Microtrauma
Encyclopedia
Microtrauma is the general term given to small injuries
to the body
.
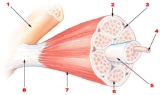
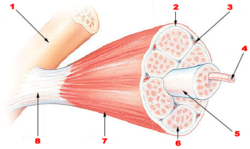 Microtrauma can include the microtearing of muscle fibres, the sheath around the muscle
Microtrauma can include the microtearing of muscle fibres, the sheath around the muscle
and the connective tissue
. It can also include stress to the tendon
s, and to the bone
s (see Wolff's law
). It is unknown whether or not the ligament
s adapt like this. Increased lubrication in response to microtrauma to the bowels is a key factor to the beneficial effects of dietary fibre in increasing bowel robustness, though this is dissimilar to muscular hypertrophy. Microtrauma to the skin (compression, impact, abrasion) can also cause increases in a skin's thickness, as seen from the callus
es formed from running barefoot. This might be due to increased skin cell replication at sites under stress where cells rapidly slough off or undergo compression or abrasion.
Most microtrauma cause a low level of inflammation
that cannot be seen or felt. These injuries can arise in muscle, ligament, vertebrae, and discs, either singly or in combination. Repetitive microtrauma which are not allowed time to heal can result in the development of more serious conditions.
can develop gradually as a result of microtrauma brought about by repetitive activity over time. Because of the slow and progressive onset of this internal injury, the condition is often ignored until the symptoms become acute, often resulting in disabling injury
. Acute back injuries can arise from stressful lifting techniques done without adequate recovery, especially when experimenting with more ballistic work, or work where the extensor spinae are stressed during spinal flexion when much of the load is commonly taken up by the slower to heal ligaments which may not adapt progressively to the stress. While the acute injury may seem to be caused by a single well-defined incident, it may have been preventable or lessened if not for the years of injury to the musculoskeletal support mechanism by repetitive microtrauma.
Injury
-By cause:*Traumatic injury, a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident*Other injuries from external physical causes, such as radiation injury, burn injury or frostbite*Injury from infection...
to the body
Body
With regard to living things, a body is the physical body of an individual. "Body" often is used in connection with appearance, health issues and death...
.

Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
and the connective tissue
Connective tissue
"Connective tissue" is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues . Connective Tissue is found throughout the body.In fact the whole framework of the skeleton and the different specialized connective tissues from the crown of the head to the toes determine the form of...
. It can also include stress to the tendon
Tendon
A tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments and fasciae as they are all made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other...
s, and to the bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s (see Wolff's law
Wolff's law
Wolff's law is a theory developed by the German Anatomist/Surgeon Julius Wolff in the 19th century that states that bone in a healthy person or animal will adapt to the loads it is placed under. If loading on a particular bone increases, the bone will remodel itself over time to become stronger...
). It is unknown whether or not the ligament
Ligament
In anatomy, the term ligament is used to denote any of three types of structures. Most commonly, it refers to fibrous tissue that connects bones to other bones and is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament.Ligament can also refer to:* Peritoneal...
s adapt like this. Increased lubrication in response to microtrauma to the bowels is a key factor to the beneficial effects of dietary fibre in increasing bowel robustness, though this is dissimilar to muscular hypertrophy. Microtrauma to the skin (compression, impact, abrasion) can also cause increases in a skin's thickness, as seen from the callus
Callus
A callus is an especially toughened area of skin which has become relatively thick and hard in response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Rubbing that is too frequent or forceful will cause blisters rather than allow calluses to form. Since repeated contact is required, calluses...
es formed from running barefoot. This might be due to increased skin cell replication at sites under stress where cells rapidly slough off or undergo compression or abrasion.
Most microtrauma cause a low level of inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
that cannot be seen or felt. These injuries can arise in muscle, ligament, vertebrae, and discs, either singly or in combination. Repetitive microtrauma which are not allowed time to heal can result in the development of more serious conditions.
Negative effects
Back painBack pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine.The pain can often be divided into neck pain, upper back pain, lower back pain or tailbone pain...
can develop gradually as a result of microtrauma brought about by repetitive activity over time. Because of the slow and progressive onset of this internal injury, the condition is often ignored until the symptoms become acute, often resulting in disabling injury
Injury
-By cause:*Traumatic injury, a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident*Other injuries from external physical causes, such as radiation injury, burn injury or frostbite*Injury from infection...
. Acute back injuries can arise from stressful lifting techniques done without adequate recovery, especially when experimenting with more ballistic work, or work where the extensor spinae are stressed during spinal flexion when much of the load is commonly taken up by the slower to heal ligaments which may not adapt progressively to the stress. While the acute injury may seem to be caused by a single well-defined incident, it may have been preventable or lessened if not for the years of injury to the musculoskeletal support mechanism by repetitive microtrauma.

