Millman's Theorem
Encyclopedia
In electrical engineering
, Millman's theorem (or the parallel generator theorem) is a method to simplify the solution of a circuit
. Specifically, Millman's theorem is used to compute the voltage
at the ends of a circuit made up of only branches in parallel
.
It is named after Jacob Millman
, who proved the theorem.
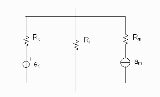
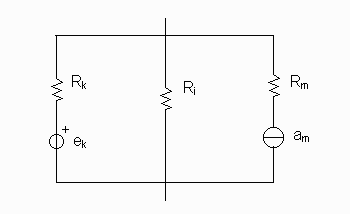 Let ek be the voltage generators
Let ek be the voltage generators
and am the current generators.
Let Ri be the resistance
s on the branches with no generator.
Let Rk be the resistances on the branches with voltage generators.
Let Rm be the resistances on the branches with current generators.
Then Millman states that the voltage at the ends of the circuit is given by:
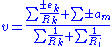
It can be proved by considering the circuit as a single supernode
. Then, according to Ohm
and Kirchhoff
, "the voltage between the ends of the circuit is equal to the total current entering the supernode divided by the total equivalent conductance of the supernode".
The total current is the sum of the currents flowing in each branch.
The total equivalent conductance of the supernode is the sum of the conductance of each branch, since all the branches are in parallel. When computing the equivalent conductance all the generators have to be switched off, so all voltage generators become short circuit
s and all current generators become open circuit
s. That's why the resistances on the branches with current generators do not appear in the expression of the total equivalent conductance.
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, Millman's theorem (or the parallel generator theorem) is a method to simplify the solution of a circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
. Specifically, Millman's theorem is used to compute the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
at the ends of a circuit made up of only branches in parallel
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
.
It is named after Jacob Millman
Jacob Millman
Jacob Millman was a professor of Electrical Engineering at Columbia University....
, who proved the theorem.
Explanation

Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
and am the current generators.
Let Ri be the resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
s on the branches with no generator.
Let Rk be the resistances on the branches with voltage generators.
Let Rm be the resistances on the branches with current generators.
Then Millman states that the voltage at the ends of the circuit is given by:
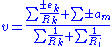
It can be proved by considering the circuit as a single supernode
Supernode (circuit)
In circuit theory, a super-node is a theoretical construct that can be used to solve a circuit. This is done by viewing a voltage source on a wire as a point source voltage in relation to other point voltages located at various nodes in the circuit, relative to a ground node assigned a zero or...
. Then, according to Ohm
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
and Kirchhoff
Kirchhoff's circuit laws
Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities that deal with the conservation of charge and energy in electrical circuits, and were first described in 1845 by Gustav Kirchhoff...
, "the voltage between the ends of the circuit is equal to the total current entering the supernode divided by the total equivalent conductance of the supernode".
The total current is the sum of the currents flowing in each branch.
The total equivalent conductance of the supernode is the sum of the conductance of each branch, since all the branches are in parallel. When computing the equivalent conductance all the generators have to be switched off, so all voltage generators become short circuit
Short circuit
A short circuit in an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path, often where essentially no electrical impedance is encountered....
s and all current generators become open circuit
Open circuit
The term Open circuit may refer to:*Open-circuit scuba, a type of SCUBA-diving equipment where the user breathes from the set and then exhales to the surroundings without recycling the exhaled air...
s. That's why the resistances on the branches with current generators do not appear in the expression of the total equivalent conductance.

