
Direct current
Encyclopedia
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge
. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouple
s, solar cell
s, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo
type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductor
s, insulator
s, or even through a vacuum
as in electron or ion beams. The electric charge
flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current
(AC). A term formerly used
for direct current was galvanic current.
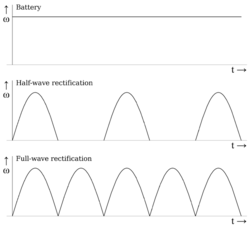 Direct current may be obtained from an alternating current supply by use of a current-switching arrangement called a rectifier
Direct current may be obtained from an alternating current supply by use of a current-switching arrangement called a rectifier
, which contains electronic
elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be made into alternating current with an inverter
or a motor-generator set.
The first commercial electric power transmission
(developed by Thomas Edison
in the late nineteenth century) used direct current. Because of the significant advantages of alternating current over direct current in transforming and transmission, electric power distribution is nearly all alternating current today. In the mid 1950s, HVDC transmission was developed, which is now replacing the older high voltage alternating current systems. For applications requiring direct current, such as third rail
power systems, alternating current is distributed to a substation, which utilizes a rectifier
to convert the power to direct current. See War of Currents
.
Direct current is used to charge batteries, and in nearly all electronic systems, as the power supply. Very large quantities of direct-current power are used in production of aluminum and other electrochemical
processes. Direct current is used for some railway propulsion, especially in urban areas. High-voltage direct current
is used to transmit large amounts of power from remote generation sites or to interconnect alternating current power grids.
, the term DC is used to refer to power systems that use only one polarity of voltage or current, and to refer to the constant, zero-frequency, or slowly varying local mean value of a voltage or current. For example, the voltage across a DC voltage source
is constant as is the current through a DC current source
. The DC solution of an electric circuit is the solution where all voltages and currents are constant. It can be shown that any stationary
voltage or current waveform can be decomposed into a sum of a DC component and a zero-mean time-varying component; the DC component is defined to be the expected value, or the average value of the voltage or current over all time.
Although DC stands for "direct current", DC often refers to "constant polarity". Under this definition, DC voltages can vary in time, as seen in the raw output of a rectifier or the fluctuating voice signal on a telephone line.
Some forms of DC (such as that produced by a voltage regulator
) have almost no variations in voltage
, but may still have variations in output power
and current.
, switch
es, and fixtures, mostly due to the low voltages used, from those suitable for alternating current. It is usually important with a direct-current appliance not to reverse polarity unless the device has a diode bridge
to correct for this (most battery-powered devices do not).
 DC is commonly found in many low-voltage
DC is commonly found in many low-voltage
applications, especially where these are powered by batteries
, which can produce only DC, or solar power
systems, since solar cell
s can produce only DC. Most automotive applications use DC, although the alternator
is an AC device which uses a rectifier
to produce DC. Most electronic
circuits require a DC power supply
. Applications using fuel cells (mixing hydrogen and oxygen together with a catalyst to produce electricity and water as byproducts) also produce only DC.
Many telephone
s connect to a twisted pair
of wires, and internally separate the AC component of the voltage between the two wires (the audio signal) from the DC component of the voltage between the two wires (used to power the phone).
Telephone exchange
communication equipment, such as DSLAM, uses standard -48V DC power supply. The negative polarity is achieved by grounding
the positive terminal of power supply system and the battery
bank. This is done to prevent electrolysis
depositions.
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouple
Thermocouple
A thermocouple is a device consisting of two different conductors that produce a voltage proportional to a temperature difference between either end of the pair of conductors. Thermocouples are a widely used type of temperature sensor for measurement and control and can also be used to convert a...
s, solar cell
Solar cell
A solar cell is a solid state electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect....
s, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo
Dynamo
- Engineering :* Dynamo, a magnetic device originally used as an electric generator* Dynamo theory, a theory relating to magnetic fields of celestial bodies* Solar dynamo, the physical process that generates the Sun's magnetic field- Software :...
type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
s, insulator
Electrical insulation
thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation...
s, or even through a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
as in electron or ion beams. The electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC). A term formerly used
Archaism
In language, an archaism is the use of a form of speech or writing that is no longer current. This can either be done deliberately or as part of a specific jargon or formula...
for direct current was galvanic current.

Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
, which contains electronic
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be made into alternating current with an inverter
Inverter (electrical)
An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
or a motor-generator set.
The first commercial electric power transmission
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
(developed by Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
in the late nineteenth century) used direct current. Because of the significant advantages of alternating current over direct current in transforming and transmission, electric power distribution is nearly all alternating current today. In the mid 1950s, HVDC transmission was developed, which is now replacing the older high voltage alternating current systems. For applications requiring direct current, such as third rail
Third rail
A third rail is a method of providing electric power to a railway train, through a semi-continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a railway track. It is used typically in a mass transit or rapid transit system, which has alignments in its own corridors, fully or almost...
power systems, alternating current is distributed to a substation, which utilizes a rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
to convert the power to direct current. See War of Currents
War of Currents
In the "War of Currents" era in the late 1880s, George Westinghouse and Thomas Edison became adversaries due to Edison's promotion of direct current for electric power distribution over alternating current advocated by several European companies and Westinghouse Electric based out of Pittsburgh,...
.
Direct current is used to charge batteries, and in nearly all electronic systems, as the power supply. Very large quantities of direct-current power are used in production of aluminum and other electrochemical
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
processes. Direct current is used for some railway propulsion, especially in urban areas. High-voltage direct current
High-voltage direct current
A high-voltage, direct current electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and suffer lower electrical losses...
is used to transmit large amounts of power from remote generation sites or to interconnect alternating current power grids.
Various definitions
Within electrical engineeringElectrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, the term DC is used to refer to power systems that use only one polarity of voltage or current, and to refer to the constant, zero-frequency, or slowly varying local mean value of a voltage or current. For example, the voltage across a DC voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
is constant as is the current through a DC current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
. The DC solution of an electric circuit is the solution where all voltages and currents are constant. It can be shown that any stationary
Stationary process
In the mathematical sciences, a stationary process is a stochastic process whose joint probability distribution does not change when shifted in time or space...
voltage or current waveform can be decomposed into a sum of a DC component and a zero-mean time-varying component; the DC component is defined to be the expected value, or the average value of the voltage or current over all time.
Although DC stands for "direct current", DC often refers to "constant polarity". Under this definition, DC voltages can vary in time, as seen in the raw output of a rectifier or the fluctuating voice signal on a telephone line.
Some forms of DC (such as that produced by a voltage regulator
Voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple "feed-forward" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components...
) have almost no variations in voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
, but may still have variations in output power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
and current.
Applications
Direct-current installations usually have different types of socketsJack (connector)
In electronics and electrical assemblies, the term jack commonly refers to a surface-mounted connector, often, but not always, with the female electrical contact or socket, and is the "more fixed" connector of a connector pair...
, switch
Switch
In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another....
es, and fixtures, mostly due to the low voltages used, from those suitable for alternating current. It is usually important with a direct-current appliance not to reverse polarity unless the device has a diode bridge
Diode bridge
A diode bridge is an arrangement of four diodes in a bridge circuit configuration that provides the same polarity of output for either polarity of input. When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating current input into direct current a output, it is known as a...
to correct for this (most battery-powered devices do not).

Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
applications, especially where these are powered by batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
, which can produce only DC, or solar power
Solar power
Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity and biomass, account for most of the available...
systems, since solar cell
Solar cell
A solar cell is a solid state electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect....
s can produce only DC. Most automotive applications use DC, although the alternator
Alternator
An alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
is an AC device which uses a rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
to produce DC. Most electronic
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
circuits require a DC power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
. Applications using fuel cells (mixing hydrogen and oxygen together with a catalyst to produce electricity and water as byproducts) also produce only DC.
Many telephone
Telephone
The telephone , colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that transmits and receives sounds, usually the human voice. Telephones are a point-to-point communication system whose most basic function is to allow two people separated by large distances to talk to each other...
s connect to a twisted pair
Twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs...
of wires, and internally separate the AC component of the voltage between the two wires (the audio signal) from the DC component of the voltage between the two wires (used to power the phone).
Telephone exchange
Telephone exchange
In the field of telecommunications, a telephone exchange or telephone switch is a system of electronic components that connects telephone calls...
communication equipment, such as DSLAM, uses standard -48V DC power supply. The negative polarity is achieved by grounding
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
the positive terminal of power supply system and the battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
bank. This is done to prevent electrolysis
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
depositions.
See also
- High voltage direct current power transmission.
- Alternating currentAlternating currentIn alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
- DC offset
- Neutral direct-current telegraph systemNeutral direct-current telegraph systemIn telecommunication, a neutral direct-current telegraph system is a telegraph system in which current flows during marking intervals and no current flows during spacing intervals for the transmission of signals over a line, and the direction of current flow is immaterial....

