the overall metering rate averaged over time equals half the average flow rate during the discharge stroke. Some single-piston pumps may have a constant slow piston motion for discharge and a quick retract motion for refilling the pump head. In such cases, the overall metering rate is practically equal to the pumping rate during the discharge stroke.
such as HPLC
and ion chromatography are much like small piston metering pumps. For wear resistance and chemical resistance to solvents, etc., typically the pistons are made of artificial sapphire
and the ball check valves have ruby
balls and sapphire seats. To produce good chromatograms, it is desirable to have a pumping flow rate as constant as possible. Either a single piston pump with a quick refill is used or a double pump head with coordinated piston strokes is used to provide as constant a pumping rate as possible.
age at the packing or seal particularly when a liquid is dangerous, toxic, or noxious, diaphragm pumps are used for metering. Diaphragm pumps have a diaphragm through which repeated compression/decompression motion is transmitted. The liquid does not penetrate through the diaphragm, so the liquid inside the pump is sealed off from the outside. Such motion changes the volume of a chamber in the pump head so that liquid enters through an inlet check valve during decompression and exits through an outlet check valve during compression, in a manner similar to piston pumps. Diaphragm pumps can also be made which discharge at fairly high pressure. Diaphragm metering pumps are commonly hydraulically driven.
Peristaltic pump
s use motor-driven rollers to roll along flexible tubing, compressing it to push forward a liquid inside. Although peristaltic pumps can be used to meter at lower pressures, the flexible tubing is limited in the level of pressure it can withstand.
downstream of the pump, a pressure relief valve
should be placed in between to prevent overpressuring of the tubing
or piping
line in case the stop valve is inadvertently shut while the pump is running. The relief valve setting should be below the maximum pressure rating that the piping, tubing, or any other components there could withstand.
Liquids are only very slightly compressible. This property of liquids lets metering pumps discharge liquids at high pressure. Since a liquid can be only slightly compressed during a discharge stroke, it is forced out of the pump head. Gas
es are much more compressible. Metering pumps are not good at pumping gases. Sometimes, a metering or similar pump has to be primed before operation, i. e. the pump head filled with the liquid to be pumped. When gas bubbles enter a pump head, the compression motion compresses the gas but has a hard time forcing it out of the pump head. The pump may stop pumping liquid with gas bubbles in the pump head even though mechanically the pump is going through the motions, repeatedly compressing and decompressing the bubbles. To prevent this type of "vapor lock", chromatography solvents are often degassed before pumping.
If the pressure at the outlet is lower than the pressure at the inlet and remains that way in spite of the pumping, then this pressure difference opens both check valves simultaneously and the liquid flows through the pump head uncontrollably from inlet to outlet. This can happen whether the pump is working or not. This situation can avoided by placing a correctly-rated positive pressure differential check valve
downstream of the pump. Such a valve will only open if a minimum rated pressure differential across the valve is exceeded, something which most high pressure metering pumps can easily exceed.
Pump
A pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps...
used to pump liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
s at adjustable flow rates which are precise
Accuracy and precision
In the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
when averaged over time. Delivery of fluids in precise adjustable flow rates is sometimes called metering. The term "metering pump" is based on the application or use rather than the exact kind of pump used, although a couple types of pumps are far more suitable than most other types of pumps.
Although metering pumps can pump water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, they are often used to pump chemicals, solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
s, or other liquids. Many metering pumps are rated to be able to pump into a high discharge pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
. They are typically made to meter at flow rates which are practically constant (when averaged over time) within a wide range of discharge (outlet) pressure. Manufacturers provide each of their models of metering pumps with a maximum discharge pressure rating against which each model is guaranteed to be able to pump against. An engineer, designer, or user should ensure that the pressure and temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
ratings and wetted pump materials are compatible for the application and the type of liquid being pumped.
Most metering pumps have a pump head and a motor. The liquid being pumped goes through the pump head, entering through an inlet line and leaving through an outlet line. The motor is commonly an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
which drives the pump head.
Piston pumps


Pounds per square inch
The pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units...
.
Piston-driven metering pumps commonly work as follows: There is a piston
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from...
(sometimes called plunger), typically cylindrical, which can go in and out of a correspondingly shaped chamber in the pump head. The inlet and outlet lines are joined to the piston chamber. There are two check valve
Check valve
A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a mechanical device, a valve, which normally allows fluid to flow through it in only one direction....
s, often ball check valves, attached to the pump head, one at the inlet line and the other at the outlet line. The inlet valve allows flow from the inlet line to the piston chamber, but not in the reverse direction. The outlet valve allows flow from the chamber to the outlet line, but not in reverse. The motor repeatedly moves the piston into and out of the piston chamber, causing the volume of the chamber to repeatedly become smaller and larger. When the piston moves out, a vacuum is created. Low pressure in the chamber causes liquid to enter and fill the chamber through the inlet check valve, but higher pressure at the outlet causes the outlet valve to shut. Then when the piston moves in, it pressurizes the liquid in the chamber. High pressure in the chamber causes the inlet valve to shut and forces the outlet valve to open, forcing liquid out at the outlet. These alternating suction
Suction
Suction is the flow of a fluid into a partial vacuum, or region of low pressure. The pressure gradient between this region and the ambient pressure will propel matter toward the low pressure area. Suction is popularly thought of as an attractive effect, which is incorrect since vacuums do not...
and discharge strokes are repeated over and over to meter the liquid. In back of the chamber, there is packing around the piston or a doughnut-shaped seal with a toroid-shaped sphincter-like spring inside compressing the seal around the piston. This holds the fluid pressure when the piston slides in and out and makes the pump leak-tight. The packing or seals can wear out after prolonged use and can be replaced. The metering rate can be adjusted by varying the strokelength by which the piston moves back and forth or varying the speed of the piston motion.
A single-piston pump delivers liquid to the outlet only during the discharge stroke. If the piston's suction and discharge strokes occur at the same speed and liquid is metered out half the time the pump is working, then the overall metering rate averaged over time equals half the average flow rate during the discharge stroke. Some single-piston pumps may have a constant slow piston motion for discharge and a quick retract motion for refilling the pump head. In such cases, the overall metering rate is practically equal to the pumping rate during the discharge stroke.
Pumps used in high pressure chromatography
Pumps used in high pressure chromatographyChromatography
Chromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
such as HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography , HPLC, is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.HPLC typically utilizes different types of stationary...
and ion chromatography are much like small piston metering pumps. For wear resistance and chemical resistance to solvents, etc., typically the pistons are made of artificial sapphire
Sapphire
Sapphire is a gemstone variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide , when it is a color other than red or dark pink; in which case the gem would instead be called a ruby, considered to be a different gemstone. Trace amounts of other elements such as iron, titanium, or chromium can give...
and the ball check valves have ruby
Ruby
A ruby is a pink to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum . The red color is caused mainly by the presence of the element chromium. Its name comes from ruber, Latin for red. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires...
balls and sapphire seats. To produce good chromatograms, it is desirable to have a pumping flow rate as constant as possible. Either a single piston pump with a quick refill is used or a double pump head with coordinated piston strokes is used to provide as constant a pumping rate as possible.
Diaphragm and peristaltic pumps
In order to avoid leakLeak
A leak is a hole or other opening, usually unintended and therefore undesired, in a container or fluid-containing system, such as a tank or a ship's hull, through which the contents of the container can escape or outside matter can enter the container...
age at the packing or seal particularly when a liquid is dangerous, toxic, or noxious, diaphragm pumps are used for metering. Diaphragm pumps have a diaphragm through which repeated compression/decompression motion is transmitted. The liquid does not penetrate through the diaphragm, so the liquid inside the pump is sealed off from the outside. Such motion changes the volume of a chamber in the pump head so that liquid enters through an inlet check valve during decompression and exits through an outlet check valve during compression, in a manner similar to piston pumps. Diaphragm pumps can also be made which discharge at fairly high pressure. Diaphragm metering pumps are commonly hydraulically driven.
Peristaltic pump
Peristaltic pump
A peristaltic pump, or roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained within a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing . A rotor with a number of "rollers", "shoes" or "wipers" attached to the external circumference...
s use motor-driven rollers to roll along flexible tubing, compressing it to push forward a liquid inside. Although peristaltic pumps can be used to meter at lower pressures, the flexible tubing is limited in the level of pressure it can withstand.
Possible problems
The maximum pressure rating of a metering pump is actually the top of the discharge pressure range the pump is guaranteed to pump against at a reasonably controllable flow rate. The pump itself is a pressurizing device often capable of exceeding its pressure rating, although not guaranteed to. For this reason, if there is any stop valveValve
A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically pipe fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category...
downstream of the pump, a pressure relief valve
Relief valve
The relief valve is a type of valve used to control or limit the pressure in a system or vessel which can build up by a process upset, instrument or equipment failure, or fire....
should be placed in between to prevent overpressuring of the tubing
Tubing
Tubing may refer to:* Tubing , flexible hose or pipe * Tubing , the act of riding an inner tube* Structural tubing* Plumbing tube used in domestic water systems* Inserting a tube* Brass instrument tubing...
or piping
Piping
Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid....
line in case the stop valve is inadvertently shut while the pump is running. The relief valve setting should be below the maximum pressure rating that the piping, tubing, or any other components there could withstand.
Liquids are only very slightly compressible. This property of liquids lets metering pumps discharge liquids at high pressure. Since a liquid can be only slightly compressed during a discharge stroke, it is forced out of the pump head. Gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es are much more compressible. Metering pumps are not good at pumping gases. Sometimes, a metering or similar pump has to be primed before operation, i. e. the pump head filled with the liquid to be pumped. When gas bubbles enter a pump head, the compression motion compresses the gas but has a hard time forcing it out of the pump head. The pump may stop pumping liquid with gas bubbles in the pump head even though mechanically the pump is going through the motions, repeatedly compressing and decompressing the bubbles. To prevent this type of "vapor lock", chromatography solvents are often degassed before pumping.
If the pressure at the outlet is lower than the pressure at the inlet and remains that way in spite of the pumping, then this pressure difference opens both check valves simultaneously and the liquid flows through the pump head uncontrollably from inlet to outlet. This can happen whether the pump is working or not. This situation can avoided by placing a correctly-rated positive pressure differential check valve
Check valve
A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a mechanical device, a valve, which normally allows fluid to flow through it in only one direction....
downstream of the pump. Such a valve will only open if a minimum rated pressure differential across the valve is exceeded, something which most high pressure metering pumps can easily exceed.

