
Switch
Encyclopedia
In electronics
, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current
or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) can be either a "toggle" (flip switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "momentary" (push-for "on" or push-for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch
. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensor
s in a process and used to automatically control a system. For example, a thermostat
is a temperature-operated switch used to control a heating process. A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay
. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be pad-locked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock.
Practical switches fall short of this ideal, and have resistance, limits on the current and voltage they can handle, etc. The ideal switch is often used in circuit analysis as it greatly simplifies the system of equations to be solved, however this can lead to a less accurate solution.
 In the simplest case, a switch has two conductive pieces, often metal
In the simplest case, a switch has two conductive pieces, often metal
, called contacts, connected to an external circuit, that touch to complete (make) the circuit, and separate to open (break) the circuit. The contact material is chosen for its resistance to corrosion
, because most metals form insulating
oxide
s that would prevent the switch from working. Contact materials are also chosen on the basis of electrical conductivity, hardness (resistance to abrasive wear), mechanical strength
, low cost and low toxicity
.
Sometimes the contacts are plated
with noble metal
s. They may be design
ed to wipe against each other to clean off any contamination. Nonmetallic conductor
s, such as conductive plastic
, are sometimes used.
In order to prevent the formation of insulating oxides, a minimum wetting current
may be specified for a given switch design.
 Switches are classified according to the arrangement of their contacts in electronics. A pair of contacts is said to be "closed" when current can flow from one to the other. When the contacts are separated by an insulating air gap, they are said to be "open", and no current can flow between them at normal voltages. The terms "make" for closure of contacts and "break" for opening of contacts are also widely used.
Switches are classified according to the arrangement of their contacts in electronics. A pair of contacts is said to be "closed" when current can flow from one to the other. When the contacts are separated by an insulating air gap, they are said to be "open", and no current can flow between them at normal voltages. The terms "make" for closure of contacts and "break" for opening of contacts are also widely used.
In a push-button type switch, in which the contacts remain in one state unless actuated, the contacts can either be normally open (abbreviated "n.o." or "no") until closed by operation of the switch, or normally closed ("n.c. or "nc") and opened by the switch action. A switch with both types of contact is called a changeover switch. These may be "make-before-break" which momentarily connect both circuits, or may be "break-before-make" which interrupts one circuit before closing the other.
The terms pole and throw are also used to describe switch contact variations. The number of "poles" is the number of separate circuits which are controlled by a switch. For example, a "2-pole" switch has two separate identical sets of contacts controlled by the same knob. The number of "throws" is the number of separate positions that the switch can adopt. A single-throw switch has one pair of contacts that can either be closed or open. A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts, a triple-throw has a contact which can be connected to one of three other contacts, etc.
These terms give rise to abbreviations for the types of switch which are used in the electronics
industry such as "single-pole, single-throw" (SPST) (the simplest type, "on or off") or "single-pole, double-throw" (SPDT), connecting either of two terminals to the common terminal. In electrical power
wiring (i.e. House and building wiring by electrician
s) names generally involving the suffixed word "-way" are used; however, these terms differ between British
and American
English
and the terms two way and three way are used in both with different meanings.
Switches with larger numbers of poles or throws can be described by replacing the "S" or "D" with a number (e.g. 3PST, 4PST, etc.) or in some cases the letter "T" (for "triple"). In the rest of this article the terms SPST, SPDT and intermediate will be used to avoid the ambiguity.
s. Switch and relay contacts are usually made of springy metals that are forced into contact by an actuator. When the contacts strike together, their momentum and elasticity act together to cause bounce. The result is a rapidly pulsed electric current instead of a clean transition from zero to full current. The effect is usually unimportant in power circuits, but causes problems in some analogue
and logic circuits that respond fast enough to misinterpret the on-off pulses as a data stream.
The effects of contact bounce can be eliminated by use of mercury-wetted contacts, but these are now infrequently used because of the hazard of mercury release.
Contact circuits can be filtered to reduce or eliminate multiple pulses. In digital systems, multiple samples of the contact state can be taken or a time delay can be implemented so that the contact bounce has settled before the contact input is used to control anything. One way to implement this with an SPDT Switch is by using an SR Latch.
. The plasma is of low resistance and is able to sustain power flow, even with the separation distance between the switch contacts steadily increasing. The plasma is also very hot and is capable of eroding the metal surfaces of the switch contacts.
Where the voltage is sufficiently high, an arc can also form as the switch is closed and the contacts approach. If the voltage potential is sufficient to exceed the breakdown voltage
of the air separating the contacts, an arc forms which is sustained until the switch closes completely and the switch surfaces make contact.
In either case, the standard method for minimizing arc formation and preventing contact damage is to use a fast-moving switch mechanism, typically using a spring-operated tipping-point mechanism
to assure quick motion of switch contacts, regardless of the speed at which the switch control is operated by the user. Movement of the switch control lever applies tension to a spring until a tipping point is reached, and the contacts suddenly snap open or closed as the spring tension is released.
As the power being switched increases, other methods are used to minimize or prevent arc formation. A plasma is hot and will rise due to convection
air currents. The arc can be quenched with a series of nonconductive blades spanning the distance between switch contacts, and as the arc rises its length increases as it forms ridges rising into the spaces between the blades, until the arc is too long to stay sustained and is extinguished. A puffer may be used to blow a sudden high velocity burst of gas across the switch contacts, which rapidly extends the length of the arc to extinguish it quickly.
Extremely large switches in excess of 100,000 watts capacity often have switch contacts surrounded by something other than air to more rapidly extinguish the arc. For example, the switch contacts may operate in a vacuum, immersed in mineral oil
, or in sulfur hexafluoride.
In AC power service, the current periodically passes through zero; this effect makes it harder to sustain an arc on opening. As a consequence, safety certification agencies commonly issue two maximum voltage ratings for switches and fuses, one for AC service and one for DC service.
For this reason, power switches intended to interrupt a load current have spring mechanisms to make sure the transition between on and off is as short as possible regardless of the speed at which the user moves the rocker.
Power switches usually come in two types. A momentary on-off switch (such as on a laser pointer
) usually takes the form of a button and only closes the circuit when the button is depressed. A regular on-off switch (such as on a flashlight
) has a constant on-off feature. Dual-action switches incorporate both of these features.
load such as an electric motor
is switched off, the current cannot drop instantaneously to zero; a spark
will jump across the opening contacts. Switches for inductive
loads must be rated to handle these cases. The spark will cause electromagnetic interference
if not suppressed; a snubber
network of a resistor
and capacitor
in series will quell the spark.
, and may be a toggle or dolly, a rocker, a push-button or any type of mechanical linkage (see photo).
.
Commercially available switches are available which can be wired to operate either normally-open or normally-closed, having two sets of contacts. Depending on the application the installer or electrician may choose whichever mode is appropriate.
Multi-throw switches are also found with a bias position. The last throw of a rotary switch may be biased to return to the penultimate position once the operator releases their hold of it.
 A toggle switch is a class of electrical switches that are manually actuated by a mechanical lever
A toggle switch is a class of electrical switches that are manually actuated by a mechanical lever
, handle, or rocking mechanism.
Toggle switches are available in many different styles and sizes, and are used in countless applications. Many are designed to provide the simultaneous actuation of multiple sets of electrical contacts, or the control of large amounts of electric current
or mains
voltages.
The word "toggle" is a reference to a kind of mechanism or joint consisting of two arms, which are almost in line with each other, connected with an elbow-like pivot. However, the phrase "toggle switch" is applied to a switch with a short handle and a positive snap-action, whether it actually contains a toggle mechanism or not. Similarly, a switch where a definitive click is heard, is called a "positive on-off switch".

), the turning of a key (key switch
), linear or rotary movement (the limit switch or microswitch), or presence of a magnetic field (the reed switch
).
consists of a drop of mercury
inside a glass
bulb with 2 or more contacts. The two contacts pass through the glass, and are connected by the mercury when the bulb is tilted to make the mercury roll on to them.
This type of switch performs much better than the ball tilt switch, as the liquid metal
connection is unaffected by dirt, debris and oxidation, it wets the contacts ensuring a very low resistance bounce-free connection, and movement and vibration do not produce a poor contact. These types can be used for precision works.
It can also be used where arcing is dangerous (such as in the presence of explosive vapour) as the entire unit is sealed.
es consist of a flat metal blade, hinged at one end, with an insulating handle for operation, and a fixed contact. When the switch is closed, current flows through the hinged pivot and blade and through the fixed contact. Such switches are usually not enclosed. The knife and contacts are typically formed of copper, steel, or brass, depending on the application. Fixed contacts may be backed up with a spring. Several parallel blades can be operated at the same time by one handle. The parts may be mounted on an insulating base with terminals for wiring, or may be directly bolted to an insulated switch board in a large assembly. Since the electrical contacts are exposed, the switch is used only where people cannot accidentally come in contact with the switch or where the voltage is so low as to not present a hazard.
Knife switches are made in many sizes from miniature switches to large devices used to carry thousands of amperes. In electrical transmission and distribution, gang-operated switches are used in circuits up to the highest voltages.
The disadvantages of the knife switch are the slow opening speed and the proximity of the operator to exposed live parts. Metal-enclosed safety disconnect switches are used for isolation of circuits in industrial power distribution. Sometimes spring-loaded auxiliary blades are fitted which momentarily carry the full current during opening, then quickly part to rapidly extinguish the arc.
. The foot control of an electric guitar is also a switch.
system for control of lamps by more than two switches.

Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching—often a silicon-controlled rectifier
or triac
.
The analogue switch
uses two MOSFET transistors in a transmission gate arrangement as a switch that works much like a relay, with some advantages and several limitations compared to an electromechanical relay.
The power transistor(s) in a switching voltage regulator, such as a power supply unit
, are used like a switch to alternately let power flow and block power from flowing.
Many people use metonymy
to call a variety of devices "switches" that conceptually connect or disconnect signals and communication paths between electrical devices, analogous to the way mechanical switches connect and disconnect paths for electrons to flow between two conductors.
Since the advent of digital logic in the 1950s, the term switch has spread to a variety of digital active devices such as transistor
s and logic gate
s whose function is to change their output state between two logic level
s or connect different signal
lines, and even computers, network switch
es, whose function is to provide connections between different ports
in a computer network
. The term 'switched' is also applied to telecommunications network
s, and signifies a network that is circuit switched, providing dedicated circuits for communication between end nodes, such as the public switched telephone network
. The common feature of all these usages is they refer to devices that control a binary
state: they are either on or off, closed or open, connected or not connected.
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) can be either a "toggle" (flip switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "momentary" (push-for "on" or push-for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch
Light switch
A light switch is a switch, most commonly used to operate electric lights, permanently connected equipment, or electrical outlets. In torches the switch is often near the bulb, but may be in the tail, or even the entire head itself may constitute the switch .-Wall-mounted switches:Switches for...
. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensor
Sensor
A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. For example, a mercury-in-glass thermometer converts the measured temperature into expansion and contraction of a liquid which can be read on a calibrated...
s in a process and used to automatically control a system. For example, a thermostat
Thermostat
A thermostat is the component of a control system which regulates the temperature of a system so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint temperature. The thermostat does this by switching heating or cooling devices on or off, or regulating the flow of a heat transfer...
is a temperature-operated switch used to control a heating process. A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay
Relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be pad-locked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock.
In circuit theory
In electronics engineering, an ideal switch describes a switch that:- has no current limit during its ON state
- has infinite resistance during its OFF state
- has no voltage drop across the switch during its ON state
- has no voltage limit during its OFF state
- has zero rise timeRise timeIn electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
and fall timeFall timeIn electronics, fall time \scriptstyle t_f\, is the time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease from a specified value to another specified value...
during state changes - switches without "bouncing" between on and off positions
Practical switches fall short of this ideal, and have resistance, limits on the current and voltage they can handle, etc. The ideal switch is often used in circuit analysis as it greatly simplifies the system of equations to be solved, however this can lead to a less accurate solution.
Contacts

Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
, called contacts, connected to an external circuit, that touch to complete (make) the circuit, and separate to open (break) the circuit. The contact material is chosen for its resistance to corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
, because most metals form insulating
Electrical insulation
thumb|250px|[[Coaxial Cable]] with dielectric insulator supporting a central coreThis article refers to electrical insulation. For insulation of heat, see Thermal insulation...
oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
s that would prevent the switch from working. Contact materials are also chosen on the basis of electrical conductivity, hardness (resistance to abrasive wear), mechanical strength
Strength of materials
In materials science, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied stress without failure. The applied stress may be tensile, compressive, or shear. Strength of materials is a subject which deals with loads, deformations and the forces acting on a material. A load applied to a...
, low cost and low toxicity
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage a living or non-living organisms. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell or an organ , such as the liver...
.
Sometimes the contacts are plated
Electroplating
Electroplating is a plating process in which metal ions in a solution are moved by an electric field to coat an electrode. The process uses electrical current to reduce cations of a desired material from a solution and coat a conductive object with a thin layer of the material, such as a metal...
with noble metal
Noble metal
Noble metals are metals that are resistant to corrosion and oxidation in moist air, unlike most base metals. They tend to be precious, often due to their rarity in the Earth's crust...
s. They may be design
Design
Design as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
ed to wipe against each other to clean off any contamination. Nonmetallic conductor
Electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons...
s, such as conductive plastic
Plastic
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs...
, are sometimes used.
In order to prevent the formation of insulating oxides, a minimum wetting current
Wetting current
In electrical engineering, a wetting current is the minimum current needing to flow through a mechanical switch or relay while it is operated in order to break through any film of oxidation that may have been deposited on the switch contacts. The film occurs often in areas with high humidity...
may be specified for a given switch design.
Contact terminology

In a push-button type switch, in which the contacts remain in one state unless actuated, the contacts can either be normally open (abbreviated "n.o." or "no") until closed by operation of the switch, or normally closed ("n.c. or "nc") and opened by the switch action. A switch with both types of contact is called a changeover switch. These may be "make-before-break" which momentarily connect both circuits, or may be "break-before-make" which interrupts one circuit before closing the other.
The terms pole and throw are also used to describe switch contact variations. The number of "poles" is the number of separate circuits which are controlled by a switch. For example, a "2-pole" switch has two separate identical sets of contacts controlled by the same knob. The number of "throws" is the number of separate positions that the switch can adopt. A single-throw switch has one pair of contacts that can either be closed or open. A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts, a triple-throw has a contact which can be connected to one of three other contacts, etc.
These terms give rise to abbreviations for the types of switch which are used in the electronics
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
industry such as "single-pole, single-throw" (SPST) (the simplest type, "on or off") or "single-pole, double-throw" (SPDT), connecting either of two terminals to the common terminal. In electrical power
Mains
Mains may refer to:* Mains electricity * Mains power around the world* Electricity transmission* Public utility, "mains services", including electricity, natural gas, water, and sewage disposal...
wiring (i.e. House and building wiring by electrician
Electrician
An electrician is a tradesman specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, stationary machines and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance and repair of existing electrical infrastructure. Electricians may also...
s) names generally involving the suffixed word "-way" are used; however, these terms differ between British
British English
British English, or English , is the broad term used to distinguish the forms of the English language used in the United Kingdom from forms used elsewhere...
and American
American English
American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States....
English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
and the terms two way and three way are used in both with different meanings.
| Electronics specification and abbreviation | Expansion of abbreviation |
British mains wiring name |
American electrical wiring name |
Description | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPST | Single pole, single throw | One-way | Two-way | A simple on-off switch: The two terminals are either connected together or disconnected from each other. An example is a light switch Light switch A light switch is a switch, most commonly used to operate electric lights, permanently connected equipment, or electrical outlets. In torches the switch is often near the bulb, but may be in the tail, or even the entire head itself may constitute the switch .-Wall-mounted switches:Switches for... . |
 |
| SPDT | Single pole, double throw | Two-way | Three-way | A simple changeover switch: C (COM, Common) is connected to L1 or to L2. |  |
| SPCO SPTT, c.o. |
Single pole changeover or Single pole, centre off or Single Pole, Triple Throw |
Similar to SPDT. Some suppliers use SPCO/SPTT for switches with a stable off position in the centre and SPDT for those without. | |||
| DPST | Double pole, single throw | Double pole | Double pole | Equivalent to two SPST switches controlled by a single mechanism | 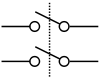 |
| DPDT | Double pole, double throw | Equivalent to two SPDT switches controlled by a single mechanism. | 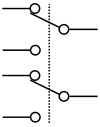 |
||
| DPCO | Double pole changeover or Double pole, centre off |
Equivalent to DPDT. Some suppliers use DPCO for switches with a stable off position in the centre and DPDT for those without. | |||
| Intermediate switch | Four-way switch | DPDT switch internally wired for polarity-reversal applications: only four rather than six wires are brought outside the switch housing. |  |
Switches with larger numbers of poles or throws can be described by replacing the "S" or "D" with a number (e.g. 3PST, 4PST, etc.) or in some cases the letter "T" (for "triple"). In the rest of this article the terms SPST, SPDT and intermediate will be used to avoid the ambiguity.
Contact bounce
Contact bounce (also called chatter) is a common problem with mechanical switches and relayRelay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
s. Switch and relay contacts are usually made of springy metals that are forced into contact by an actuator. When the contacts strike together, their momentum and elasticity act together to cause bounce. The result is a rapidly pulsed electric current instead of a clean transition from zero to full current. The effect is usually unimportant in power circuits, but causes problems in some analogue
Analogue electronics
Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal...
and logic circuits that respond fast enough to misinterpret the on-off pulses as a data stream.
The effects of contact bounce can be eliminated by use of mercury-wetted contacts, but these are now infrequently used because of the hazard of mercury release.
Contact circuits can be filtered to reduce or eliminate multiple pulses. In digital systems, multiple samples of the contact state can be taken or a time delay can be implemented so that the contact bounce has settled before the contact input is used to control anything. One way to implement this with an SPDT Switch is by using an SR Latch.
Arcs and quenching
When the power being switched is sufficiently large, the electron flow across opening switch contacts is sufficient to ionize the air molecules across the tiny gap between the contacts as the switch is opened, forming a gas plasma, also known as an electric arcElectric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
. The plasma is of low resistance and is able to sustain power flow, even with the separation distance between the switch contacts steadily increasing. The plasma is also very hot and is capable of eroding the metal surfaces of the switch contacts.
Where the voltage is sufficiently high, an arc can also form as the switch is closed and the contacts approach. If the voltage potential is sufficient to exceed the breakdown voltage
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive.The breakdown voltage of a diode is the minimum reverse voltage to make the diode conduct in reverse...
of the air separating the contacts, an arc forms which is sustained until the switch closes completely and the switch surfaces make contact.
In either case, the standard method for minimizing arc formation and preventing contact damage is to use a fast-moving switch mechanism, typically using a spring-operated tipping-point mechanism
Tipping point (physics)
A tipping point is the point at which an object is displaced from a state of stable equilibrium into a new equilibrium state qualitatively dissimilar from the first.- In electric power :...
to assure quick motion of switch contacts, regardless of the speed at which the switch control is operated by the user. Movement of the switch control lever applies tension to a spring until a tipping point is reached, and the contacts suddenly snap open or closed as the spring tension is released.
As the power being switched increases, other methods are used to minimize or prevent arc formation. A plasma is hot and will rise due to convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
air currents. The arc can be quenched with a series of nonconductive blades spanning the distance between switch contacts, and as the arc rises its length increases as it forms ridges rising into the spaces between the blades, until the arc is too long to stay sustained and is extinguished. A puffer may be used to blow a sudden high velocity burst of gas across the switch contacts, which rapidly extends the length of the arc to extinguish it quickly.
Extremely large switches in excess of 100,000 watts capacity often have switch contacts surrounded by something other than air to more rapidly extinguish the arc. For example, the switch contacts may operate in a vacuum, immersed in mineral oil
Mineral oil
A mineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of alkanes in the C15 to C40 range from a non-vegetable source, particularly a distillate of petroleum....
, or in sulfur hexafluoride.
In AC power service, the current periodically passes through zero; this effect makes it harder to sustain an arc on opening. As a consequence, safety certification agencies commonly issue two maximum voltage ratings for switches and fuses, one for AC service and one for DC service.
Power switching
When a switch is designed to switch significant power, the transitional state of the switch as well as the ability to stand continuous operating currents must be considered. When a switch is in the on state its resistance is near zero and very little power is dropped in the contacts; when a switch is in the off state its resistance is extremely high and even less power is dropped in the contacts. However when the switch is flicked the resistance must pass through a state where briefly a quarter (or worse if the load is not purely resistive) of the load's rated power is dropped in the switch.For this reason, power switches intended to interrupt a load current have spring mechanisms to make sure the transition between on and off is as short as possible regardless of the speed at which the user moves the rocker.
Power switches usually come in two types. A momentary on-off switch (such as on a laser pointer
Laser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a small portable device with a power source and a laser emitting a very narrow coherent low-powered beam of visible light, intended to be used to highlight something of interest by illuminating it with a small bright spot of colored light...
) usually takes the form of a button and only closes the circuit when the button is depressed. A regular on-off switch (such as on a flashlight
Flashlight
A flashlight is a hand-held electric-powered light source. Usually the light source is a small incandescent lightbulb or light-emitting diode...
) has a constant on-off feature. Dual-action switches incorporate both of these features.
Inductive loads
When a strongly inductiveInductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
load such as an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
is switched off, the current cannot drop instantaneously to zero; a spark
Electric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
will jump across the opening contacts. Switches for inductive
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
loads must be rated to handle these cases. The spark will cause electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
if not suppressed; a snubber
Snubber
A snubber is a device used to suppress voltage transients in electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems, or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems.-Electrical systems:...
network of a resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
and capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
in series will quell the spark.
Actuator
The moving part that applies the operating force to the contacts is called the actuatorActuator
An actuator is a type of motor for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. It is operated by a source of energy, usually in the form of an electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure or pneumatic pressure, and converts that energy into some kind of motion. An actuator is the mechanism by which...
, and may be a toggle or dolly, a rocker, a push-button or any type of mechanical linkage (see photo).
Biased switches
The momentary push-button switch is a type of biased switch. The most common type is a "push-to-make" (or normally-open or NO) switch, which makes contact when the button is pressed and breaks when the button is released. Each key of a computer keyboard, for example, is a normally-open "push-to-make" switch. A "push-to-break" (or normally-closed or NC) switch, on the other hand, breaks contact when the button is pressed and makes contact when it is released. An example of a push-to-break switch is a button used to release a door held open by an electromagnetElectromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
.
Commercially available switches are available which can be wired to operate either normally-open or normally-closed, having two sets of contacts. Depending on the application the installer or electrician may choose whichever mode is appropriate.
Multi-throw switches are also found with a bias position. The last throw of a rotary switch may be biased to return to the penultimate position once the operator releases their hold of it.
Toggle switch

Lever
In physics, a lever is a rigid object that is used with an appropriate fulcrum or pivot point to either multiply the mechanical force that can be applied to another object or resistance force , or multiply the distance and speed at which the opposite end of the rigid object travels.This leverage...
, handle, or rocking mechanism.
Toggle switches are available in many different styles and sizes, and are used in countless applications. Many are designed to provide the simultaneous actuation of multiple sets of electrical contacts, or the control of large amounts of electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
or mains
Mains electricity
Mains is the general-purpose alternating current electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power...
voltages.
The word "toggle" is a reference to a kind of mechanism or joint consisting of two arms, which are almost in line with each other, connected with an elbow-like pivot. However, the phrase "toggle switch" is applied to a switch with a short handle and a positive snap-action, whether it actually contains a toggle mechanism or not. Similarly, a switch where a definitive click is heard, is called a "positive on-off switch".

Special types
Switches can be designed to respond to any type of mechanical stimulus: for example, vibration (the trembler switch), tilt, air pressure, fluid level (the float switchFloat switch
A float switch is a device used to detect the level of liquid within a tank. The switch may be used in a pump, an indicator, an alarm, or other devices....
), the turning of a key (key switch
Key switch
A key switch is a switch that can be activated only by a key.Key switches are usually used in situations where access needs to be restricted to the switch's functions....
), linear or rotary movement (the limit switch or microswitch), or presence of a magnetic field (the reed switch
Reed switch
The reed switch is an electrical switch operated by an applied magnetic field. It was invented at Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1936 by W. B. Ellwood. It consists of a pair of contacts on ferrous metal reeds in a hermetically sealed glass envelope...
).
Mercury tilt switch
The mercury switchMercury switch
A mercury switch is a switch whose purpose is to allow or interrupt the flow of electric current in an electrical circuit in a manner that is dependent on the switch's physical position or alignment relative to the direction of the "pull" of earth's gravity, or other inertia.Mercury switches...
consists of a drop of mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
inside a glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
bulb with 2 or more contacts. The two contacts pass through the glass, and are connected by the mercury when the bulb is tilted to make the mercury roll on to them.
This type of switch performs much better than the ball tilt switch, as the liquid metal
Liquid metal
Liquid Metal may refer to:* Metals in a liquid state** Metals which have a relatively low melting point, such as tin or lead.** A fusible alloy** A poor metal.* Liquid Metal , a radio channel* XM Liquid Metal, a radio channel...
connection is unaffected by dirt, debris and oxidation, it wets the contacts ensuring a very low resistance bounce-free connection, and movement and vibration do not produce a poor contact. These types can be used for precision works.
It can also be used where arcing is dangerous (such as in the presence of explosive vapour) as the entire unit is sealed.
Knife switch
Knife switchKnife switch
A knife switch is a type of switch used to control the flow of electricity in a circuit. It is composed of a hinge which allows a metal lever, or knife, to be lifted from or inserted into a slot or jaw. The hinge and jaw are both fixed to an insulated base, and the knife has an insulated handle to...
es consist of a flat metal blade, hinged at one end, with an insulating handle for operation, and a fixed contact. When the switch is closed, current flows through the hinged pivot and blade and through the fixed contact. Such switches are usually not enclosed. The knife and contacts are typically formed of copper, steel, or brass, depending on the application. Fixed contacts may be backed up with a spring. Several parallel blades can be operated at the same time by one handle. The parts may be mounted on an insulating base with terminals for wiring, or may be directly bolted to an insulated switch board in a large assembly. Since the electrical contacts are exposed, the switch is used only where people cannot accidentally come in contact with the switch or where the voltage is so low as to not present a hazard.
Knife switches are made in many sizes from miniature switches to large devices used to carry thousands of amperes. In electrical transmission and distribution, gang-operated switches are used in circuits up to the highest voltages.
The disadvantages of the knife switch are the slow opening speed and the proximity of the operator to exposed live parts. Metal-enclosed safety disconnect switches are used for isolation of circuits in industrial power distribution. Sometimes spring-loaded auxiliary blades are fitted which momentarily carry the full current during opening, then quickly part to rapidly extinguish the arc.
Footswitch
A footswitch is a rugged switch which is operated by foot pressure. An example of use is for the control of an electric sewing machineSewing machine
A sewing machine is a textile machine used to stitch fabric, cards and other material together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies...
. The foot control of an electric guitar is also a switch.
Reversing switch
A DPDT switch has six connections, but since polarity reversal is a very common usage of DPDT switches, some variations of the DPDT switch are internally wired specifically for polarity reversal. These crossover switches only have four terminals rather than six. Two of the terminals are inputs and two are outputs. When connected to a battery or other DC source, the 4-way switch selects from either normal or reversed polarity. Such switches can also be used as intermediate switches in a multiway switchingMultiway switching
In building wiring, multiway switching is interconnection of two or more light switches to control lighting from more than one location. This allows lighting in a hallway or stairwell to be controlled from either end.-Three-way and four-way:...
system for control of lamps by more than two switches.
Light switches
In building wiring, light switches are installed at convenient locations to control lighting and occasionally other circuits. By use of multiple-pole switches, control of a lamp can be obtained from two or more places, such as the ends of a corridor or stairwell.
Electronic switches
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used.Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching—often a silicon-controlled rectifier
Silicon-controlled rectifier
A silicon-controlled rectifier is a four-layer solid state device that controls current. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" or SCR is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W...
or triac
Triac
Triac may refer to:* TRIAC , an electronics component* Triac , a green vehicle* Tiratricol, a common thyroid hormone analogue used for treating thyroid hormone resistance syndrome...
.
The analogue switch
Analogue switch
The analog switch, also called the bilateral switch, is an electronic component that behaves in a similar way to a relay, but has no moving parts. The switching element is normally a MOSFET transistor...
uses two MOSFET transistors in a transmission gate arrangement as a switch that works much like a relay, with some advantages and several limitations compared to an electromechanical relay.
The power transistor(s) in a switching voltage regulator, such as a power supply unit
Power supply unit (computer)
A power supply unit converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of the computer. Modern personal computers universally use a switched-mode power supply...
, are used like a switch to alternately let power flow and block power from flowing.
Many people use metonymy
Metonymy
Metonymy is a figure of speech used in rhetoric in which a thing or concept is not called by its own name, but by the name of something intimately associated with that thing or concept...
to call a variety of devices "switches" that conceptually connect or disconnect signals and communication paths between electrical devices, analogous to the way mechanical switches connect and disconnect paths for electrons to flow between two conductors.
Since the advent of digital logic in the 1950s, the term switch has spread to a variety of digital active devices such as transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s and logic gate
Logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and...
s whose function is to change their output state between two logic level
Logic level
In digital circuits, a logic level is one of a finite number of states that a signal can have. Logic levels are usually represented by the voltage difference between the signal and ground , although other standards exist...
s or connect different signal
Digital signal
A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal...
lines, and even computers, network switch
Network switch
A network switch or switching hub is a computer networking device that connects network segments.The term commonly refers to a multi-port network bridge that processes and routes data at the data link layer of the OSI model...
es, whose function is to provide connections between different ports
Computer port (hardware)
In computer hardware, a port serves as an interface between the computer and other computers or peripheral devices. Physically, a port is a specialized outlet on a piece of equipment to which a plug or cable connects...
in a computer network
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
. The term 'switched' is also applied to telecommunications network
Telecommunications network
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. Each terminal in the network must have a unique address so messages or connections...
s, and signifies a network that is circuit switched, providing dedicated circuits for communication between end nodes, such as the public switched telephone network
Public switched telephone network
The public switched telephone network is the network of the world's public circuit-switched telephone networks. It consists of telephone lines, fiber optic cables, microwave transmission links, cellular networks, communications satellites, and undersea telephone cables, all inter-connected by...
. The common feature of all these usages is they refer to devices that control a binary
Binary numeral system
The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, represents numeric values using two symbols, 0 and 1. More specifically, the usual base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2...
state: they are either on or off, closed or open, connected or not connected.
See also
- Analogue switchAnalogue switchThe analog switch, also called the bilateral switch, is an electronic component that behaves in a similar way to a relay, but has no moving parts. The switching element is normally a MOSFET transistor...
- Centrifugal switchCentrifugal switchA centrifugal switch is an electric switch that operates using the centrifugal force created from a rotating shaft, most commonly that of an electric motor or gasoline engine. The switch is designed to activate or de-activate as a function of the rotational speed of the shaft.Perhaps the most...
- Circuit breakerCircuit breakerA circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
- Commutator (electric)Commutator (electric)A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
- ContactorContactorA contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching a power circuit, similar to a relay except with higher current ratings. A contactor is controlled by a circuit which has a much lower power level than the switched circuit....
- Crossbar switchCrossbar switchIn electronics, a crossbar switch is a switch connecting multiple inputs to multiple outputs in a matrix manner....
- Cutout
- Dead man's switchDead man's switchA dead man's switch is a switch that is automatically operated in case the human operator becomes incapacitated, such as through death or loss of consciousness....
- DIP switchDIP switchDIP switches are manual electric switches that are packaged in a group in a standard dual in-line package...
- Fireman's switchFireman's switchA Fireman’s switch is an electrical isolation switch located within a staircase enclosure to permit the disconnection of electrical power supply to the relevant floor or zone served. In England, it is code that every floor or zone of any floor with a net area exceeding 929 square metres shall be...
- Flip-flop (electronics)Flip-flop (electronics)In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic...
- Float switchFloat switchA float switch is a device used to detect the level of liquid within a tank. The switch may be used in a pump, an indicator, an alarm, or other devices....
- Hall-effect switch
- Inertial switchInertial switchAn inertial switch is a switch, firmly mounted upon a vehicle or other mobile device, that senses shock or vibration. It is a part of electrical circuits that may either enable or disable some function.-Disconnect:...
- Isolator switchIsolator switchIn electrical engineering, a disconnector or isolator switch is used to make sure that an electrical circuit can be completely de-energised for service or maintenance. Such switches are often found in electrical distribution and industrial applications where machinery must have its source of...
- Key switchKey switchA key switch is a switch that can be activated only by a key.Key switches are usually used in situations where access needs to be restricted to the switch's functions....
- Kill switchKill switchKill switch, also called an e-stop, is a security measure used to shut off a device in an emergency situation in which it cannot be shut down in the usual manner...
- Latching switchLatching switchA latching switch is a switch that maintains its state after being activated. A push-to-make, push-to-break switch would therefore be a latching switch - each time you actuate it, whichever state the switch is left in will persist until the switch is actuated again....
- Load control switchLoad control switchA Load control switch is a remotely controlled relay that is placed on home appliances which consume large amounts of electricity, such as air conditioner units and electric water heaters....
- Membrane switchMembrane switchA membrane switch is an electrical switch for turning a circuit on and off. It differs from a mechanical switch, which is usually made of copper and plastic parts: a membrane switch is a circuit printed on PET or ITO...
- Mercury switchMercury switchA mercury switch is a switch whose purpose is to allow or interrupt the flow of electric current in an electrical circuit in a manner that is dependent on the switch's physical position or alignment relative to the direction of the "pull" of earth's gravity, or other inertia.Mercury switches...
- Micro switchMicro switchA miniature snap-action switch, also trademarked and frequently known as a micro switch, is an electric switch that is actuated by very little physical force, through the use of a tipping-point mechanism, sometimes called an "over-center" mechanism. Switching happens reliably at specific and...
- MultivibratorMultivibratorA multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state systems such as oscillators, timers and flip-flops. It is characterized by two amplifying devices cross-coupled by resistors or capacitors...
- Multiway switchingMultiway switchingIn building wiring, multiway switching is interconnection of two or more light switches to control lighting from more than one location. This allows lighting in a hallway or stairwell to be controlled from either end.-Three-way and four-way:...
- Network protectorNetwork protectorA network protector is a type of electric protective device used in electricity distribution systems. The function of the network protector is to automatically connect and disconnect its associated power transformer from the secondary network when the power starts flowing in reverse direction...
- Piezo switchPiezo switchA piezo switch is an electrical switch based on the piezoelectric effect.The folcharge generated by the piezoelectric element in the switch is typically used to turn on an integrated semiconductor device such as a field effect transistor , causing the switch assembly's output to be active, or "on"...
- Pressure switch
- Pull switchPull switchA pull switch is a switch that is actuated by means of a chain or string.An electric pull switch is attached to a toggle type switch: one pull to switch on and next pull to switch off....
- Push switchPush switchA push switch is is a momentary or non-latching switch which causes a temporary change in the state of a electrical circuit only while the switch is physically actuated. An automatic mechanism returns the switch to its default position immediately afterwards, restoring the initial circuit condition...
- Reed switchReed switchThe reed switch is an electrical switch operated by an applied magnetic field. It was invented at Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1936 by W. B. Ellwood. It consists of a pair of contacts on ferrous metal reeds in a hermetically sealed glass envelope...
- RelayRelayA relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
- RF Switch MatrixRF Switch MatrixRF Switch Matrix or Microwave Switch Matrix or Switch MatrixAn RF/Microwave Switch Matrix is used in test systems, in both design verification and manufacturing test, to route high frequency signals between the device under test and the test and measurement equipment...
- Rotary switchRotary switchA rotary switch is a switch operated by rotation. These are often chosen when more than 2 positions are needed, such as a three-speed fan or a CB radio with multiple frequencies of reception or "channels"....
- Sail switchSail switchA sail switch, vane switch or flow switch is a mechanical switch that is switched on or off in response to the flow or non-flow of a fluid such as air or water. A sail switch typically operates through the use of a paddle which gets displaced due to the force of fluid moving past it. Sail switches...
- Sense switchSense switchA sense switch or program switch, is a switch on the console of a computer whose state can be tested by conditional branch instructions in software. Most early computers had several sense switches...
- Slotted optical switchSlotted optical switchThe slotted optical switch, sometimes known as opto switch or optical switch but not to be confused with the optical component, is a device comprising a photoemitter and a photodetector The slotted optical switch, sometimes known as opto switch or optical switch but not to be confused with the...
- Stepping switchStepping switchIn electrical controls, a stepping switch, also known as a stepping relay, is an electromechanical device which allows an input connection to be connected to one of a number of possible output connections, under the control of a series of electrical pulses. It can step on one axis , or on two axes...
- Strowger switchStrowger switchThe Strowger switch, also known as Step-by-Step or SXS, is an early electromechanical telephone switching system invented by Almon Brown Strowger...
- Switch accessSwitch AccessMany people with severe physical or cognitive impairment use one or more switches to access computers. A switch is an assistive technology device that replaces the need to use a computer keyboard or a mouse.-Types of switch:...
assistive technology - SwitchboardSwitchboardThe term switchboard, when used by itself, may refer to:*Telephone switchboard*Electric switchboard*Printed circuit board*Mixing console*In computing, Switch board...
- SwitchgearSwitchgearThe term switchgear, used in association with the electric power system, or grid, refers to the combination of electrical disconnects, fuses and/or circuit breakers used to isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be done and to clear faults...
- Thermal switch
- Time switchTime switchA time switch is a timer that plugs into an electric socket, between the socket itself and a power plug. This physical arrangement allows the connected device to automatically receive power for a desired duration of time...
- Touch switchTouch switchA touch switch is a type of switch that only has to be touched by an object to operate. It is used in many lamps and wall switches that have a metal exterior as well as on public computer terminals...
- Transfer switchTransfer switchA transfer switch is an electrical switch that reconnects electric power source from its primary source to a standby source. Switches may be manually or automatically operated...
- Vandal resistant switchVandal resistant switchVandal resistant switches are electrical switches designed to be installed in a location and application where they may be subject to vandalism or tampering, as in the case of pedestrian crossing switches, or fraudulent or unauthorized use, as in the case of vending machine switches...
- Wetting currentWetting currentIn electrical engineering, a wetting current is the minimum current needing to flow through a mechanical switch or relay while it is operated in order to break through any film of oxidation that may have been deposited on the switch contacts. The film occurs often in areas with high humidity...
- Wireless light switchWireless light switchA wireless light switch is a light switch that commands a light or home appliance to turn itself off or on, instead of interrupting the power line going to the light fixture...

