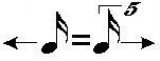
Metric modulation
Encyclopedia
In music
a metric modulation is a change (modulation
) from one time signature
/tempo
(meter
) to another, wherein a note value
from the first is made equivalent to a note value in the second, like a pivot
. The term was invented to describe the practice of Elliott Carter
, who prefers to call it temporal modulation.
For metric modulation to exist 3 things have to occur:
The following formula illustrates how to determine the tempo before or after a metric modulation, or, alternatively, how many of the associated note values will be in each measure before or after the modulation:
Thus if the two half notes in 4/4 time at a tempo of quarter note = 84 are made equivalent with three half notes at a new tempo, that tempo will be:

, Fantasy, mm. 16-17.)
A tempo (or metric) modulation causes a change in the hierarchical relationship between the perceived beat subdivision
and all potential subdivisions belonging to the new tempo. Benadon (2004) has explored some compositional uses of tempo modulations, such as tempo networks and beat subdivision spaces.
For example,
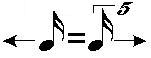
This notation is also normally followed by the new tempo in parentheses.
This is analogous with the assignment in imperative computer languages:
{x = f(x);} ≡ {xnew = f(xold);}
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
a metric modulation is a change (modulation
Modulation (music)
In music, modulation is most commonly the act or process of changing from one key to another. This may or may not be accompanied by a change in key signature. Modulations articulate or create the structure or form of many pieces, as well as add interest...
) from one time signature
Time signature
The time signature is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats are in each measure and which note value constitutes one beat....
/tempo
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo is the speed or pace of a given piece. Tempo is a crucial element of any musical composition, as it can affect the mood and difficulty of a piece.-Measuring tempo:...
(meter
Meter (music)
Meter or metre is a term that music has inherited from the rhythmic element of poetry where it means the number of lines in a verse, the number of syllables in each line and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented...
) to another, wherein a note value
Note value
In music notation, a note value indicates the relative duration of a note, using the color or shape of the note head, the presence or absence of a stem, and the presence or absence of flags/beams/hooks/tails....
from the first is made equivalent to a note value in the second, like a pivot
Pivot
Pivot may refer to:* Pivot, the point of rotation in a lever system* More generally, the center point of any rotational system* Pivot joint, a kind of joint between bones in the body* Pivot turn, a dance move- Computing :...
. The term was invented to describe the practice of Elliott Carter
Elliott Carter
Elliott Cook Carter, Jr. is a two-time Pulitzer Prize-winning American composer born and living in New York City. He studied with Nadia Boulanger in Paris in the 1930s, and then returned to the United States. After a neoclassical phase, he went on to write atonal, rhythmically complex music...
, who prefers to call it temporal modulation.
For metric modulation to exist 3 things have to occur:
- There has to be an exact relationship between two different tempi
- A common pulsePulse (music)In music and music theory, the pulse or tactus consists of beats in a series of identical yet distinct periodic short-duration stimuli perceived as points in time occurring at the mensural level...
must exist between these two tempi - The name and function of the pulse changes.
The following formula illustrates how to determine the tempo before or after a metric modulation, or, alternatively, how many of the associated note values will be in each measure before or after the modulation:
- (Winold 1975, 230-31)
Thus if the two half notes in 4/4 time at a tempo of quarter note = 84 are made equivalent with three half notes at a new tempo, that tempo will be:

, Fantasy, mm. 16-17.)
A tempo (or metric) modulation causes a change in the hierarchical relationship between the perceived beat subdivision
Meter (music)
Meter or metre is a term that music has inherited from the rhythmic element of poetry where it means the number of lines in a verse, the number of syllables in each line and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented...
and all potential subdivisions belonging to the new tempo. Benadon (2004) has explored some compositional uses of tempo modulations, such as tempo networks and beat subdivision spaces.
Score notation
Metric modulations are generally notated as 'note value' = 'note value'.For example,
This notation is also normally followed by the new tempo in parentheses.
This is analogous with the assignment in imperative computer languages:
{x = f(x);} ≡ {xnew = f(xold);}


