
Capacity factor
Encyclopedia
The net capacity factor or load factor of a power plant is the ratio of the actual output of a power plant over a period of time and its potential output if it had operated at full nameplate capacity the entire time. To calculate the capacity factor, take the total amount of energy
the plant produced during a period of time and divide by the amount of energy the plant would have produced at full capacity. Capacity factors vary greatly depending on the type of fuel
that is used and the design of the plant. The capacity factor should not be confused with the availability factor
, capacity credit (firm capacity) or with efficiency
.
with a capacity of 1,000 megawatts (MW) might produce 648,000 megawatt-hours (MW·h) in a 30-day month. The number of megawatt-hours that would have been produced had the plant been operating at full capacity can be determined by multiplying the plant's maximum capacity by the number of hours in the time period. 1,000 MW × 30 days × 24 hours/day is 720,000 MW·h. The capacity factor is determined by dividing the actual output with the maximum possible output. In this case, the capacity factor is 0.9 (90%).
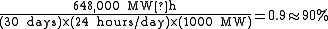
consists of ten Enercon
E70-E4 wind turbine
s @ 2 MW nameplate capacity
for a total installed capacity of 20 MW. In 2008 the wind farm generated 43,416 MW·h of electricity. (Note 2008 was a leap year.) The capacity factor for this wind farm in 2008 was just under 25%:
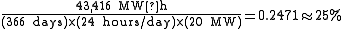
As of April 2011, the Danish wind farm Horns Rev 2
(the world's largest when it was inaugurated in September 2009 comprising 91 Siemens
SWT-2.3-93 wind turbines each of 2.3 MW) with a nominal total capacity of 209 MW, has the best capacity factor of any offshore wind farm at 46.7% having produced over 1.5 years 1,278 GW·h. The record for an onshore wind farm is held by Burradale, which reached an annual capacity factor of 57.9% for 2005.
is the largest power generating station in the world by nameplate capacity. In 2009, not yet fully complete, it had 26 main generator units @ 700 MW and two auxiliary generator units @ 50 MW for a total installed capacity of 18,300 MW. Total generation in 2009 was 79.47 TW·h, for a capacity factor of just under 50%:
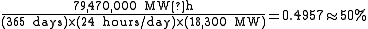
Hoover Dam
has a nameplate capacity of 2080 MW and an annual generation averaging 4.2 TW·h. (The annual generation has varied between a high of 10.348 TW·h in 1984, and a low of 2.648 TW·h in 1956.) Taking the average figure for annual generation gives a capacity factor of:
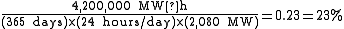
, nuclear plants
, coal plants
and bioenergy plants
that burn solid material are almost always operated as base load plants.
The second reason that a plant would have a capacity factor lower than 100% is that output is curtailed because the electricity is not needed or because the price of electricity is too low to make production economical. This accounts for most of the unused capacity of peaking power plant
s. Peaking plants may operate for only a few hours per year or up to several hours per day. Their electricity is relatively expensive. It is uneconomical, even wasteful, to make a peaking power plant as efficient as a base load plant because they do not operate enough to pay for the extra equipment cost, and perhaps not enough to offset the embodied energy
of the additional components.
A third reason is a variation on the second: the operators of a hydroelectric dam may uprate its nameplate capacity by adding more generator units. Since the supply of fuel (i.e. water) remains unchanged, the uprated dam obtains a higher peak output in exchange for a lower capacity factor. Because hydro plants are highly dispatchable, they are able to act as load following power plant
s. Having a higher peak capacity allows a dam's operators to sell more of the annual output of electricity during the hours of highest electricity demand (and thus the highest spot price
). In practical terms, uprating a dam allows it to balance
a larger amount of intermittent energy sources on the grid such as wind farm
s and solar power plants, and to compensate for unscheduled shutdowns of baseload power plants, or brief surges in demand for electricity.
s, also called intermediate power plants, are in between these extremes in terms of capacity factor, efficiency and cost per unit of electricity. They produce most of their electricity during the day, when prices and demand are highest. However, the demand and price of electricity is far lower during the night and intermediate plants shutdown or reduce their output to low levels overnight.
sources such as solar power
, wind power
and hydroelectricity
, there is a third reason for unused capacity. The plant may be capable of producing electricity, but its fuel (wind
, sunlight
or water
) may not be available
. A hydroelectric plant's production may also be affected by requirements to keep the water level from getting too high or low and to provide water for fish
downstream. However, solar, wind and hydroelectric plants do have high availability factor
s, so when they have fuel available, they are almost always able to produce electricity.
When hydroelectric plants have water available, they are also useful for load following, because of their high dispatchability. A typical hydroelectric plant's operators can bring it from a stopped condition to full power in just a few minutes.
Wind farm
s are variable, due to the natural variability of the wind. For a wind farm, the capacity factor is mostly determined by the availability of wind. Transmission line capacity and electricity demand also affect the capacity factor.
Solar energy is variable because of the daily rotation of the earth and because of cloud cover. However, according to the SolarPACES
programme of the International Energy Agency
(IEA), solar power plants designed for solar-only generation are well matched to summer noon peak loads in areas with significant cooling demands, such as Spain
or the south-western United States
., although in some locations solar PV does not reduce the need for generation of network upgrades given that air conditioner peak demand often occurs in the late afternoon or early evening when solar output is zero. SolarPACES states that by using thermal energy storage systems the operating periods of solar thermal power (CSP) stations can be extended to meet baseload needs. The IEA CSP Technology Roadmap (2010) suggests that "in the sunniest countries, CSP can be expected to become a competitive source of bulk power in peak and intermediate loads by 2020, and of base-load power by 2025 to 2030".
Geothermal
has a higher capacity factor than many other power sources, and geothermal resources are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. While the carrier medium for geothermal electricity
(water) must be properly managed, the source of geothermal energy, the Earth's heat, will be available for the foreseeable future. Geothermal power can be looked at as a nuclear battery where the heat is produced via the decay of radioactive elements in the core and mantle of the earth.
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
the plant produced during a period of time and divide by the amount of energy the plant would have produced at full capacity. Capacity factors vary greatly depending on the type of fuel
Fuel
Fuel is any material that stores energy that can later be extracted to perform mechanical work in a controlled manner. Most fuels used by humans undergo combustion, a redox reaction in which a combustible substance releases energy after it ignites and reacts with the oxygen in the air...
that is used and the design of the plant. The capacity factor should not be confused with the availability factor
Availability factor
The availability factor of a power plant is the amount of time that it is able to produce electricity over a certain period, divided by the amount of the time in the period. Occasions where only partial capacity is available may or may not be deducted...
, capacity credit (firm capacity) or with efficiency
Betz' law
Betz's law is a theory about the maximum possible energy to be derived from a "hydraulic wind engine", or a wind turbine such as the Éolienne Bollée , the Eclipse Windmill , and the Aermotor...
.
Baseload power plant
A base load power plantBase load power plant
Baseload is the minimum amount of power that a utility or distribution company must make available to its customers, or the amount of power required to meet minimum demands based on reasonable expectations of customer requirements...
with a capacity of 1,000 megawatts (MW) might produce 648,000 megawatt-hours (MW·h) in a 30-day month. The number of megawatt-hours that would have been produced had the plant been operating at full capacity can be determined by multiplying the plant's maximum capacity by the number of hours in the time period. 1,000 MW × 30 days × 24 hours/day is 720,000 MW·h. The capacity factor is determined by dividing the actual output with the maximum possible output. In this case, the capacity factor is 0.9 (90%).
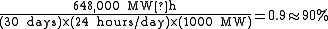
Wind farm
The Burton Wold Wind FarmBurton Wold Wind Farm
Burton Wold Wind Farm is a wind farm located near Burton Latimer in the English county of Northamptonshire, UK. The Wind Farm was developed by Your Energy Ltd, is owned by Mistral Windfarms and operated by Engineering Renewables Ltd. E.ON UK is buying the electricity output of the project under a...
consists of ten Enercon
Enercon
Enercon GmbH, based in Aurich, Germany, is the fourth-largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world and has been the market leader in Germany since the mid-nineties. Enercon has production facilities in Germany , Sweden, Brazil, India, Canada, Turkey and Portugal...
E70-E4 wind turbine
Wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
s @ 2 MW nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity or maximum effect, refers to the intended technical full–load sustained output of a facility such as a power plant, a chemical plant, fuel plant, metal refinery, mine, and many others.For dispatchable power,...
for a total installed capacity of 20 MW. In 2008 the wind farm generated 43,416 MW·h of electricity. (Note 2008 was a leap year.) The capacity factor for this wind farm in 2008 was just under 25%:
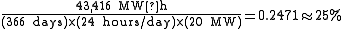
As of April 2011, the Danish wind farm Horns Rev 2
Horns Rev 2
Horns Rev 2 is an offshore wind farm located on Horns Rev in a shallow area in the eastern North Sea, about off the westernmost point of Denmark, Blåvands Huk...
(the world's largest when it was inaugurated in September 2009 comprising 91 Siemens
Siemens Wind Power
Siemens Wind Power, or SWP, is a wind turbine manufacturer with headquarters and main production facilities established in 1980 in Brande, Denmark. SWP is wholly owned by Siemens of Germany since 2004 through the Renewable Energy division in the Siemens Energy sector...
SWT-2.3-93 wind turbines each of 2.3 MW) with a nominal total capacity of 209 MW, has the best capacity factor of any offshore wind farm at 46.7% having produced over 1.5 years 1,278 GW·h. The record for an onshore wind farm is held by Burradale, which reached an annual capacity factor of 57.9% for 2005.
Hydroelectric dam
As of 2010, Three Gorges DamThree Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, located in the Yiling District of Yichang, in Hubei province, China...
is the largest power generating station in the world by nameplate capacity. In 2009, not yet fully complete, it had 26 main generator units @ 700 MW and two auxiliary generator units @ 50 MW for a total installed capacity of 18,300 MW. Total generation in 2009 was 79.47 TW·h, for a capacity factor of just under 50%:
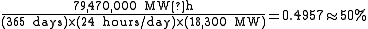
Hoover Dam
Hoover Dam
Hoover Dam, once known as Boulder Dam, is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the US states of Arizona and Nevada. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression and was dedicated on September 30, 1935, by President...
has a nameplate capacity of 2080 MW and an annual generation averaging 4.2 TW·h. (The annual generation has varied between a high of 10.348 TW·h in 1984, and a low of 2.648 TW·h in 1956.) Taking the average figure for annual generation gives a capacity factor of:
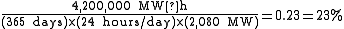
Reasons for reduced capacity factor
There are several reasons why a plant would have a capacity factor lower than 100%. The first reason is that it was out of service or operating at reduced output for part of the time due to equipment failures or routine maintenance. This accounts for most of the unused capacity of base load power plants. Base load plants have the lowest costs per unit of electricity because they are designed for maximum efficiency and are operated continuously at high output. Geothermal plantsGeothermal power
Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Earth's geothermal energy originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of minerals...
, nuclear plants
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
, coal plants
Fossil fuel power plant
A fossil-fuel power station is a power station that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum to produce electricity. Central station fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation...
and bioenergy plants
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is renewable energy made available from materials derived from biological sources. Biomass is any organic material which has stored sunlight in the form of chemical energy. As a fuel it may include wood, wood waste, straw, manure, sugarcane, and many other byproducts from a variety of...
that burn solid material are almost always operated as base load plants.
The second reason that a plant would have a capacity factor lower than 100% is that output is curtailed because the electricity is not needed or because the price of electricity is too low to make production economical. This accounts for most of the unused capacity of peaking power plant
Peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers," are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity.-Peak hours:...
s. Peaking plants may operate for only a few hours per year or up to several hours per day. Their electricity is relatively expensive. It is uneconomical, even wasteful, to make a peaking power plant as efficient as a base load plant because they do not operate enough to pay for the extra equipment cost, and perhaps not enough to offset the embodied energy
Embodied energy
Embodied energy is defined as the sum of energy inputs that was used in the work to make any product, from the point of extraction and refining materials, bringing it to market, and disposal / re-purposing of it...
of the additional components.
A third reason is a variation on the second: the operators of a hydroelectric dam may uprate its nameplate capacity by adding more generator units. Since the supply of fuel (i.e. water) remains unchanged, the uprated dam obtains a higher peak output in exchange for a lower capacity factor. Because hydro plants are highly dispatchable, they are able to act as load following power plant
Load following power plant
A load following power plant is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load following plants are typically in-between base load and peaking power plants in efficiency, speed of startup and shutdown, construction cost, cost of electricity...
s. Having a higher peak capacity allows a dam's operators to sell more of the annual output of electricity during the hours of highest electricity demand (and thus the highest spot price
Spot price
The spot price or spot rate of a commodity, a security or a currency is the price that is quoted for immediate settlement . Spot settlement is normally one or two business days from trade date...
). In practical terms, uprating a dam allows it to balance
Load balancing (electrical power)
Load balancing refers to the use of various techniques by electrical power stations to store excess electrical power during low demand periods for release as demand rises....
a larger amount of intermittent energy sources on the grid such as wind farm
Wind farm
A wind farm is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other...
s and solar power plants, and to compensate for unscheduled shutdowns of baseload power plants, or brief surges in demand for electricity.
Load following power plants
Load following power plantLoad following power plant
A load following power plant is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load following plants are typically in-between base load and peaking power plants in efficiency, speed of startup and shutdown, construction cost, cost of electricity...
s, also called intermediate power plants, are in between these extremes in terms of capacity factor, efficiency and cost per unit of electricity. They produce most of their electricity during the day, when prices and demand are highest. However, the demand and price of electricity is far lower during the night and intermediate plants shutdown or reduce their output to low levels overnight.
Capacity factor and renewable energy
When it comes to several renewable energyRenewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
sources such as solar power
Solar power
Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity and biomass, account for most of the available...
, wind power
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
and hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
, there is a third reason for unused capacity. The plant may be capable of producing electricity, but its fuel (wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
, sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
or water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
) may not be available
Intermittent power source
An intermittent energy source is any source of energy that is not continuously available due to some factor outside direct control. The intermittent source may be quite predictable, for example, tidal power, but cannot be dispatched to meet the demand of a power system. Examples of intermittent...
. A hydroelectric plant's production may also be affected by requirements to keep the water level from getting too high or low and to provide water for fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
downstream. However, solar, wind and hydroelectric plants do have high availability factor
Availability factor
The availability factor of a power plant is the amount of time that it is able to produce electricity over a certain period, divided by the amount of the time in the period. Occasions where only partial capacity is available may or may not be deducted...
s, so when they have fuel available, they are almost always able to produce electricity.
When hydroelectric plants have water available, they are also useful for load following, because of their high dispatchability. A typical hydroelectric plant's operators can bring it from a stopped condition to full power in just a few minutes.
Wind farm
Wind farm
A wind farm is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other...
s are variable, due to the natural variability of the wind. For a wind farm, the capacity factor is mostly determined by the availability of wind. Transmission line capacity and electricity demand also affect the capacity factor.
Solar energy is variable because of the daily rotation of the earth and because of cloud cover. However, according to the SolarPACES
SolarPACES
SolarPACES is an international programme of the International Energy Agency to further the collaborative development, testing and marketing of concentrating solar power plants...
programme of the International Energy Agency
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
(IEA), solar power plants designed for solar-only generation are well matched to summer noon peak loads in areas with significant cooling demands, such as Spain
Solar power in Spain
Spain is one of the most advanced countries in the development of solar energy, since it is one of the countries of Europe with more hours of sunshine. The Spanish government committed to achieving a target of 12 percent of primary energy from renewable energy by 2010 with an installed solar...
or the south-western United States
Solar power plants in the Mojave Desert
There are several solar power plants in the Mojave Desert which supply power to the electricity grid. Solar Energy Generating Systems is the name given to nine solar power plants in the Mojave Desert which were built in the 1980s. These plants have a combined capacity of 354 megawatts making them...
., although in some locations solar PV does not reduce the need for generation of network upgrades given that air conditioner peak demand often occurs in the late afternoon or early evening when solar output is zero. SolarPACES states that by using thermal energy storage systems the operating periods of solar thermal power (CSP) stations can be extended to meet baseload needs. The IEA CSP Technology Roadmap (2010) suggests that "in the sunniest countries, CSP can be expected to become a competitive source of bulk power in peak and intermediate loads by 2020, and of base-load power by 2025 to 2030".
Geothermal
Geothermal
Geothermal is related to energy and may refer to:* The geothermal gradient and associated heat flows from within the Earth- Renewable technology :...
has a higher capacity factor than many other power sources, and geothermal resources are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. While the carrier medium for geothermal electricity
Geothermal electricity
Geothermal electricity is electricity generated from geothermal energy.Technologies in use include dry steam power plants, flash steam power plants and binary cycle power plants...
(water) must be properly managed, the source of geothermal energy, the Earth's heat, will be available for the foreseeable future. Geothermal power can be looked at as a nuclear battery where the heat is produced via the decay of radioactive elements in the core and mantle of the earth.
Typical capacity factors
- Wind farms 20-40%.
- Photovoltaic solar in Massachusetts 12-15%.
- Photovoltaic solar in Arizona 19%.
- Hydroelectricity, worldwide average 44% , range of 10% - 99% depending on design (small plant in big river will always have enough water to operate and vice versa), water availability (with or without regulation via storage dam, where a storage dam is designed to store at least enough water to operate the plant at full capacity for around half a year to allow full regulation of the annual flow of the river).
- Nuclear energy 70% (1971-2009 average of USA's plants).
- Nuclear energy 91.2% (2010 average of USA's plants).

