
Wind turbine
Encyclopedia
.jpg)
- This article discusses wind-powered electrical generators. See windmillWindmillA windmill is a machine which converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by means of vanes called sails or blades. Originally windmills were developed for milling grain for food production. In the course of history the windmill was adapted to many other industrial uses. An important...
for wind-powered machinery used to grind grain or pump water.
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
from the wind into mechanical energy
Mechanical energy
In physics, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy present in the components of a mechanical system. It is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object. The law of conservation of energy states that in an isolated system that is only subject to...
. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or pumping water, the device is called a windmill
Windmill
A windmill is a machine which converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by means of vanes called sails or blades. Originally windmills were developed for milling grain for food production. In the course of history the windmill was adapted to many other industrial uses. An important...
or wind pump. Developed for over a millennium, today's wind turbines are manufactured in a range of vertical and horizontal axis types. The smallest turbines are used for applications such as battery charging or auxiliary power on sailing boats; while large grid-connected arrays of turbines are becoming an increasingly large source of commercial electric power.
History
Windmills were used in Persia (present-day Iran) as early as 200 B.C. The windwheel of Heron of Alexandria marks one of the first known instances of wind powering a machine in history. However, the first known practical windmills were built in SistanSistan
Sīstān is a border region in eastern Iran , southwestern Afghanistan and northern tip of Southwestern Pakistan .-Etymology:...
, a region between Afghanistan and Iran, from the 7th century. These "Panemone" were vertical axle windmills, which had long vertical driveshaft
Driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a mechanical component for transmitting torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement...
s with rectangular blades. Made of six to twelve sail
Windmill sail
Windmills are powered by their sails. Sails are found in different designs, from primitive common sails to the advanced patent sails.-Jib sails:...
s covered in reed matting or cloth material, these windmills were used to grind grain or draw up water, and were used in the gristmill
Gristmill
The terms gristmill or grist mill can refer either to a building in which grain is ground into flour, or to the grinding mechanism itself.- Early history :...
ing and sugarcane industries.
Windmills first appeared in Europe during the middle ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. The first historical records of their use in England date to the 11th or 12th centuries and there are reports of German crusaders
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
taking their windmill-making skills to Syria around 1190. By the 14th century, Dutch windmills were in use to drain areas of the Rhine delta.

James Blyth (engineer)
Professor James Blyth MA, LLD, FRSE , was a Scottish electrical engineer and academic at Anderson's College, now the University of Strathclyde, in Glasgow...
to light his holiday home in Marykirk
Marykirk
Marykirk is a small village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland next to the border with the county of Angus at the River North Esk.The village is approximately 6 miles ENE of Montrose at the southern end of the Howe of the Mearns. The road bridge carrying the A937 over the River North Esk is a substantial...
, Scotland. Some months later American inventor Charles F Brush
Charles F. Brush
Charles Francis Brush was a U.S. inventor, entrepreneur and philanthropist.-Biography:Born in Euclid Township, Ohio, Brush was raised on a farm about 10 miles from downtown Cleveland...
built the first automatically operated wind turbine for electricity production in Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Cuyahoga County, the most populous county in the state. The city is located in northeastern Ohio on the southern shore of Lake Erie, approximately west of the Pennsylvania border...
. Although Blyth's turbine was considered uneconomical in the United Kingdom electricity generation by wind turbines was more cost effective in countries with widely scattered populations. In Denmark by 1900, there were about 2500 windmills for mechanical loads such as pumps and mills, producing an estimated combined peak power of about 30 MW. The largest machines were on 24 metres (78.7 ft) towers with four-bladed 23 metres (75.5 ft) diameter rotors. By 1908 there were 72 wind-driven electric generators operating in the US from 5 kW to 25 kW. Around the time of World War I, American windmill makers were producing 100,000 farm windmills each year, mostly for water-pumping.
By the 1930s, wind generators for electricity were common on farms, mostly in the United States where distribution systems had not yet been installed. In this period, high-tensile steel was cheap, and the generators were placed atop prefabricated open steel lattice towers.
A forerunner of modern horizontal-axis wind generators was in service at Yalta
Yalta
Yalta is a city in Crimea, southern Ukraine, on the north coast of the Black Sea.The city is located on the site of an ancient Greek colony, said to have been founded by Greek sailors who were looking for a safe shore on which to land. It is situated on a deep bay facing south towards the Black...
, USSR in 1931. This was a 100 kW generator on a 30 metres (98.4 ft) tower, connected to the local 6.3 kV distribution system. It was reported to have an annual capacity factor
Capacity factor
The net capacity factor or load factor of a power plant is the ratio of the actual output of a power plant over a period of time and its potential output if it had operated at full nameplate capacity the entire time...
of 32 per cent, not much different from current wind machines.
In the fall of 1941, the first megawatt-class wind turbine was synchronized to a utility grid in Vermont
Vermont
Vermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
. The Smith-Putnam wind turbine
Smith-Putnam wind turbine
In 1941 the Smith-Putnam wind turbine, the world's first megawatt-size wind turbine, was connected to the local electrical distribution system on Grandpa's Knob in Castleton, Vermont, USA. It was designed by Palmer Cosslett Putnam and manufactured by the S. Morgan Smith Company...
only ran for 1,100 hours before suffering a critical failure. The unit was not repaired because of shortage of materials during the war.
The first utility grid-connected wind turbine to operate in the U.K. was built by John Brown & Company
John Brown & Company
John Brown and Company of Clydebank was a pre-eminent Scottish marine engineering and shipbuilding firm, responsible for building many notable and world-famous ships, such as the , the , the , the , the , and the...
in 1951 in the Orkney Islands
Orkney Islands
Orkney also known as the Orkney Islands , is an archipelago in northern Scotland, situated north of the coast of Caithness...
.
Resources
A quantitative measure of the wind energy available at any location is called the Wind Power Density (WPD) It is a calculation of the mean annual power available per square meter of swept area of a turbine, and is tabulated for different heights above ground. Calculation of wind power density includes the effect of wind velocity and air density. Color-coded maps are prepared for a particular area described, for example, as "Mean Annual Power Density at 50 Meters." In the United States, the results of the above calculation are included in an index developed by the U.S.Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
National Renewable Energy Lab
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory , located in Golden, Colorado, is the United States' primary laboratory for renewable energy and energy efficiency research and development. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory is a government-owned, contractor-operated facility; it is funded through...
and referred to as "NREL CLASS." The larger the WPD calculation, the higher it is rated by class. Classes range from Class 1 (200 watts/square meter or less at 50 meters altitude) to Class 7 (800 to 2000 watts/square meter). Commercial wind farms generally are sited in Class 3 or higher areas, although isolated points in an otherwise Class 1 area may be practical to exploit.
Types
Wind turbines can rotate about either a horizontalHorizontal
Horizontal may refer to:*Horizontal plane, in astronomy, geography, geometry and other sciences and contexts*Horizontal coordinate system, in astronomy*Horizontalism, in monetary circuit theory*Horizontalism, in sociology...
or a vertical
Vertical
Vertical may refer to:*Vertical direction, the direction aligned with the direction of the force of gravity, as materialized with a plumb line...
axis, the former being both older and more common.
Horizontal axis

Rotor
Rotor may refer to:*A rotating part of a mechanical device, for example in an electric motor, generator, alternator or pump.In engineering:...
shaft and electrical generator
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
at the top of a tower, and must be pointed into the wind. Small turbines are pointed by a simple wind vane, while large turbines generally use a wind sensor coupled with a servo motor
Servo motor
thumb|right|200px|Industrial servomotorThe grey/green cylinder is the [[Brush |brush-type]] [[DC motor]]. The black section at the bottom contains the [[Epicyclic gearing|planetary]] [[Reduction drive|reduction gear]], and the black object on top of the motor is the optical [[rotary encoder]] for...
. Most have a gearbox, which turns the slow rotation of the blades into a quicker rotation that is more suitable to drive an electrical generator.
Since a tower produces turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
behind it, the turbine is usually positioned upwind of its supporting tower. Turbine blades are made stiff to prevent the blades from being pushed into the tower by high winds. Additionally, the blades are placed a considerable distance in front of the tower and are sometimes tilted forward into the wind a small amount.
Downwind machines have been built, despite the problem of turbulence (mast wake), because they don't need an additional mechanism for keeping them in line with the wind, and because in high winds the blades can be allowed to bend which reduces their swept area and thus their wind resistance. Since cyclical (that is repetitive) turbulence may lead to fatigue
Fatigue (material)
'In materials science, fatigue is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. The nominal maximum stress values are less than the ultimate tensile stress limit, and may be below the yield stress limit of the material.Fatigue occurs...
failures, most HAWTs are of upwind design.
Modern wind turbines

Wind farm
A wind farm is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other...
s for commercial production of electric power are usually three-bladed and pointed into the wind by computer-controlled motors. These have high tip speeds of over 320 kilometres per hour (198.8 mph), high efficiency, and low torque ripple, which contribute to good reliability. The blades are usually colored light gray to blend in with the clouds and range in length from 20 to 40 m (65.6 to 131.2 ft) or more. The tubular steel towers range from 60 to 90 m (196.9 to 295.3 ft) tall. The blades rotate at 10-22 revolutions per minute. At 22 rotations per minute the tip speed exceeds 90 metres per second (295.3 ft/s). A gear box is commonly used for stepping up the speed of the generator, although designs may also use direct drive of an annular generator. Some models operate at constant speed, but more energy can be collected by variable-speed turbines which use a solid-state power converter to interface to the transmission system. All turbines are equipped with protective features to avoid damage at high wind speeds, by feathering the blades into the wind which ceases their rotation, supplemented by brake
Brake
A brake is a mechanical device which inhibits motion. Its opposite component is a clutch. The rest of this article is dedicated to various types of vehicular brakes....
s.
Vertical axis design
Vertical-axis wind turbines (or VAWTs) have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically. Key advantages of this arrangement are that the turbine does not need to be pointed into the wind to be effective. This is an advantage on sites where the wind direction is highly variable, for example when integrated into buildings. The key disadvantages include the low rotational speed with the consequential higher torqueTorque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
and hence higher cost of the drive train, the inherently lower power coefficient
Wind turbine aerodynamics
The primary application of wind turbines is to extract energy from the wind. Hence, the aerodynamics is a very important aspect of wind turbines. Like many machines, there are many different types all based on different energy extraction concepts...
, the 360 degree rotation of the aerofoil within the wind flow during each cycle and hence the highly dynamic loading on the blade, the pulsating torque generated by some rotor designs on the drive train, and the difficulty of modelling the wind flow accurately and hence the challenges of analysing and designing the rotor prior to fabricating a prototype.
With a vertical axis, the generator and gearbox can be placed near the ground, using a direct drive from the rotor assembly to the ground-based gearbox, hence improving accessibility for maintenance.
When a turbine is mounted on a rooftop, the building generally redirects wind over the roof and this can double the wind speed at the turbine. If the height of the rooftop mounted turbine tower is approximately 50% of the building height, this is near the optimum for maximum wind energy and minimum wind turbulence. It should be borne in mind that wind speeds within the built environment are generally much lower than at exposed rural sites.
Another type of vertical axis is the Parallel turbine similar to the crossflow fan or centrifugal fan it uses the Ground effect
Ground effect
As it pertains to fixed wing aircraft, "ground effect" refers to the increased lift and decreased drag that an aircraft airfoil or wing generates when an aircraft is about one wingspan's length or less over the ground...
. Vertical axis turbines of this type have been tried for many years The Magenn WindKite blimp
Blimp
A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is a floating airship without an internal supporting framework or keel. A non-rigid airship differs from a semi-rigid airship and a rigid airship in that it does not have any rigid structure, neither a complete framework nor a partial keel, to help the airbag...
uses this configuration as well, chosen because of the ease of running.
Subtypes

Darrieus wind turbine
The Darrieus wind turbine is a type of vertical axis wind turbine used to generate electricity from the energy carried in the wind. The turbine consists of a number of aerofoils usually—but not always—vertically mounted on a rotating shaft or framework...
: "Eggbeater" turbines, or Darrieus turbines, were named after the French inventor, Georges Darrieus. They have good efficiency, but produce large torque ripple and cyclical stress on the tower, which contributes to poor reliability. They also generally require some external power source, or an additional Savonius rotor to start turning, because the starting torque is very low. The torque ripple is reduced by using three or more blades which results in greater solidity of the rotor. Solidity is measured by blade area divided by the rotor area. Newer Darrieus type turbines are not held up by guy-wire
Guy-wire
A guy-wire or guy-rope, also known as simply a guy, is a tensioned cable designed to add stability to structures . One end of the cable is attached to the structure, and the other is anchored to the ground at a distance from the structure's base...
s but have an external superstructure connected to the top bearing.
Giromill: A subtype of Darrieus turbine with straight, as opposed to curved, blades. The cycloturbine variety has variable pitch to reduce the torque pulsation and is self-starting. The advantages of variable pitch are: high starting torque; a wide, relatively flat torque curve; a lower blade speed ratio; a higher coefficient of performance; more efficient operation in turbulent winds; and a lower blade speed ratio which lowers blade bending stresses. Straight, V, or curved blades may be used.
Savonius wind turbine
Savonius wind turbine
Savonius wind turbines are a type of vertical-axis wind turbine , used for converting the force of the wind into torque on a rotating shaft...
: These are drag-type devices with two (or more) scoops that are used in anemometers, Flettner vents (commonly seen on bus and van roofs), and in some high-reliability low-efficiency power turbines. They are always self-starting if there are at least three scoops.
Twisted Savonius : Twisted Savonius is a modified savonius, with long helical scoops to give a smooth torque, this is mostly used as roof windturbine or on some boats (like the Hornblower Hybrid
Hornblower Hybrid
In 2006 San Francisco based Hornblower Cruises & Events began working on developing hybrid propulsion systems for its vessels. After two years of development and engineering their first vessel was introduced in San Francisco Bay in 2008...
).
Turbine design and construction
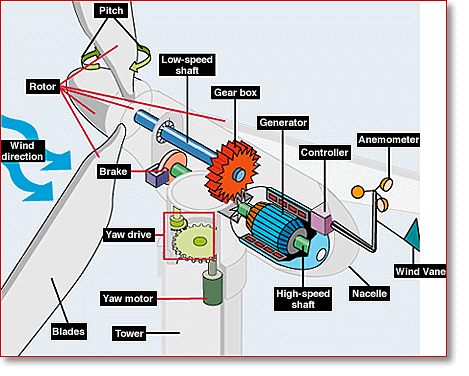
Wind turbines are designed to exploit the wind energy that exists at a location. Aerodynamic modelling
Wind turbine aerodynamics
The primary application of wind turbines is to extract energy from the wind. Hence, the aerodynamics is a very important aspect of wind turbines. Like many machines, there are many different types all based on different energy extraction concepts...
is used to determine the optimum tower height, control systems, number of blades and blade shape.
Wind turbines convert wind energy to electricity for distribution. Conventional horizontal axis turbines can be divided into three components.
- The rotor component, which is approximately 20% of the wind turbine cost, includes the blades for converting wind energy to low speed rotational energy.
- The generator component, which is approximately 34% of the wind turbine cost, includes the electrical generatorElectrical generatorIn electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
, the control electronics, and most likely a gearbox (e.g. planetary gearboxEpicyclic gearingEpicyclic gearing or planetary gearing is a gear system consisting of one or more outer gears, or planet gears, revolving about a central, or sun gear. Typically, the planet gears are mounted on a movable arm or carrier which itself may rotate relative to the sun gear...
, adjustable-speed drive or continuously variable transmissionContinuously variable transmissionA continuously variable transmission is a transmission that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios...
) component for converting the low speed incoming rotation to high speed rotation suitable for generating electricity. - The structural support component, which is approximately 15% of the wind turbine cost, includes the tower and rotor yaw mechanism.
A 1.5 MW wind turbine of a type frequently seen in the United States has a tower 80 meters high. The rotor assembly (blades and hub) weighs 48000 lbs. The nacelle, which contains the generator component, weighs 115000 lbs. The concrete base for the tower is constructed using 58000 lbs of reinforcing steel and contains 250 cubic yards (190 cubic meters) of concrete. The base is 50 feet (15.2 m) in diameter and 8 feet (2.4 m) thick near the center.
Unconventional wind turbines
One E-66 wind turbine at Windpark HoltriemWindpark Holtriem
Constructed in 1998, Windpark Holtriem is one of the largest European windfarms, comprising thirty-three Enercon E-66 wind turbines. Holtriem is a low lying area adjacent to the North Sea in East Frisia ....
, Germany, carries an observation deck, open for visitors. Another turbine of the same type, with an observation deck, is located in Swaffham
Swaffham
Swaffham is a market town and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. The town is situated east of King's Lynn and west of Norwich.The civil parish has an area of and in the 2001 census had a population of 6,935 in 3,130 households...
, England. Airborne wind turbine
Airborne wind turbine
An airborne wind turbine is a design concept for a wind turbine that is supported in the air without a tower. Airborne wind turbines may operate in low or high altitudes; they are part of a wider class of airborne wind energy systems addressed by high-altitude wind power...
s have been investigated many times but have yet to produce significant energy. Conceptually, wind turbines may also be used in conjunction with a large vertical solar updraft tower
Solar updraft tower
The solar updraft tower is a renewable-energy power plant. It combines the chimney effect, the greenhouse effect and the wind turbine. Air is heated by sunshine and contained in a very large greenhouse-like structure around the base of a tall chimney, and the resulting convection causes air to...
to extract the energy due to air heated by the sun.
Wind turbines which utilise the Magnus effect
Magnus effect
The Magnus effect is the phenomenon whereby a spinning object flying in a fluid creates a whirlpool of fluid around itself, and experiences a force perpendicular to the line of motion...
have been developed.http://www.mecaro.jp/eng/introduction.html
The Ram air turbine
Ram air turbine
A ram air turbine is a small turbine that is connected to a hydraulic pump, or electrical generator, installed in an aircraft and used as a power source...
is a specialist form of small turbine that is fitted to some aircraft. When deployed, the RAT is spun by the airstream going past the aircraft and can provide power for the most essential systems if there is a loss of all on–board electrical power.
Small wind turbines

Small wind turbines may be as small as a fifty-watt generator for boat or caravan use. The US Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) defines small wind turbines as those smaller than or equal to 100 kilowatts. Small units often have direct drive generators, direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
output, aeroelastic blades, lifetime bearings and use a vane to point into the wind.
Wind turbine spacing
On most horizontal windturbine farms, a spacing of about 6-10 times the rotor diameter is often upheld. However, for large wind farms distances of about 15 rotor diameters should be more economically optimal, taking into account typical wind turbine and land costs. This conclusion has been reached by research conducted by Charles Meneveau of the Johns Hopkins University and Johan Meyers of Leuven University in Belgium, based on computer simulations that take into account the detailed interactions among wind turbines (wakes) as well as with the entire turbulent atmospheric boundary layer. Moreover, recent research by John Dabiri of Caltech suggests that vertical wind turbines may be placed much more closely together so long as an alternating pattern of rotation is created allowing blades of neighboring turbines to move in the same direction as they approach one another .Accidents
Several cases occurred where the housing of wind turbines caught fire. As it is normally out of the range of standard fire extinction equipment, it is nearly impossible to extinguish such fires.In several cases one or more blades were damaged or torn away. In 2010 70 MPH storm winds damaged some blades, prompting blade removal and inspection of all 25 wind turbines in Campo Indian Reservation in California, USA. Also several wind turbines collapsed catastrophically.
| Place | Date | Type | Height of nacelle | Rotor diametre | Year of construction | Reason | Source | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ellenstedt, Germany | October 19, 2002 | http://mitglied.multimania.de/WilfriedHeck/ellenst.htm | ||||||
| Schneebergerhof, Germany | December 20, 2003 | Vestas V80 | 80 m | http://mitglied.multimania.de/WilfriedHeck/ellenst.htm | ||||
| Wasco, Oregon, USA | August 26, 2007 | http://www.nowpublic.com/wind-turbine-collapse-kills-one-injures-second-worker-0 | 1 killed, 1 injured | |||||
| Stobart Mill, UK | December 30, 2007 | Vestas | 1982 | http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/england/cumbria/7168275.stml | ||||
| Hornslet, Denmark | February 22, 2008 | Nordtank NKT 600-180 | 44.5 m | 43 m | 1996 | Brake failure | http://ronslog.typepad.com/ronslog/2008/02/wind-energy.html | Collapse was filmed http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CqEccgR0q-o |
| Searsburg, New Hampshire, USA | October 16, 2008 | Zond Z-P40-FS | 1997 | Rotor blade collided with tower during strong wind and destroyed it | http://www.windaction.org/releases/18394 | |||
| Altona, New York, USA | March 6, 2009 | http://www.wptz.com/news/18870331/detail.html | ||||||
| Fenner, New York, USA | December 27, 2009 | http://www.windaction.org/pictures/24818 | ||||||
| Kirtorf, Germany | June 19, 2011 | DeWind D-6 | 68.5 m | 62 m | 2001 | http://www.windaction.org/pictures/24818 |
Largest capacity
The Enercon E-126Enercon E-126
The Enercon E-126 is the largest wind turbine model build to date, manufactured by the German wind turbine producer Enercon. With a hub height of , rotor diameter of and a total height of , this large model can generate up to of power per turbine. The nameplate capacity was changed from to ...
has a rated capacity of 7.58 MW, has an overall height of 198 m (650 ft), a diameter of 126 m (413 ft), and is the world's largest-capacity wind turbine since its introduction in 2007.
At least four companies are working on the development of a 10MW turbine:
- American SuperconductorAmerican SuperconductorAmerican Superconductor is an American energy technologies company based in Devens, Massachusetts specializing in the design and manufacture of power systems and superconducting wire...
- Wind Power Ltd are developing a 10 MW VAWT, the Aerogenerator X
- Sway AS announced the proposed development of a prototype 10 MW wind turbine with a height of 162.5 m (533 ft) and a rotor diameter of 145 m (475 ft).
- Astralux Ltd are developing vertical axis magneto levitated 10 MW turbine with 230 m height and 260 m rotor diameter
- Clipper WindpowerClipper WindpowerClipper Windpower is a wind turbine manufacturing company formed in 2001 by James G.P. Dehlsen, who also formed Zond in 1980. In December 2010 Clipper Windpower was acquired by United Technologies Corporation.-History:...
were developing the Britannia 10 MW HAWT, but terminated the project due to financial challenges.
Largest swept area
The turbine with the largest swept area is a prototype installed by GamesaGamesa Corporación Tecnológica
Gamesa Corporación Tecnológica , is a manufacturing company principally involved in the fabrication of wind turbines and the construction of wind farms....
at Jaulín
Jaulín Gamesa G10X – 4.5 MW Wind Turbine
Jaulín Gamesa G10X – 4.5 MW Wind Turbine near Jaulín, Zaragoza, Spain is a wind turbine with the largest rotor, which surpasses with 128 metres that of Enercon E-126 by 2 metres. It is the prototype of this model. The rotor is fixed on a 120 metres tall tower consisting of concrete and steel...
, Zaragoza, Spain in 2009. The G10X – 4.5 MW has a rotor diameter of 128m.
Tallest
The tallest wind turbine is Fuhrländer Wind Turbine LaasowFuhrländer Wind Turbine Laasow
Fuhrländer Wind Turbine Laasow is a wind turbine, built in 2006 near the village of Laasow, Brandenburg, Germany. It consists of a 160 metre lattice tower, which carries a rotor 90 metres in diameter. It is the tallest wind turbine in the world...
. Its axis is 160 meters above ground and its rotor tips can reach a height of 205 meters. It is the only wind turbine in the world taller than 200 meters.
Largest vertical-axis
Le Nordais wind farm in Cap-Chat, QuebecCap-Chat, Quebec
Cap-Chat is a town in the Canadian province of Québec, in the Regional County Municipality of Haute-Gaspésie, and in the administrative region of Gaspésie-Îles-de-la-Madeleine. Its geographical co-ordinates are lat. 49°6′ N; long. 66°41′ W. Cap-Chat is found 16 km west of...
has a vertical axis wind turbine
Vertical axis wind turbine
Vertical-axis wind turbines are a type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft is set vertically and the main components are located at the base of the turbine...
(VAWT) named Éole, which is the world's largest at 110 m. It has a nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity or maximum effect, refers to the intended technical full–load sustained output of a facility such as a power plant, a chemical plant, fuel plant, metal refinery, mine, and many others.For dispatchable power,...
of 3.8MW.
Most southerly
The turbines currently operating closest to the South PoleSouth Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole...
are three Enercon E-33 in Antarctica, powering New Zealand's Scott Base
Scott Base
Scott Base is a research facility located in Antarctica and is operated by New Zealand. It was named after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy, leader of two British expeditions to the Ross Sea area of Antarctica...
and the United States' McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is a U.S. Antarctic research center located on the southern tip of Ross Island, which is in the New Zealand-claimed Ross Dependency on the shore of McMurdo Sound in Antarctica. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program, a branch of the National...
since December 2009 although a modified HR3 turbine from Northern Power Systems operated at the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station
Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station
The Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station is the American scientific research station on the high plateau of Antarctica. This station is located at the southernmost place on the Earth, the Geographic South Pole, at an elevation of 2,835 meters above sea level.The original Amundsen-Scott Station was...
in 1997 and 1998. In March 2010 CITEDEF designed, built and installed a wind turbine in Argentine Marambio Base
Marambio Base
Prior to the base's foundation a team led by Vice-Commodore Mario Luis Olezza built the 1200 m long, 40 m wide landing track, the first one in the continent. Nowadays, the track, oriented 05/23, is equipped with VOR, DME and NDB electronic landing systems. It also has a radio beacon,...
.
Most productive
Four turbines at Rønland wind farmWind farm
A wind farm is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other...
in Denmark share the record for the most productive wind turbines, with each having generated 63.2 GWh by June 2010
Highest-situated
The world's highest-situated wind turbine is made by DeWindDewind
DeWind is an internationally active producer of wind power plants, originating in Germany. The company was founded in 1995 and is based in Irvine, California and Lübeck, Germany. DeWind has the legal form of a corporation, and, since Summer 2006, it is a subsidiary company of the Californian...
installed by the Seawind Group and located in the Andes, Argentina around 4100 metres (13,451.4 ft) above sea level. The site uses a type D8.2 - 2000 kW / 50 Hz turbine. This turbine has a new drive train concept with a special torque converter (WinDrive) made by Voith
Voith
The Voith GmbH, which is headquartered in Germany, is a family-run corporation in the mechanical engineering sector with worldwide operations....
and a synchronous generator. The WKA was put into operation in December 2007 and has supplied the Veladero mine of Barrick Gold
Barrick Gold
Barrick Gold Corporation is the largest pure gold mining company in the world, with its headquarters in Toronto, Ontario, Canada; and four regional business units located in Australia, Africa, North America and South America...
with electricity since then.
Largest floating wind turbine
The world's largest—and also the first operational deep-water large-capacity—floating wind turbineFloating wind turbine
A floating wind turbine is an offshore wind turbine mounted on a floating structure that allows the turbine to generate electricity in water depths where bottom-mounted towers are not feasible...
is the 2.3 MW Hywind currently operating 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) offshore in 220-meter-deep water, southwest of Karmøy
Karmøy
Karmøy is a municipality in Rogaland county, Norway. It is located southwest of the city of Haugesund in the traditional district of Haugaland....
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
. The turbine began operating in September 2009 and utilizes a Siemens
Siemens Wind Power
Siemens Wind Power, or SWP, is a wind turbine manufacturer with headquarters and main production facilities established in 1980 in Brande, Denmark. SWP is wholly owned by Siemens of Germany since 2004 through the Renewable Energy division in the Siemens Energy sector...
2.3 MW turbine
See also
- American Wind Energy AssociationAmerican Wind Energy AssociationFormed in 1974, the American Wind Energy Association is a Washington, D.C.-based national trade association representing wind power project developers, equipment suppliers, service providers, parts manufacturers, utilities, researchers, and others involved in the wind industry.With over 2,500...
- Atmospheric icingAtmospheric icingAtmospheric icing occurs when water droplets in the atmosphere freeze on objects they contact. This can be extremely dangerous to aircraft, as the built-up ice changes the aerodynamics of the flight surfaces, which can increase the risk of a subsequent stalling of the airfoil...
- Balancing machineBalancing MachineA balancing machine is a measuring tool used for balancing rotating machine parts such as rotors for electric motors, fans, turbines, disc brakes, disc drives, propellers and pumps. The machine usually consists of two rigid pedestals, with suspension and bearings on top supporting a mounting...
- Compact wind acceleration turbineCompact wind acceleration turbineCompact Wind Acceleration Turbines are a class of wind turbine that uses structures to accelerate wind before it enters the wind-generating element....
- Environmental concerns with electricity generationEnvironmental concerns with electricity generationThe environmental impact of electricity generation is significant because modern society uses large amounts of electrical power. This power is normally generated at power plants that convert some other kind of energy into electrical power...
- Environmental effects of wind powerEnvironmental effects of wind powerCompared to the environmental impact of traditional energy sources, the environmental impact of wind power is relatively minor. Wind power consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a...
- Éolienne BolléeÉolienne BolléeThe Éolienne Bollée is an unusual wind turbine, unique for having a stator and a rotor, as a water turbine has. The eponymous invention was first patented in 1868 by Ernest Sylvain Bollée in France...
- Floating wind turbineFloating wind turbineA floating wind turbine is an offshore wind turbine mounted on a floating structure that allows the turbine to generate electricity in water depths where bottom-mounted towers are not feasible...
- GE 1.5 MW wind turbineGE 1.5 MW wind turbineGE Wind Energy is a branch of GE Energy, a subsidiary of General Electric. The company manufactures and sells wind turbines to the international market. In 2009, GE was the second largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world.-History:...
- Green energy
- High altitude wind powerHigh altitude wind powerHigh-altitude wind power has been imagined as a source of useful energy since 1833 with John Etzler's vision of capturing the power of winds high in the sky by use of tether and cable technology...
- Hybrid power sourceHybrid power sourceThe hybrid power plant is a complete electrical power supply system that can be easily configured to meet a broad range of remote power needs. There are three basic elements to the system - the power source, the battery, and the power management center. The power sources are a wind turbine, diesel...
- Lists of wind farms by country
- List of wind turbine manufacturers
- List of wind turbines
- Maglev wind turbine
- MicrogenerationMicrogenerationMicrogeneration is the small-scale generation of heat and power by individuals, small businesses and communities to meet their own needs, as alternatives or supplements to traditional centralized grid-connected power...
- Ram air turbineRam air turbineA ram air turbine is a small turbine that is connected to a hydraulic pump, or electrical generator, installed in an aircraft and used as a power source...
- Renewable energyRenewable energyRenewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
- Thomas O. PerryThomas O. PerryThomas Osborn Perry was a mechanical engineer, designer, and the original innovator of the all-metal windmill. Perry made significant contributions to the field of wind powered turbines and was an early pioneer of modern wind power technology.- History :...
- TurbineTurbineA turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
- Wind farmWind farmA wind farm is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other...
- Wind lensWind lensA Wind lens is a modification made to a wind turbine to make it a more efficient way to capture wind energy. The modification is a ring structure called a brim or wind lens which surrounds the blades, diverting air away from the exhaust outflow behind the blades...
- Wind runWind runWind run is a meteorological term used to categorize or determine the total distance of the traveled wind over a period of time. The readings are collected using an anemometer ....
- Wind turbines (UK domestic)Wind turbines (UK domestic)Small wind turbines intended for installation on an individual home have been on the market in the United Kingdom for many years, but their popularity and public awareness is now increasing substantially....
- WindbeltWindbeltThe Windbelt is a device for converting wind power to electricity. A windbelt is essentially an aeolian harp except that it exploits the motion of the string produced by the aeroelastic flutter effect to move a magnet closer and farther from one or more electromagnetic coil and thus induce current...
- WindpumpWindpumpA windpump is a windmill used for pumping water, either as a source of fresh water from wells, or for draining low-lying areas of land. Once a common fixture on farms in semi-arid areas, windpumps are still used today where electric power is not available or too expensive.-History:Windmills were...
Further reading
- Tony Burton, David Sharpe, Nick Jenkins, Ervin Bossanyi: Wind Energy Handbook, John Wiley & Sons, 1st edition (2001), ISBN 0-471-48997-2
- Darrell, Dodge, Early History Through 1875, TeloNet Web Development, Copyright 1996–2001
- David, Macaulay, New Way Things Work, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Copyright 1994–1999, pg.41-42
- Erich Hau Wind turbines: fundamentals, technologies, application, economics Birkhäuser, 2006 ISBN 3540242406 (preview on Google Books)
- David Spera (ed,) Wind Turbine Technology: Fundamental Concepts in Wind Turbine Engineering, Second Edition (2009), ASME Press, ISBN #: 9780791802601
External links
- Harvesting the Wind (45 lectures about wind turbines by professor Magdi Ragheb
- Time-lapse video of wind turbine installation at the WMRA Deer Island Wastewater Treatment Plant
- Wind Projects
- Guided tour on wind energy
- Wind Energy Technology World Wind Energy Association
- Wind turbine simulation, National Geographic
- Airborne Wind Industry Association international

