Mevalonate kinase
Encyclopedia
Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme
that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene
. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals. This enzyme catalyzes the following reaction;
is a key intermediate, and mevalonate kinase a key early enzyme, in isoprenoid and sterol synthesis.
Mevalonate kinase deficiency caused by mutation of this gene results in mevalonic aciduria, a disease characterized psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and recurrent febrile crises. Defects in this gene also cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome, a disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of fever associated with lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, gastrointestinal dismay and skin rash.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals. This enzyme catalyzes the following reaction;
- ATPAdenosine triphosphateAdenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
+ (R)-mevalonateMevalonic acidMevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
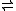 ADPAdenosine diphosphateAdenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine....
ADPAdenosine diphosphateAdenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine....
+ (R)-5-phosphomevalonatePhosphomevalonic acidPhosphomevalonic acid is an intermediate in the Mevalonate pathway....
Function
MevalonateMevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
is a key intermediate, and mevalonate kinase a key early enzyme, in isoprenoid and sterol synthesis.
 |
Clinical significance
Defects can be associated with hyperimmunoglobulinemia D with recurrent fever.Mevalonate kinase deficiency caused by mutation of this gene results in mevalonic aciduria, a disease characterized psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and recurrent febrile crises. Defects in this gene also cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome, a disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of fever associated with lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, gastrointestinal dismay and skin rash.

