
Electrical generator
Encyclopedia

Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy
Mechanical energy
In physics, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy present in the components of a mechanical system. It is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object. The law of conservation of energy states that in an isolated system that is only subject to...
to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
(usually carried by electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s) to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump
Water Pump
Water Pump is one of the neighbourhoods of Gulberg Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. It is near main Water Pump that supplies fresh water to the city of Karachi....
, which causes water to flow (but does not create water). The source of mechanical energy may be a reciprocating or turbine steam engine
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
, water falling through a turbine or waterwheel
Hydropower
Hydropower, hydraulic power, hydrokinetic power or water power is power that is derived from the force or energy of falling water, which may be harnessed for useful purposes. Since ancient times, hydropower has been used for irrigation and the operation of various mechanical devices, such as...
, an internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
, a wind turbine
Wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
, a hand crank
Crank (mechanism)
A crank is an arm attached at right angles to a rotating shaft by which reciprocating motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. It is used to change circular into reciprocating motion, or reciprocating into circular motion. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm...
, compressed air
Compressed air
Compressed air is air which is kept under a certain pressure, usually greater than that of the atmosphere. In Europe, 10 percent of all electricity used by industry is used to produce compressed air, amounting to 80 terawatt hours consumption per year....
or any other source of mechanical energy.


Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
, and motors and generators have many similarities. In fact many motors can be mechanically driven to generate electricity, and very frequently make acceptable generators.
Historical developments
Before the connection between magnetismMagnetism
Magnetism is a property of materials that respond at an atomic or subatomic level to an applied magnetic field. Ferromagnetism is the strongest and most familiar type of magnetism. It is responsible for the behavior of permanent magnets, which produce their own persistent magnetic fields, as well...
and electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
was discovered, electrostatic generator
Electrostatic generator
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is a mechanical device that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current...
s were invented that used electrostatic principles. These generated very high voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
s and low current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
s. They operated by using moving electrically charged
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
belts, plates and disks to carry charge to a high potential electrode. The charge was generated using either of two mechanisms:
- Electrostatic inductionElectrostatic inductionElectrostatic induction is a redistribution of electrical charge in an object, caused by the influence of nearby charges. Induction was discovered by British scientist John Canton in 1753 and Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke in 1762. Electrostatic generators, such as the Wimshurst machine, the...
- The triboelectric effectTriboelectric effectThe triboelectric effect is a type of contact electrification in which certain materials become electrically charged after they come into contact with another different material and are then separated...
, where the contact between two insulators leaves them charged.
Because of their inefficiency and the difficulty of insulating
Electrical insulation
thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation...
machines producing very high voltages, electrostatic generators had low power ratings and were never used for generation of commercially significant quantities of electric power. The Wimshurst machine
Wimshurst machine
The Wimshurst influence machine is an electrostatic generator, a machine for generating high voltages developed between 1880 and 1883 by British inventor James Wimshurst ....
and Van de Graaff generator
Van de Graaff generator
A Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate very high voltages on a hollow metal globe on the top of the stand. It was invented in 1929 by American physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff. The potential differences achieved in modern Van de Graaff...
are examples of these machines that have survived.
Jedlik's dynamo
In 1827, Hungarian Anyos JedlikÁnyos Jedlik
Stephen Ányos Jedlik was a Hungarian inventor, engineer, physicist, and Benedictine priest. He was also member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and author of several books. He is considered by Hungarians and Slovaks to be the unsung father of the dynamo and electric motor.-Career:He was born...
started experimenting with electromagnetic rotating devices which he called electromagnetic self-rotors. In the prototype of the single-pole electric starter (finished between 1852 and 1854) both the stationary and the revolving parts were electromagnetic. He formulated the concept of the dynamo at least 6 years before Siemens
Ernst Werner von Siemens
Ernst Werner Siemens, von Siemens since 1888, was a German inventor and industrialist. Siemens' name has been adopted as the SI unit of electrical conductance, the siemens...
and Wheatstone
Charles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS , was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope , and the Playfair cipher...
but didn't patent it as he thought he wasn't the first to realize this. In essence the concept is that instead of permanent magnets, two electromagnets opposite to each other induce the magnetic field around the rotor. It was also the discovery of the principle of self-excitation.
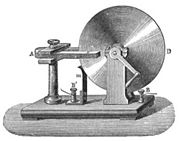
Faraday's disk
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday, FRS was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry....
discovered the operating principle of electromagnetic generators. The principle, later called Faraday's law
Faraday's law of induction
Faraday's law of induction dates from the 1830s, and is a basic law of electromagnetism relating to the operating principles of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors and generators...
, is that an electromotive force
Electromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
is generated in an electrical conductor that encircles a varying magnetic flux
Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux , is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a given surface . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber...
. He also built the first electromagnetic generator, called the Faraday disk, a type of homopolar generator
Homopolar generator
A homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc rotating in a plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential difference is created between the center of the disc and the rim, the electrical polarity depending on the direction of...
, using a copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
disc rotating between the poles of a horseshoe magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
. It produced a small DC voltage.
This design was inefficient due to self-cancelling counterflows of current in regions not under the influence of the magnetic field. While current was induced directly underneath the magnet, the current would circulate backwards in regions outside the influence of the magnetic field. This counterflow limits the power output to the pickup wires and induces waste heating of the copper disc. Later homopolar generators would solve this problem by using an array of magnets arranged around the disc perimeter to maintain a steady field effect in one current-flow direction.
Another disadvantage was that the output voltage was very low, due to the single current path through the magnetic flux. Experimenters found that using multiple turns of wire in a coil could produce higher more useful voltages. Since the output voltage is proportional to the number of turns, generators could be easily designed to produce any desired voltage by varying the number of turns. Wire windings became a basic feature of all subsequent generator designs.
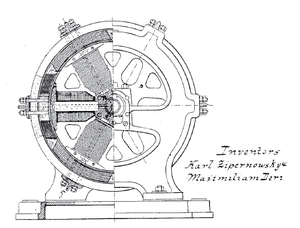
Dynamo

Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
principles to convert mechanical rotation into pulsed DC
Pulsed DC
Pulsed DC or PDC is the form of wave produced from a half-wave rectifier or a full-wave rectifier. Full wave rectified ac is more commonly known as Rectified AC. PDC has some characteristics of both alternating current and direct current waveforms...
through the use of a commutator
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
. The first dynamo was built by Hippolyte Pixii
Hippolyte Pixii
Hippolyte Pixii was an instrument maker from Paris, France. In 1832 he built an early form of alternating current electrical generator, based on the principle of magnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday. Pixii's device was a spinning magnet, operated by a hand crank, where the North and...
in 1832.
Through a series of accidental discoveries, the dynamo became the source of many later inventions, including the DC electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
, the AC alternator
Alternator
An alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
, the AC synchronous motor
Synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC motor distinguished by a rotor spinning with coils passing magnets at the same rate as the power supply frequency and resulting rotating magnetic field which drives it....
, and the rotary converter
Rotary converter
A rotary converter is a type of electrical machine which acts as a mechanical rectifier or inverter. It was used to convert AC to DC or DC to AC power before the advent of chemical or solid state power rectification...
.
A dynamo machine consists of a stationary structure, which provides a constant magnetic field, and a set of rotating windings which turn within that field. On small machines the constant magnetic field may be provided by one or more permanent magnets; larger machines have the constant magnetic field provided by one or more electromagnets, which are usually called field coils.
Large power generation dynamos are now rarely seen due to the now nearly universal use of alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
for power distribution and solid state
Solid state (electronics)
Solid-state electronics are those circuits or devices built entirely from solid materials and in which the electrons, or other charge carriers, are confined entirely within the solid material...
electronic AC to DC power conversion. But before the principles of AC were discovered, very large direct-current dynamos were the only means of power generation and distribution. Now power generation dynamos are mostly a curiosity.
Alternator
Without a commutatorCommutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
, a dynamo becomes an alternator
Alternator
An alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
, which is a synchronous singly fed generator. When used to feed an electric power grid
Grid (electricity)
An electrical grid is a vast, interconnected network for delivering electricity from suppliers to consumers. It consists of three main components: 1) generating plants that produce electricity from combustible fuels or non-combustible fuels ; 2) transmission lines that carry electricity from power...
, an alternator must always operate at a constant speed that is precisely synchronized to the electrical frequency of the power grid. A DC generator can operate at any speed within mechanical limits, but always outputs direct current.
Typical alternators use a rotating field winding excited with direct current, and a stationary (stator) winding that produces alternating current. Since the rotor field only requires a tiny fraction of the power generated by the machine, the brushes for the field contact can be relatively small. In the case of a brushless exciter, no brushes are used at all and the rotor shaft carries rectifiers to excite the main field winding.
Other rotating electromagnetic generators
Other types of generators, such as the asynchronous or induction singly fed generator, the doubly fed generator, or the brushless wound-rotor doubly fed generator, do not incorporate permanent magnets or field windings (i.e., electromagnets) that establish a constant magnetic field, and as a result, are seeing success in variable speed constant frequency applications, such as wind turbineWind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
s or other renewable energy technologies
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
.
The full output performance of any generator can be optimized with electronic control but only the doubly fed generators or the brushless wound-rotor doubly fed generator incorporate electronic control with power ratings that are substantially less than the power output of the generator under control, a feature which, by itself, offers cost, reliability and efficiency benefits.
MHD generator
A magnetohydrodynamic generator directly extracts electric power from moving hot gases through a magnetic field, without the use of rotating electromagnetic machinery. MHD generators were originally developed because the output of a plasma MHD generator is a flame, well able to heat the boilers of a steamRankine cycle
The Rankine cycle is a cycle that converts heat into work. The heat is supplied externally to a closed loop, which usually uses water. This cycle generates about 90% of all electric power used throughout the world, including virtually all solar thermal, biomass, coal and nuclear power plants. It is...
power plant. The first practical design was the AVCO Mk. 25, developed in 1965. The U.S. government funded substantial development, culminating in a 25 MW demonstration plant in 1987. In the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
from 1972 until the late 1980s, the MHD plant U 25 was in regular commercial operation on the Moscow power system with a rating of 25 MW, the largest MHD plant rating in the world at that time. MHD generators operated as a topping cycle are currently (2007) less efficient than combined-cycle gas turbines.
Terminology
The two main parts of a generator or motor can be described in either mechanical or electrical terms.Mechanical:
- RotorRotor (electric)The rotor is the non-stationary part of a rotary electric motor, electric generator or alternator, which rotates because the wires and magnetic field of the motor are arranged so that a torque is developed about the rotor's axis. In some designs, the rotor can act to serve as the motor's armature,...
: The rotating part of an electrical machineElectrical machineAn electrical machine is the generic name for a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, or changes alternating current from one voltage level to a different voltage level.... - StatorStatorThe stator is the stationary part of a rotor system, found in an electric generator, electric motor and biological rotors.Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the field magnet, interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the...
: The stationary part of an electrical machine
Electrical:
- ArmatureArmature (electrical engineering)In electrical engineering, an armature generally refers to one of the two principal electrical components of an electromechanical machine–generally in a motor or generator, but it may also mean the pole piece of a permanent magnet or electromagnet, or the moving iron part of a solenoid or relay....
: The power-producing component of an electrical machine. In a generator, alternator, or dynamo the armature windings generate the electric current. The armature can be on either the rotor or the stator. - FieldField coilA field coil is a component of an electro-magnetic machine, typically a rotating electrical machine such as a motor or generator. A current-carrying coil is used to generate a magnetic field....
: The magnetic field component of an electrical machine. The magnetic field of the dynamo or alternator can be provided by either electromagnets or permanent magnets mounted on either the rotor or the stator.
Because power transferred into the field circuit is much less than in the armature circuit, AC generators nearly always have the field winding on the rotor and the stator as the armature winding. Only a small amount of field current must be transferred to the moving rotor, using slip ring
Slip ring
A slip ring is a method of making an electrical connection through a rotating assembly. Slip rings, also called rotary electrical interfaces, rotating electrical connectors, collectors, swivels, or electrical rotary joints, are commonly found in electric motors, electrical generators for AC...
s. Direct current machines (dynamos) require a commutator
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
on the rotating shaft to convert the alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
produced by the armature to direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
, so the armature winding is on the rotor of the machine.
Excitation

An electric generator or electric motor that uses field coils rather than permanent magnets requires a current to be present in the field coils for the device to be able to work. If the field coils are not powered, the rotor in a generator can spin without producing any usable electrical energy, while the rotor of a motor may not spin at all.
Smaller generators are sometimes self-excited, which means the field coils are powered by the current produced by the generator itself. The field coils are connected in series or parallel with the armature winding. When the generator first starts to turn, the small amount of remanent magnetism present in the iron core provides a magnetic field to get it started, generating a small current in the armature. This flows through the field coils, creating a larger magnetic field which generates a larger armature current. This "bootstrap" process continues until the magnetic field in the core levels off due to saturation
Saturation (magnetic)
Seen in some magnetic materials, saturation is the state reached when an increase in applied external magnetizing field H cannot increase the magnetization of the material further, so the total magnetic field B levels off...
and the generator reaches a steady state power output.
Very large power station generators often utilize a separate smaller generator to excite the field coils of the larger. In the event of a severe widespread power outage
Power outage
A power outage is a short- or long-term loss of the electric power to an area.There are many causes of power failures in an electricity network...
where islanding
Islanding
Islanding refers to the condition in which a distributed generation generator continues to power a location even though electrical grid power from the electric utility is no longer present. Islanding can be dangerous to utility workers, who may not realize that a circuit is still powered, and it...
of power stations has occurred, the stations may need to perform a black start
Black start
A black start is the process of restoring a power station to operation without relying on the external electric power transmission network.Normally, the electric power used within the plant is provided from the station's own generators...
to excite the fields of their largest generators, in order to restore customer power service.
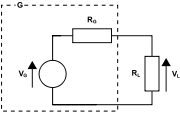
Equivalent circuit
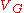 and
and  parameters can be determined by measuring the winding resistance (corrected to operating temperature), and measuring the open-circuit and loaded voltage for a defined current load.
parameters can be determined by measuring the winding resistance (corrected to operating temperature), and measuring the open-circuit and loaded voltage for a defined current load.Vehicle-mounted generators
Early motor vehicles until about the 1960s tended to use DC generators with electromechanical regulators. These have now been replaced by alternatorAlternator
An alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
s with built-in rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
circuits, which are less costly and lighter for equivalent output. Moreover, the power output of a DC generator is proportional to rotational speed, whereas the power output of an alternator is independent of rotational speed. As a result, the charging output of an alternator at engine idle speed can be much greater than that of a DC generator. Automotive alternators power the electrical systems on the vehicle and recharge the battery
Car battery
An automotive battery is a type of rechargeable battery that supplies electric energy to an automobile. Usually this refers to an SLI battery to power the starter motor, the lights, and the ignition system of a vehicle’s engine...
after starting. Rated output will typically be in the range 50-100 A at 12 V, depending on the designed electrical load within the vehicle. Some cars now have electrically powered steering assistance
Power steering
Power steering helps drivers steer vehicles by augmenting steering effort of the steering wheel.Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver needs to provide only modest effort regardless of conditions. Power steering helps considerably when a...
and air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
, which places a high load on the electrical system. Large commercial vehicles are more likely to use 24 V to give sufficient power at the starter motor to turn over a large diesel engine
Diesel engine
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber...
. Vehicle alternators do not use permanent magnets and are typically only 50-60% efficient over a wide speed range.Horst Bauer Bosch Automotive Handbook 4th Edition Robert Bosch GmbH, Stuttgart 1996 ISBN 0-8376-0333-1, page 813 Motorcycle alternators often use permanent magnet stator
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotor system, found in an electric generator, electric motor and biological rotors.Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the field magnet, interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the...
s made with rare earth
Rare earth element
As defined by IUPAC, rare earth elements or rare earth metals are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium...
magnets, since they can be made smaller and lighter than other types. See also hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
.
Some of the smallest generators commonly found power bicycle lights
Bicycle lighting
Bicycle lighting improves the visibility of the bicycle rider to others in dark conditions, i.e. to increase the rider's conspicuity and to enhance the ability of the rider to see, illuminating the way forward. Both reflectors and active lights are used to make the rider more visible, and many ...
. These tend to be 0.5 ampere, permanent-magnet alternators supplying 3-6 W at 6 V or 12 V. Being powered by the rider, efficiency is at a premium, so these may incorporate rare-earth magnet
Rare-earth magnet
Rare-earth magnets are strong permanent magnets made from alloys of rare earth elements. Developed in the 1970s and 80s, rare-earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets made and have significant performance advantages over ferrite or alnico magnets...
s and are designed and manufactured with great precision. Nevertheless, the maximum efficiency is only around 80% for the best of these generators—60% is more typical—due in part to the rolling friction at the tyre–generator interface from poor alignment, the small size of the generator, bearing losses and cheap design. The use of permanent magnets means that efficiency falls even further at high speeds because the magnetic field strength cannot be controlled in any way. Hub generators remedy many of these flaws since they are internal to the bicycle hub and do not require an interface between the generator and tyre. Until recently, these generators have been expensive and hard to find. Major bicycle component manufacturers like Shimano and SRAM have only just entered this market. However, significant gains can be expected in future as cycling becomes more mainstream transportation and LED technology allows brighter lighting at the reduced current these generators are capable of providing.
Sailing yachts may use a water or wind powered generator to trickle-charge the batteries. A small propeller
Propeller
A propeller is a type of fan that transmits power by converting rotational motion into thrust. A pressure difference is produced between the forward and rear surfaces of the airfoil-shaped blade, and a fluid is accelerated behind the blade. Propeller dynamics can be modeled by both Bernoulli's...
, wind turbine
Wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
or impeller
Impeller
An impeller is a rotor inside a tube or conduit used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid.- Impellers in pumps :...
is connected to a low-power alternator and rectifier to supply currents of up to 12 A at typical cruising speeds.
Engine-generator
An engine-generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engineEngine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
(prime mover) mounted together to form a single piece of self-contained equipment. The engines used are usually piston engines, but gas turbines can also be used. Many different versions are available - ranging from very small portable petrol powered sets to large turbine installations.
Human powered electrical generators
A generator can also be driven by human muscle power (for instance, in field radio station equipment).Human powered direct current generators are commercially available, and have been the project of some DIY enthusiasts. Typically operated by means of pedal power, a converted bicycle trainer, or a foot pump, such generators can be practically used to charge batteries, and in some cases are designed with an integral inverter. The average adult could generate about 125-200 watts on a pedal powered generator, but at a power of 200 W, a typical healthy human will reach complete exhaustion and fail to produce any more power after approximately 1.3 hours. Portable radio receivers with a crank are made to reduce battery purchase requirements, see clockwork radio
Clockwork radio
A windup radio or clockwork radio is a radio that is powered by human muscle power rather than batteries or the electrical grid. In the most common arrangement, an internal electrical generator is run by a mainspring, which is wound by a hand crank on the case. Turning the crank winds the spring...
. During the mid 20th century, pedal powered radios were used throughout the Australian outback, to provide schooling,(school of the air) medical and other needs in remote stations and towns.
Linear electric generator
In the simplest form of linear electric generator, a sliding magnetMagnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
moves back and forth through a solenoid
Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. Solenoids are important because they can create...
- a spool of copper wire. An alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
is induced in the loops of wire by Faraday's law of induction
Faraday's law of induction
Faraday's law of induction dates from the 1830s, and is a basic law of electromagnetism relating to the operating principles of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors and generators...
each time the magnet slides through. This type of generator is used in the Faraday flashlight
Faraday Flashlight
A mechanically powered flashlight is one of several varieties of flashlight that are powered by electricity generated by the muscle power of the user, so they do not need replacement of batteries, or recharging from an electrical source...
. Larger linear electricity generators are used in wave power
Wave power
Wave power is the transport of energy by ocean surface waves, and the capture of that energy to do useful work — for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or the pumping of water...
schemes.
Tachogenerator
Tachogenerators are frequently used to power tachometerTachometer
A tachometer is an instrument measuring the rotation speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. The device usually displays the revolutions per minute on a calibrated analogue dial, but digital displays are increasingly common...
s to measure the speeds of electric motors, engines, and the equipment they power. Generators generate voltage roughly proportional to shaft speed. With precise construction and design, generators can be built to produce very precise voltages for certain ranges of shaft speeds
See also
- Faraday's law of inductionFaraday's law of inductionFaraday's law of induction dates from the 1830s, and is a basic law of electromagnetism relating to the operating principles of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors and generators...
- AlternatorAlternatorAn alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
- Homopolar generatorHomopolar generatorA homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc rotating in a plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential difference is created between the center of the disc and the rim, the electrical polarity depending on the direction of...
- Superconducting electric machineSuperconducting electric machineSuperconducting electric machines are electromechanical systems that rely on the use of one or more superconducting elements. Since superconductors have no DC resistance, they typically have greater efficiency...
- Hybrid vehicleHybrid vehicleA hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
- Solar cellSolar cellA solar cell is a solid state electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect....
- Radioisotope thermoelectric generatorRadioisotope thermoelectric generatorA radioisotope thermoelectric generator is an electrical generator that obtains its power from radioactive decay. In such a device, the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioactive material is converted into electricity by the Seebeck effect using an array of thermocouples.RTGs can be...
- ThermogeneratorThermogeneratorThermoelectric generators are devices which convert heat directly into electrical energy, using a phenomenon called the "Seebeck effect" . Their typical efficiencies are around 5-10%...
- Wind turbineWind turbineA wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
- Diesel generatorDiesel generatorA diesel generator is the combination of a diesel engine with an electrical generator to generate electrical energy....
- Turbine hallTurbine HallThe turbine hall, generating hall or turbine building is a building that is a part of any steam cycle or hydroelectric power plant which houses a number of components vital to the generation of electricity from the steam that comes from the boiler, or from the water coming from the reservoir...

