Continuously variable transmission
Encyclopedia
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is a transmission
that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratio
s between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios. The flexibility of a CVT allows the driving shaft to maintain a constant angular velocity over a range of output velocities. This can provide better fuel economy
than other transmissions by enabling the engine
to run at its most efficient revolutions per minute
(RPM) for a range of vehicle speeds. Alternatively it can be used to maximize the performance of a vehicle by allowing the engine to turn at the RPM at which it produces peak power. This is typically higher than the RPM that achieves peak efficiency. Finally, a CVT does not strictly require the presence of a clutch
, allowing the dismissal thereof. In some vehicles though (i.e. motorcycles), a centrifugal clutch
is nevertheless added, however this is only to provide a "neutral" stance on a motorcycle (useful when idling).
 Many small tractor
Many small tractor
s for home and garden use have simple rubber belt CVTs. For example, the John Deere Gator
line of small utility vehicles use a belt with a conical pulley system. They can deliver an abundance of power and can reach speeds of 10 mile per hour, all without need for a clutch or shifting gears. Nearly all snowmobile
s, old and new, and motorscooters use CVTs, typically the rubber belt/variable pulley variety.
Some combine harvester
s have CVTs. The CVT allows the forward speed of the combine to be adjusted independently of the engine speed. This allows the operator to slow or accelerate as needed to accommodate variations in thickness of the crop.
CVTs have been used in aircraft
electrical power generating systems since the 1950s and in Sports Car Club of America
(SCCA) Formula 500
race cars since the early 1970s. CVTs were banned from Formula 1 in 1994 due to concerns that the best-funded teams would dominate if they managed to create a viable F1 CVT transmission. More recently, CVT systems have been developed for go-karts
and have proven to increase performance and engine life expectancy. The Tomcar
range of off-road vehicles also utilizes the CVT system.
Some drill presses and milling machine
s contain a pulley-based CVT where the output shaft has a pair of manually-adjustable conical pulley halves through which a wide drive belt from the motor loops. The pulley on the motor, however, is usually fixed in diameter, or may have a series of given-diameter steps to allow a selection of speed ranges. A handwheel on the drill press, marked with a scale corresponding to the desired machine speed, is mounted to a reduction gearing system for the operator to precisely control the width of the gap between the pulley halves. This gap width thus adjusts the gearing ratio between the motor's fixed pulley and the output shaft's variable pulley, changing speed of the chuck. A tensioner pulley is implemented in the belt transmission to take up or release the slack in the belt as the speed is altered. In most cases the speed must be changed with the motor running.
CVTs should be distinguished from Power Sharing Transmissions (PSTs), as used in newer hybrid cars
, such as the Toyota Prius
, Highlander
and Camry, the Nissan Altima
, and newer-model Ford Escape Hybrid SUVs
. CVT technology uses only one input from a prime mover, and delivers variable output speeds and torque; whereas PST technology uses two prime mover inputs, and varies the ratio of their contributions to output speed and power. These transmissions are fundamentally different. However the Mitsubishi Lancer
, Proton Inspira, Honda Insight
, Honda Fit
, and Honda CR-Z
hybrids, the Nissan Tiida
/Versa (only the SL model), Nissan Cube
, Juke, Sentra
, Altima
, Maxima
, Rogue
, Murano
, Honda Capa
, Honda Civic HX, Jeep Patriot
and Compass
use CVT.
The V-belt needs to be very stiff in the pulley's axial direction in order to make only short radial movements while sliding in and out of the pulleys. This can be achieved by a chain and not by homogeneous rubber. To dive out of the pulleys one side of the belt must push. This again can be done only with a chain. Each element of the chain has conical sides, which perfectly fit to the pulley if the belt is running on the outermost radius. As the belt moves into the pulleys the contact area gets smaller. The contact area is proportional to the number of elements, thus the chain has lots of very small elements. The shape of the elements is governed by the static of a column
. The pulley-radial thickness of the belt is a compromise between maximum gear ratio and torque. For the same reason the axis between the pulleys is as thin as possible. A film of lubricant is applied to the pulleys. It needs to be thick enough so that the pulley and the belt never touch and it must be thin in order not to waste power when each element dives into the lubrication film. Additionally, the chain elements stabilize about 12 steel bands. Each band is thin enough so that it bends easily. If bending, it has a perfect conical surface on its side. In the stack of bands each band corresponds to a slightly different gear ratio, and thus they slide over each other and need oil between them. Also the outer bands slide through the stabilizing chain, while the center band can be used as the chain linkage.
. One disc is the input, and the other is the output (they do not quite touch). Power is transferred from one side to the other by rollers. When the roller's axis is perpendicular to the axis of the near-conical parts, it contacts the near-conical parts at same-diameter locations and thus gives a 1:1 gear ratio. The roller can be moved along the axis of the near-conical parts, changing angle as needed to maintain contact. This will cause the roller to contact the near-conical parts at varying and distinct diameters, giving a gear ratio of something other than 1:1. Systems may be partial or full toroidal. Full toroidal systems are the most efficient design while partial toroidals may still require a torque converter, and hence lose efficiency.
Diagrams:
in 2006 and is now (2011) commercially available. Two rotating transmission disks, each with magnets attached, synchronously revolve. A change in the radius of the magnets on each of the disks causes a change in the transmission ratio.
The IVT dates back to before the 1930s; the original design converts rotary motion to oscillating motion and back to rotary motion using roller clutches. The stroke of the intermediate oscillations is adjustable, varying the output speed of the shaft. This original design is still manufactured today, and an example and animation of this IVT can be found here. Paul B. Pires created a more compact (radially symmetric) variation that employs a ratchet mechanism instead of roller clutches, so it doesn't have to rely on friction to drive the output. An article and sketch of this variation can be found here
Most IVTs result from the combination of a CVT with a planetary gear system (which is also known as an epicyclic gear system) which enforces an IVT output shaft rotation speed which is equal to the difference between two other speeds within the IVT. This IVT configuration uses its CVT as a continuously variable regulator (CVR) of the rotation speed of any one of the three rotators of the planetary gear system (PGS). If two of the PGS rotator speeds are the input and output of the CVR, there is a setting of the CVR that results in the IVT output speed of zero. The maximum output/input ratio can be chosen from infinite practical possibilities through selection of additional input or output gear, pulley or sprocket sizes without affecting the zero output or the continuity of the whole system. The IVT is always engaged, even during its zero output adjustment.
IVTs can in some implementations offer better efficiency when compared to other CVTs as in the preferred range of operation because most of the power flows through the planetary gear system and not the controlling CVR. Torque transmission capability can also be increased. There's also possibility to stage power splits for further increase in efficiency, torque transmission capability and better maintenance of efficiency over a wide gear ratio range.
An example of a true IVT is the SIMKINETICS SIVAT that uses a ratcheting CVR. Its CVR ratcheting mechanism contributes minimal IVT output ripple across its range of ratios.
Another example of a true IVT is the Hydristor
because the front unit connected to the engine can displace from zero to 27 cubic inches per revolution forward and zero to -10 cubic inches per revolution reverse. The rear unit is capable of zero to 75 cubic inches per revolution.
These CVTs can transfer substantial torque, because their static friction actually increases relative to torque throughput, so slippage is impossible in properly designed systems. Efficiency is generally high, because most of the dynamic friction is caused by very slight transitional clutch speed changes. The drawback to ratcheting CVTs is vibration caused by the successive transition in speed required to accelerate the element, which must supplant the previously operating and decelerating, power transmitting element.
Ratcheting CVTs are distinguished from VDPs and roller-based CVTs by being static friction-based devices, as opposed to being dynamic friction-based devices that waste significant energy through slippage of twisting surfaces. An example of a ratcheting CVT is one prototyped as a bicycle transmission protected under in which strong pedalling torque causes this mechanism to react against the spring, moving the ring gear/chainwheel assembly toward a concentric, lower gear position. When the pedaling torque relaxes to lower levels, the transmission self-adjusts toward higher gears, accompanied by an increase in transmission vibration.
A running prototype and animation of a functioning two stage ratcheting CVT can be found below:
 Hydrostatic transmissions use a variable displacement pump
Hydrostatic transmissions use a variable displacement pump
and a hydraulic motor
. All power is transmitted by hydraulic fluid
. These types can generally transmit more torque, but can be sensitive to contamination. Some designs are also very expensive. However, they have the advantage that the hydraulic motor can be mounted directly to the wheel hub, allowing a more flexible suspension system and eliminating efficiency losses from friction in the drive shaft and differential components. This type of transmission is relatively easy to use because all forward and reverse speeds can be accessed using a single lever.
An integrated hydrostatic transaxle (IHT) uses a single housing for both hydraulic elements and gear-reducing elements. This type of transmission, most commonly manufactured by Hydro-Gear, has been effectively applied to a variety of inexpensive and expensive versions of ridden lawn mower
s and garden tractors. Many versions of riding lawn mowers and garden tractors propelled by a hydrostatic transmission are capable of pulling a reverse tine tiller and even a single bladed plow.
One class of riding lawn mower that has recently gained in popularity with consumers is zero turning radius
mowers. These mowers have traditionally been powered with wheel hub mounted hydraulic motors driven by continuously variable pumps, but this design is relatively expensive. Hydro-Gear, created the first cost-effective integrated hydrostatic transaxle suitable for propelling consumer zero turning radius mowers.
Some heavy equipment
may also be propelled by a hydrostatic transmission; e.g. agricultural machinery including foragers, combines, and some tractors. A variety of heavy earth-moving equipment manufactured by Caterpillar Inc.
, e.g. compact and small wheel loaders, track type loaders and tractors, skid-steered loaders and asphalt compactors use hydrostatic transmission. Hydrostatic CVTs are usually not used for extended duration high torque applications due to the heat that is generated by the flowing oil.
The Honda DN-01
motorcycle is the first road-going consumer vehicle with hydrostatic drive that employs a variable displacement axial piston pump with a variable-angle swashplate
.
Also, a choking pulley is very small so that its moment arm is very small. A larger moment arm reduces the force needed to rotate a pulley. For example, using a long wrench, which has a large moment arm, to open a nut requires less force than using a short wrench, which has a small moment arm. Assuming that the diameter of a choking pulley is twice the diameter of its shaft, which is a generous estimate, then the frictional resistance force at the outer diameter of a choking pulley is half the frictional resistance force at the shaft of a choking pulley.
Regarding the previous paragraph, the chain of an iCVT forms an open loop on its variator pulley that partially covers its variator pulley such that an open section, which is not covered by the chain, exist. This is similar to a sprocket of a bicycle where there is a section of the sprocket that is covered by its chain, and a section of the sprocket that is not covered by its chain. During one complete rotation, the toothed section of the variator pulley of an iCVT passes by the open section and re-engages with the chain. Here if the transmission diameter of the variator pulley does not represent an integer number of teeth, improper re-engagement between the teeth of the variator pulley and its chain will occur. Also, the transmission diameter of the variator pulley cannot be changed while the toothed section of the variator pulley is covering the entire open section of its chain loop. Since this is similar to where a plate is glued across the open section of a chain loop, which does not allow expansion or contraction of the chain loop as required for transmission diameter change of the variator pulley. Therefore the transmission diameter of the variator pulley has to be changed one increment during an interval where the variator pulley rotates from an initial position where a portion of the toothed section of the variator pulley is positioned at the open section of the chain loop but not covering the entire open section, to the final position where the toothed section of the variator pulley passes by the open section of the chain loop and is about to re-engage with the chain. Since it takes less than one full rotation to rotate the variator pulley from its initial position to its final position mentioned in the previous sentence, the transmission diameter of the variator pulley has to be changed one increment within less than one full rotation.
In addition, as the transmission diameter is increased, the chain has to be pushed up the inclined surfaces of the pulley halves of the variator pulley, while the tension in the chain tends to pull the chain towards the opposite direction. Hence a large force, which is larger than the tension in the chain, is required to change the transmission diameter. Since the transmission ratio has to be changed within less than one full rotation of the variator pulley, a large force has to be applied on the pulley halves within a very short duration. If for example the variator pulley rotates at 3600 rpm, which is equivalent to 60 revolutions per second, then the force required to change the transmission ratio has to be applied within 1/60 seconds. This would be similar to hitting something with a hammer. Therefore, here significant shock loads are applied to the variator pulley during transmission ratio change that increases the transmission diameter. These shock loads my cause comfort problem for the driver of the vehicle using an iCVT. Also an iCVT has to be designed as to be able to resist these shock loads which would most likely increases the cost and weight of an iCVT.
Another possible problem with an iCVT is that the pins of the variator pulley can fall-out when they are not engaged with their chain. And wear of the pins and the grooves of the pulley halves can cause some serious performance and reliability problems.
Diagram and video clip:
The more sophisticated twin cone mesh system is also a type of cone CVT.
In a CVT with oscillating cones, the torque is transmitted via friction from a variable number of cones (according to the torque to be transmitted) to a central, barrel-shaped hub.
The side surface of the hub is convex with a specific radius of curvature which is smaller than the concavity radius of the cones. In this way, there will be only one (theoretical) contact point between each cone and the hub at any time.
A new CVT using this technology, the Warko, was presented in Berlin during the 6th International CTI Symposium of Innovative Automotive Transmissions, on December 3–7, 2007.
A particular characteristic of the Warko is the absence of a clutch: the engine is always connected to the wheels, and the rear drive is obtained by means of an epicyclic system
in output. This system, named “power split”, allows the engine to have a "neutral gear": when the engine turns (connected to the sun gear of the epicyclic system), the variator (i.e., the planetary gears) will compensate for the engine rotation, so the outer ring gear (which provides output) remains stationary.
Diagrams:
For more details see EP1688645A1
Prototype applications for wind farms Video 1
Inside mechanical parts Video 2
The motion transmission between rollers and rotors is assisted by an adapted traction fluid, which ensures the proper friction between the surfaces and slows down wearing thereof. Unlike other systems, the radial rollers do not show a tangential speed variation (delta) along the contact lines on the rotors. From this, a greater mechanical efficiency and working life are obtained.
The main advantages of this CVT are the manufacturing inexpensiveness and the high power efficiency.
, in 1490, conceptualized a stepless continuously variable transmission. The first patent
for a friction-based belt CVT was filed in Europe by Daimler and Benz in 1886, and a US Patent for a toroidal CVT was granted in 1935.
In 1910 Zenith Motorcycles
built a V2-Motorcycle with the Gradua-Gear which was a CVT. This Zenith-Gradua was so successful in hillclimb events, that it was eventually barred, so that other manufacturers had a chance to win.
1912 the British motorcycle manufacturer Rudge-Whitworth built the Rudge Multigear. The Multi was a much improved version of Zenith’s Gradua-Gear. The Rudge Multi was so successful that CVT-gears were eventually barred at the famous Tourist Trophy
race (which was the world's most important motorcycle race before World War I) from 1913 on.
In 1922 Browne offered a motorcycle with variable-stroke ratchet drive using a face ratchet.
An early application of CVT was in the British Clyno
car, introduced in 1923.
A CVT, called Variomatic
, was designed and built by Hub van Doorne
, co-founder of Van Doorne's Automobiel Fabriek
(DAF), in the late 1950s, specifically to produce an automatic transmission for a small, affordable car. The first DAF car using van Doorne's CVT, the DAF 600
,was produced in 1958. Van Doorne's patents were later transferred to a company called VDT (Van Doorne Transmissie B.V.) when the passenger car division was sold to Volvo
in 1975; its CVT was used in the Volvo 340.
In 1995, VDT was acquired by Robert Bosch GmbH
.
Many snowmobiles use a rubber belt CVT. In 1974, Rokon
offered a motorcycle with a rubber belt CVT.
CVTs are used in some ATVs. The first ATV equipped with CVT was Suzuki
's LT80 mini in 1987.
In early 1987, Subaru
launched the Justy in Tokyo with an electronically controlled continuously variable transmission (ECVT) developed by Fuji Heavy Industries
, which owns Subaru. In 1989 the Justy became the first production car in the U.S. to offer CVT technology. While the Justy saw only limited success, Subaru continues to use CVT in its kei car
s to this day, while also supplying it to other manufacturers.
In the summer of 1987 the Ford Fiesta
and Fiat Uno
became the first mainstream European cars to be equipped with steel-belted CVT (as opposed to the less robust rubber-belted DAF design). This CVT, the Ford CTX was developed by Ford, Van Doorne, and Fiat, with work on the transmission starting in 1976.
The 1992 Nissan March
contained Nissan's N-CVT based on the Fuji Heavy Industries ECVT. In the late 1990s, Nissan designed its own CVT that allowed for higher torque and included a torque converter
. This gearbox was used in a number of Japanese-market models. Nissan is also the only car maker to bring a roller-based CVT to the market in recent years. Their toroidal CVT, named the Extroid, was available in the Japanese market Y34 Nissan Gloria
and V35 Skyline GT-8
. However, the gearbox was not carried over when the Cedric/Gloria was replaced by the Nissan Fuga
in 2004. The Nissan Murano
, introduced in 2003, and the Nissan Rogue
, introduced in 2007, also use CVT in their automatic transmission models. In a Nissan Press Release, July 12, 2006, Nissan announced a huge shift to CVT transmissions when they selected their XTronic CVT technology for all automatic versions of the Nissan Versa, Cube
, Sentra
, Altima
and Maxima
vehicles in North America, making the CVT a mainstream transmission system. One major motivator for Nissan to make a switch to CVTs was as a part of their 'Green Program 2010' aimed at reducing CO2 emissions by 2010. To date Nissan has had the most success with producing their CVTs in high volume and on a wide range of vehicles. The CVT found in Nissan’s Maxima
, Murano
and the V6 version of Altima is considered to be the worlds first "3.5L class" belt CVT and can hold much higher torque loads than other belt CVTs.
After studying pulley-based CVT for years, Honda also introduced their own version on the 1995 Honda Civic
VTi. Dubbed Honda Multi Matic, this CVT gearbox accepted higher torque than traditional pulley CVTs, and also includes a torque converter for "creep" action. The CVT is also currently employed in the Honda City ZX that is manufactured in India and Honda City Vario manufactured in Pakistan.
Toyota used a Power Split Transmission (PST) in the 1997 Prius
, and all subsequent Toyota and Lexus
hybrids sold internationally continue to use the system (marketed under the Hybrid Synergy Drive
name). The HSD is also referred to as an Electronically-controlled Continuously-variable Transmission. The PST allows either the electric motor or the internal combustion engine
(ICE) or both to propel the vehicle. In ICE-only mode, part of the engine's power is mechanically coupled to the drivetrain, with the other part going through a generator and a motor. The amount of power being channeled through the electrical path determine the effective gear ratio. Toyota also offers a non-hybrid CVT called Multidrive for models such as Avensis
.
Audi
has, since 2000, offered a chain
-type CVT (Multitronic) as an option on some of its larger-engine models, for example the A4
3.0 L V6.
Fiat
in 2000 offered a Cone
-type CVT as an option on its hit model Fiat Punto
(16v 80 PS ELX,Sporting) and Lancia Y (1.2 16V).
BMW
used a belt-drive CVT (manufactured by ZF Friedrichshafen
) as an option for the low- and middle-range MINI in 2001, forsaking it only on the supercharged version of the car where the increased torque levels demanded a conventional automatic gearbox. The CVT could also be manually "shifted" if desired with software-simulated shift points.
MG-Rover used an identical ZF CVT transmission on its Rover 45 and MG ZS
models.
GM introduced its version of CVT known as VTi
in 2002. It was used in the Saturn Vue
and Saturn Ion
models. This transmission was quickly withdrawn in 2005 models due to high failure rates.
Ford introduced a chain-driven CVT known as the CFT30 in their 2005 Ford Freestyle, Ford Five Hundred
and Mercury Montego
. The transmission was designed in cooperation with German automotive supplier ZF Friedrichshafen
and was produced in Batavia, Ohio at Batavia Transmissions LLC (a subsidiary of Ford Motor Company) until March 22, 2007. The Batavia plant also produced the belt-driven CFT23 CVT which went in the Ford Focus C-MAX
. Ford also sold Escort and Orion
models in Europe with CVTs in the 1980s and 1990s.
Contract agreements were established in 2006 between MTD Products
and Torotrak for the first full toroidal system to be manufactured for outdoor power equipment such as jet skis, ski-mobiles and ride-on mowers.
The 2007 Dodge Caliber
and the related Jeep Compass
and Jeep Patriot
employ a CVT using a variable pulley system as their optional automatic transmission.
The 2008 Mitsubishi Lancer
model is available with CVT transmission as the automatic transmission. DE and ES models receive a standard CVT with Drive and Low gears; the GTS model is equipped with a standard Drive and also a Sportronic mode that allows the driver to use 6 different preset gear ratios (either with the shifter or steering wheel-mounted paddle shifters).
The 2009 SEAT Exeo
is available with a CVT automatic transmission (multitronic
) as an option for the 2.0 TSI 200 hp petrol engine, with selectable 'six-speeds'.
Subaru
offers CVT on the 2010 Legacy and 2010 Outback (Lineartronic).
The US Patent Office issued patent number 7,647,768 B1 for a Torque Converter Transmission that offers a continuously variable tranmission that does not use belts or friction. This transmission can be used in any application where any automatic is currently used.
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratio
Gear ratio
The gear ratio of a gear train is the ratio of the angular velocity of the input gear to the angular velocity of the output gear, also known as the speed ratio of the gear train. The gear ratio can be computed directly from the numbers of teeth of the various gears that engage to form the gear...
s between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios. The flexibility of a CVT allows the driving shaft to maintain a constant angular velocity over a range of output velocities. This can provide better fuel economy
Fuel economy in automobiles
Fuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
than other transmissions by enabling the engine
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
to run at its most efficient revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute is a measure of the frequency of a rotation. It annotates the number of full rotations completed in one minute around a fixed axis...
(RPM) for a range of vehicle speeds. Alternatively it can be used to maximize the performance of a vehicle by allowing the engine to turn at the RPM at which it produces peak power. This is typically higher than the RPM that achieves peak efficiency. Finally, a CVT does not strictly require the presence of a clutch
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device which provides for the transmission of power from one component to another...
, allowing the dismissal thereof. In some vehicles though (i.e. motorcycles), a centrifugal clutch
Centrifugal clutch
A centrifugal clutch is a clutch that uses centrifugal force to connect two concentric shafts, with the driving shaft nested inside the driven shaft....
is nevertheless added, however this is only to provide a "neutral" stance on a motorcycle (useful when idling).
Uses

Tractor
A tractor is a vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a trailer or machinery used in agriculture or construction...
s for home and garden use have simple rubber belt CVTs. For example, the John Deere Gator
John Deere Gator
The John Deere Gator is a family of small all-terrain utility vehicles produced by the John Deere Corporation. They typically feature a box bed, similar in function to a pickup truck, and have been made in a variety of configurations, ranging from 4 to 6 wheels. The Gator line of vehicles are...
line of small utility vehicles use a belt with a conical pulley system. They can deliver an abundance of power and can reach speeds of 10 mile per hour, all without need for a clutch or shifting gears. Nearly all snowmobile
Snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known in some places as a snowmachine, or sled,is a land vehicle for winter travel on snow. Designed to be operated on snow and ice, they require no road or trail. Design variations enable some machines to operate in deep snow or forests; most are used on open terrain, including...
s, old and new, and motorscooters use CVTs, typically the rubber belt/variable pulley variety.
Some combine harvester
Combine harvester
The combine harvester, or simply combine, is a machine that harvests grain crops. The name derives from the fact that it combines three separate operations, reaping, threshing, and winnowing, into a single process. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, oats, rye, barley, corn ,...
s have CVTs. The CVT allows the forward speed of the combine to be adjusted independently of the engine speed. This allows the operator to slow or accelerate as needed to accommodate variations in thickness of the crop.
CVTs have been used in aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
electrical power generating systems since the 1950s and in Sports Car Club of America
Sports Car Club of America
The Sports Car Club of America is a club and sanctioning body supporting road racing, rallying, and autocross in the United States. Formed in 1944, it runs many programs for both amateur and professional racers.-History:...
(SCCA) Formula 500
Formula 500
Formula 500 is a Sports Car Club of America and Midwestern Council of Sports Car Clubs open wheel road racing class.Formula 500 was originally introduced in the early 1980s as Formula 440...
race cars since the early 1970s. CVTs were banned from Formula 1 in 1994 due to concerns that the best-funded teams would dominate if they managed to create a viable F1 CVT transmission. More recently, CVT systems have been developed for go-karts
Kart racing
Kart racing or karting is a variant of open-wheel motorsport with small, open, four-wheeled vehicles called karts, go-karts, or gearbox/shifter karts depending on the design. They are usually raced on scaled-down circuits...
and have proven to increase performance and engine life expectancy. The Tomcar
Tomcar
The Tomcar is a type of commercial off-road utility vehicle.The Tomcar is made in two and four seat models, and is powered by either unleaded petrol or diesel engines...
range of off-road vehicles also utilizes the CVT system.
Some drill presses and milling machine
Milling machine
A milling machine is a machine tool used to machine solid materials. Milling machines are often classed in two basic forms, horizontal and vertical, which refers to the orientation of the main spindle. Both types range in size from small, bench-mounted devices to room-sized machines...
s contain a pulley-based CVT where the output shaft has a pair of manually-adjustable conical pulley halves through which a wide drive belt from the motor loops. The pulley on the motor, however, is usually fixed in diameter, or may have a series of given-diameter steps to allow a selection of speed ranges. A handwheel on the drill press, marked with a scale corresponding to the desired machine speed, is mounted to a reduction gearing system for the operator to precisely control the width of the gap between the pulley halves. This gap width thus adjusts the gearing ratio between the motor's fixed pulley and the output shaft's variable pulley, changing speed of the chuck. A tensioner pulley is implemented in the belt transmission to take up or release the slack in the belt as the speed is altered. In most cases the speed must be changed with the motor running.
CVTs should be distinguished from Power Sharing Transmissions (PSTs), as used in newer hybrid cars
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
, such as the Toyota Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
, Highlander
Toyota Highlander
The Toyota Highlander is a midsize crossover SUV produced by Toyota. It is a taller, heavier version of the Toyota Camry.Announced in April 2000 at the New York Auto Show and arriving in late 2000 in Japan and January, 2001, in North America, the Highlander became the first car-based midsize SUV or...
and Camry, the Nissan Altima
Nissan Altima
The Nissan Altima is a mid-size automobile manufactured by Nissan, and is arguably a continuation of the Nissan Bluebird line, which began in 1957. It has historically been larger, more powerful, and more luxurious than the Nissan Sentra but less so than the Nissan Maxima. The Altima is available...
, and newer-model Ford Escape Hybrid SUVs
Sport utility vehicle
A sport utility vehicle is a generic marketing term for a vehicle similar to a station wagon, but built on a light-truck chassis. It is usually equipped with four-wheel drive for on- or off-road ability, and with some pretension or ability to be used as an off-road vehicle. Not all four-wheel...
. CVT technology uses only one input from a prime mover, and delivers variable output speeds and torque; whereas PST technology uses two prime mover inputs, and varies the ratio of their contributions to output speed and power. These transmissions are fundamentally different. However the Mitsubishi Lancer
Mitsubishi Lancer
The Mitsubishi Lancer is a family car built by Mitsubishi Motors. It has been known as the Colt Lancer, Dodge/Plymouth Colt, Chrysler Valiant Lancer, Chrysler Lancer, Eagle Summit, Hindustan Lancer, Soueast Lioncel, Mitsubishi Carisma, and Mitsubishi Mirage in various countries at different times,...
, Proton Inspira, Honda Insight
Honda Insight
The Honda Insight is a hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by Honda and the first production vehicle to feature Honda's Integrated Motor Assist system. The first-generation Insight was produced from 1999 to 2006 as a three-door hatchback...
, Honda Fit
Honda Fit
The Honda Jazz is a five-door hatchback subcompact manufactured by the Honda Motor Company of Japan, first introduced in June 2001 and is now in its second generation. The Jazz shares Honda's Global Small Car Platform with the City/Fit Aria, Airwave/Partner, Mobilio, Mobilio Spike, Freed and Freed...
, and Honda CR-Z
Honda CR-Z
The Honda CR-Z is a compact hybrid electric automobile manufactured by Honda and marketed as a "sport hybrid coupe." The CR-Z combines a hybrid gasoline-electric powertrain with traditional sports car elements...
hybrids, the Nissan Tiida
Nissan Tiida
The Nissan Tiida is a compact car, manufactured by Japanese automaker Nissan, replacing the Pulsar and the Sunny, and marketed also as the Nissan Versa, prominently in the United States...
/Versa (only the SL model), Nissan Cube
Nissan Cube
The Nissan Cube is a Mini MPV produced by Nissan for the Japanese market since 1998, and now sold in export markets such as North America and Europe.-First generation:...
, Juke, Sentra
Nissan Sentra
The Nissan Sentra is a compact car produced by automaker Nissan Motors and is generally a rebadged export version of the Japanese Nissan Sunny. The name "Sentra" is not used in Japan....
, Altima
Nissan Altima
The Nissan Altima is a mid-size automobile manufactured by Nissan, and is arguably a continuation of the Nissan Bluebird line, which began in 1957. It has historically been larger, more powerful, and more luxurious than the Nissan Sentra but less so than the Nissan Maxima. The Altima is available...
, Maxima
Nissan Maxima
The first car to wear the Maxima name was introduced in 1981. It was essentially a Japanese-market Bluebird 910 with a longer nose. The car was offered as the 810 Deluxe or 810 Maxima that first year, and all 810s became Maximas for 1982...
, Rogue
Nissan Rogue
The Nissan Rogue is a compact crossover SUV that debuted in October 2007 for the 2008 model year, produced by the Japanese automaker Nissan. It is the North American counterpart of the X-Trail sold outside North America , as well as the Qashqai in Europe and the Dualis in Japan and Australia.The...
, Murano
Nissan Murano
The first generation Nissan Murano was powered by a 3.5 litre 245 bhp V6 engine, also used in several other Nissan models like the Altima, Maxima, and Nissan 350Z, but specifically tuned for use in the Murano. Available with standard front-wheel-drive and optional all-wheel-drive , the Nissan...
, Honda Capa
Honda Capa
The Honda Capa, with the Honda series code GA4 and GA6, is a subcompact five-door hatchback produced by Honda between 1998 and 2002. It was introduced at the 1997 Tokyo Motor Show as the concept car "J-MW". It was introduced for retail sale April 24, 1998...
, Honda Civic HX, Jeep Patriot
Jeep Patriot
The Jeep Patriot is a compact crossover SUV introduced in early 2007 for the 2007 model year by the Jeep marque of Chrysler. It debuted publicly in April 2006 at the New York Auto Show and slots between the Compass and Liberty in the Jeep lineup...
and Compass
Jeep Compass
The Jeep Compass is a compact crossover SUV introduced for the 2007 model year. The Jeep Compass, along with the Patriot both slot below the Jeep Wrangler as Jeep's entry-level sport utility vehicles, and is one of Jeep's first crossover SUVs....
use CVT.
Variable-diameter pulley (VDP) or Reeves drive
In this most common CVT system, there are two V-belt pulleys that are split perpendicular to their axes of rotation, with a V-belt running between them. The gear ratio is changed by moving the two sheaves of one pulley closer together and the two sheaves of the other pulley farther apart. Due to the V-shaped cross section of the belt, this causes the belt to ride higher on one pulley and lower on the other. Doing this changes the effective diameters of the pulleys, which in turn changes the overall gear ratio. The distance between the pulleys does not change, and neither does the length of the belt, so changing the gear ratio means both pulleys must be adjusted (one bigger, the other smaller) simultaneously in order to maintain the proper amount of tension on the belt.The V-belt needs to be very stiff in the pulley's axial direction in order to make only short radial movements while sliding in and out of the pulleys. This can be achieved by a chain and not by homogeneous rubber. To dive out of the pulleys one side of the belt must push. This again can be done only with a chain. Each element of the chain has conical sides, which perfectly fit to the pulley if the belt is running on the outermost radius. As the belt moves into the pulleys the contact area gets smaller. The contact area is proportional to the number of elements, thus the chain has lots of very small elements. The shape of the elements is governed by the static of a column
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a vertical structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces...
. The pulley-radial thickness of the belt is a compromise between maximum gear ratio and torque. For the same reason the axis between the pulleys is as thin as possible. A film of lubricant is applied to the pulleys. It needs to be thick enough so that the pulley and the belt never touch and it must be thin in order not to waste power when each element dives into the lubrication film. Additionally, the chain elements stabilize about 12 steel bands. Each band is thin enough so that it bends easily. If bending, it has a perfect conical surface on its side. In the stack of bands each band corresponds to a slightly different gear ratio, and thus they slide over each other and need oil between them. Also the outer bands slide through the stabilizing chain, while the center band can be used as the chain linkage.
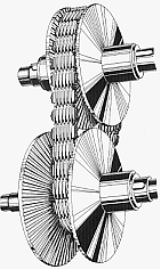
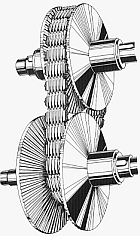
Toroidal or roller-based CVT (Extroid CVT )
Toroidal CVTs are made up of discs and rollers that transmit power between the discs. The discs can be pictured as two almost conical parts, point to point, with the sides dished such that the two parts could fill the central hole of a torusTorus
In geometry, a torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle...
. One disc is the input, and the other is the output (they do not quite touch). Power is transferred from one side to the other by rollers. When the roller's axis is perpendicular to the axis of the near-conical parts, it contacts the near-conical parts at same-diameter locations and thus gives a 1:1 gear ratio. The roller can be moved along the axis of the near-conical parts, changing angle as needed to maintain contact. This will cause the roller to contact the near-conical parts at varying and distinct diameters, giving a gear ratio of something other than 1:1. Systems may be partial or full toroidal. Full toroidal systems are the most efficient design while partial toroidals may still require a torque converter, and hence lose efficiency.
Diagrams:
Magnetic CVT
A magnetic continuous variable transmission system has been developed at the University of SheffieldUniversity of Sheffield
The University of Sheffield is a research university based in the city of Sheffield in South Yorkshire, England. It is one of the original 'red brick' universities and is a member of the Russell Group of leading research intensive universities...
in 2006 and is now (2011) commercially available. Two rotating transmission disks, each with magnets attached, synchronously revolve. A change in the radius of the magnets on each of the disks causes a change in the transmission ratio.
Infinitely variable transmission (IVT)
A specific type of CVT is the infinitely variable transmission (IVT), in which the range of ratios of output shaft speed to input shaft speed includes a zero ratio that can be continuously approached from a defined "higher" ratio. A zero output speed (low gear) with a finite input speed implies an infinite input-to-output speed ratio, which can be continuously approached from a given finite input value with an IVT. Low gears are a reference to low ratios of output speed to input speed. This low ratio is taken to the extreme with IVTs, resulting in a "neutral", or non-driving "low" gear limit, in which the output speed is zero. Unlike neutral in a normal automotive transmission, IVT output rotation may be prevented because the backdriving (reverse IVT operation) ratio may be infinite, resulting in impossibly high backdriving torque; ratcheting IVT output may freely rotate forward, though.The IVT dates back to before the 1930s; the original design converts rotary motion to oscillating motion and back to rotary motion using roller clutches. The stroke of the intermediate oscillations is adjustable, varying the output speed of the shaft. This original design is still manufactured today, and an example and animation of this IVT can be found here. Paul B. Pires created a more compact (radially symmetric) variation that employs a ratchet mechanism instead of roller clutches, so it doesn't have to rely on friction to drive the output. An article and sketch of this variation can be found here
Most IVTs result from the combination of a CVT with a planetary gear system (which is also known as an epicyclic gear system) which enforces an IVT output shaft rotation speed which is equal to the difference between two other speeds within the IVT. This IVT configuration uses its CVT as a continuously variable regulator (CVR) of the rotation speed of any one of the three rotators of the planetary gear system (PGS). If two of the PGS rotator speeds are the input and output of the CVR, there is a setting of the CVR that results in the IVT output speed of zero. The maximum output/input ratio can be chosen from infinite practical possibilities through selection of additional input or output gear, pulley or sprocket sizes without affecting the zero output or the continuity of the whole system. The IVT is always engaged, even during its zero output adjustment.
IVTs can in some implementations offer better efficiency when compared to other CVTs as in the preferred range of operation because most of the power flows through the planetary gear system and not the controlling CVR. Torque transmission capability can also be increased. There's also possibility to stage power splits for further increase in efficiency, torque transmission capability and better maintenance of efficiency over a wide gear ratio range.
An example of a true IVT is the SIMKINETICS SIVAT that uses a ratcheting CVR. Its CVR ratcheting mechanism contributes minimal IVT output ripple across its range of ratios.
Another example of a true IVT is the Hydristor
Hydristor
Hydristor is a joining of the words 'hydraulic' and 'transistor'. Thedevice invented by Tom Kasmer is based on the dual pressure balanced hydraulic vane pump invented by Harry F. Vickers in 1925.-Vane pump details:...
because the front unit connected to the engine can displace from zero to 27 cubic inches per revolution forward and zero to -10 cubic inches per revolution reverse. The rear unit is capable of zero to 75 cubic inches per revolution.
Ratcheting CVT
The ratcheting CVT is a transmission that relies on static friction and is based on a set of elements that successively become engaged and then disengaged between the driving system and the driven system, often using oscillating or indexing motion in conjunction with one-way clutches or ratchets that rectify and sum only "forward" motion. The transmission ratio is adjusted by changing linkage geometry within the oscillating elements, so that the summed maximum linkage speed is adjusted, even when the average linkage speed remains constant. Power is transferred from input to output only when the clutch or ratchet is engaged, and therefore when it is locked into a static friction mode where the driving & driven rotating surfaces momentarily rotate together without slippage.These CVTs can transfer substantial torque, because their static friction actually increases relative to torque throughput, so slippage is impossible in properly designed systems. Efficiency is generally high, because most of the dynamic friction is caused by very slight transitional clutch speed changes. The drawback to ratcheting CVTs is vibration caused by the successive transition in speed required to accelerate the element, which must supplant the previously operating and decelerating, power transmitting element.
Ratcheting CVTs are distinguished from VDPs and roller-based CVTs by being static friction-based devices, as opposed to being dynamic friction-based devices that waste significant energy through slippage of twisting surfaces. An example of a ratcheting CVT is one prototyped as a bicycle transmission protected under in which strong pedalling torque causes this mechanism to react against the spring, moving the ring gear/chainwheel assembly toward a concentric, lower gear position. When the pedaling torque relaxes to lower levels, the transmission self-adjusts toward higher gears, accompanied by an increase in transmission vibration.
A running prototype and animation of a functioning two stage ratcheting CVT can be found below:
Hydrostatic CVTs

Variable displacement pump
A variable displacement pump is a device that converts mechanical energy to hydraulic energy. The displacement, or amount of fluid pumped per revolution of the pump's input shaft can be varied while the pump is running....
and a hydraulic motor
Hydraulic motor
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic pressure and flow into torque and angular displacement . The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder....
. All power is transmitted by hydraulic fluid
Hydraulic fluid
Hydraulic fluids, also called hydraulic liquids, are the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water...
. These types can generally transmit more torque, but can be sensitive to contamination. Some designs are also very expensive. However, they have the advantage that the hydraulic motor can be mounted directly to the wheel hub, allowing a more flexible suspension system and eliminating efficiency losses from friction in the drive shaft and differential components. This type of transmission is relatively easy to use because all forward and reverse speeds can be accessed using a single lever.
An integrated hydrostatic transaxle (IHT) uses a single housing for both hydraulic elements and gear-reducing elements. This type of transmission, most commonly manufactured by Hydro-Gear, has been effectively applied to a variety of inexpensive and expensive versions of ridden lawn mower
Lawn mower
A lawn mower is a machine that uses a revolving blade or blades to cut a lawn at an even length.Lawn mowers employing a blade that rotates about a vertical axis are known as rotary mowers, while those employing a blade assembly that rotates about a horizontal axis are known as cylinder or reel...
s and garden tractors. Many versions of riding lawn mowers and garden tractors propelled by a hydrostatic transmission are capable of pulling a reverse tine tiller and even a single bladed plow.
One class of riding lawn mower that has recently gained in popularity with consumers is zero turning radius
Turning radius
The turning radius or turning circle of a vehicle is the size of the smallest circular turn that the vehicle is capable of making. The term turning radius is actually a misnomer, since the size of a circle is actually its diameter, not its radius. The less ambiguous term turning circle is preferred...
mowers. These mowers have traditionally been powered with wheel hub mounted hydraulic motors driven by continuously variable pumps, but this design is relatively expensive. Hydro-Gear, created the first cost-effective integrated hydrostatic transaxle suitable for propelling consumer zero turning radius mowers.
Some heavy equipment
Hydraulic machinery
Hydraulic machines are machinery and tools that use liquid fluid power to do simple work. Heavy equipment is a common example.In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is transmitted throughout the machine to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders and which becomes pressurised according to...
may also be propelled by a hydrostatic transmission; e.g. agricultural machinery including foragers, combines, and some tractors. A variety of heavy earth-moving equipment manufactured by Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar Inc. , also known as "CAT", designs, manufactures, markets and sells machinery and engines and sells financial products and insurance to customers via a worldwide dealer network. Caterpillar is the world's largest manufacturer of construction and mining equipment, diesel and natural gas...
, e.g. compact and small wheel loaders, track type loaders and tractors, skid-steered loaders and asphalt compactors use hydrostatic transmission. Hydrostatic CVTs are usually not used for extended duration high torque applications due to the heat that is generated by the flowing oil.
The Honda DN-01
Honda DN-01
-External links:* official page* in Popular Science...
motorcycle is the first road-going consumer vehicle with hydrostatic drive that employs a variable displacement axial piston pump with a variable-angle swashplate
Swashplate
A swashplate is a device used in mechanical engineering to translate the motion of a rotating shaft into reciprocating motion, or to translate a reciprocating motion into a rotating one to replace the crankshaft in engine designs.- Construction :...
.
Variable toothed wheel transmission
A variable toothed wheel transmission is not a true CVT that can alter its ratio in infinitessimal increments, but rather approaches CVT capability by having a large number of ratios, typically 49. This transmission relies on a toothed wheel positively engaged with a chain where the toothed wheel has the ability to add or subtract a tooth at a time in order to alter its ratio relative to the chain it is driving. The "toothed wheel" can take on many configurations including ladder chains, drive bars and sprocket teeth. The huge advantage of this type of CVT is that it is a positive mechanical drive and thus does not have the frictional losses and limitations of the roller-based or VDP CVT’s. The challenge in this type of CVT is to add or subtract a tooth from the toothed wheel in a very precise and controlled way in order to maintain synchronized engagement with the chain. This type of transmission has the potential to change ratios under load because of the large number of ratios, resulting in the order of 3% ratio change differences between ratios, thus a clutch or torque converter is necessary only for pull-away. No CVTs of this type are in commercial use, probably because of above mentioned development challenge.Naudic Incremental CVT (iCVT)
This is a chain-driven system which is advertised at *http://www.varibox.com/ Although an iCVT works, it has the following weakness:High Frictional Losses
The variator pulley of an iCVT is choked using two small choking pulleys. Here one choking pulley is positioned on the tense side of the chain of the iCVT. Hence there is a considerable load on that choking pulley, the magnitude of which is proportional to the tension in its chain. Each choking pulley is pulled up by two chain segments, one chain segment to the left and one to the right of the choking pulley; here if the two chain segments are parallel to each other than the load on the choking pulley is twice the tension in the chain. But since the two chain segments are most likely not parallel to each other during operations of an iCVT, it is estimated that the load on a choking pulley is between 1 to 1.8 times of the tension of its chain.Also, a choking pulley is very small so that its moment arm is very small. A larger moment arm reduces the force needed to rotate a pulley. For example, using a long wrench, which has a large moment arm, to open a nut requires less force than using a short wrench, which has a small moment arm. Assuming that the diameter of a choking pulley is twice the diameter of its shaft, which is a generous estimate, then the frictional resistance force at the outer diameter of a choking pulley is half the frictional resistance force at the shaft of a choking pulley.
Shock and Durability
The transmission ratio of an iCVT has to be changed one increment within less than one full rotation of its variator pulley. Has to be changed one increment means that the transmission diameter of the variator pulley has to be changed from a diameter that has a circumferential length that is equal to an integer number of teeth to another diameter that has a circumferential length that is equal to an integer number of teeth; such as changing the transmission diameter of the variator pulley from a diameter that has a circumferential length of 7 teeth to a diameter that has a circumferential length of 8 teeth for example. This is because if the transmission diameter of the variator pulley does not have a circumferential length that is equal to an integer number of teeth, such as a circumferential length of 7½ teeth for example, improper engagement between the teeth of the variator pulley and its chain will occur. For example, imagine having a bicycle pulley with 7½ teeth; here improper engagement between the bicycle pulley and its chain will occur when the tooth behind the ½ tooth space is about to engage with its chain, since it is positioned a distance of ½ tooth too late relative to its chain.Regarding the previous paragraph, the chain of an iCVT forms an open loop on its variator pulley that partially covers its variator pulley such that an open section, which is not covered by the chain, exist. This is similar to a sprocket of a bicycle where there is a section of the sprocket that is covered by its chain, and a section of the sprocket that is not covered by its chain. During one complete rotation, the toothed section of the variator pulley of an iCVT passes by the open section and re-engages with the chain. Here if the transmission diameter of the variator pulley does not represent an integer number of teeth, improper re-engagement between the teeth of the variator pulley and its chain will occur. Also, the transmission diameter of the variator pulley cannot be changed while the toothed section of the variator pulley is covering the entire open section of its chain loop. Since this is similar to where a plate is glued across the open section of a chain loop, which does not allow expansion or contraction of the chain loop as required for transmission diameter change of the variator pulley. Therefore the transmission diameter of the variator pulley has to be changed one increment during an interval where the variator pulley rotates from an initial position where a portion of the toothed section of the variator pulley is positioned at the open section of the chain loop but not covering the entire open section, to the final position where the toothed section of the variator pulley passes by the open section of the chain loop and is about to re-engage with the chain. Since it takes less than one full rotation to rotate the variator pulley from its initial position to its final position mentioned in the previous sentence, the transmission diameter of the variator pulley has to be changed one increment within less than one full rotation.
In addition, as the transmission diameter is increased, the chain has to be pushed up the inclined surfaces of the pulley halves of the variator pulley, while the tension in the chain tends to pull the chain towards the opposite direction. Hence a large force, which is larger than the tension in the chain, is required to change the transmission diameter. Since the transmission ratio has to be changed within less than one full rotation of the variator pulley, a large force has to be applied on the pulley halves within a very short duration. If for example the variator pulley rotates at 3600 rpm, which is equivalent to 60 revolutions per second, then the force required to change the transmission ratio has to be applied within 1/60 seconds. This would be similar to hitting something with a hammer. Therefore, here significant shock loads are applied to the variator pulley during transmission ratio change that increases the transmission diameter. These shock loads my cause comfort problem for the driver of the vehicle using an iCVT. Also an iCVT has to be designed as to be able to resist these shock loads which would most likely increases the cost and weight of an iCVT.
Torque Transfer Ability & Reliability
The teeth of the variator pulley of an iCVT are formed by pins that extend from one pulley half to the other pulley half and slide in the grooves of the pulley halves of the variator pulley. Here torque from the chain is transferred to the pins and then from the pins to the pulley halves. Since the pins are round and the grooves are curved, line contact between the pins and the grooves are used to transfer force from the pins to the grooves. The amount of force that can be transmitted between two parts depend on the contact area of the two parts. Since the contact areas between the pins and their grooves are very small, the amount of force that can be transmitted between them, and hence also the torque capacity of an iCVT, is limited.Another possible problem with an iCVT is that the pins of the variator pulley can fall-out when they are not engaged with their chain. And wear of the pins and the grooves of the pulley halves can cause some serious performance and reliability problems.
Diagram and video clip:
Cone CVTs
A cone CVT varies the effective gear ratio using one or more conical rollers. The simplest type of cone CVT, the single-cone version, uses a wheel that moves along the slope of the cone, creating the variation between the narrow and wide diameters of the cone.The more sophisticated twin cone mesh system is also a type of cone CVT.
In a CVT with oscillating cones, the torque is transmitted via friction from a variable number of cones (according to the torque to be transmitted) to a central, barrel-shaped hub.
The side surface of the hub is convex with a specific radius of curvature which is smaller than the concavity radius of the cones. In this way, there will be only one (theoretical) contact point between each cone and the hub at any time.
A new CVT using this technology, the Warko, was presented in Berlin during the 6th International CTI Symposium of Innovative Automotive Transmissions, on December 3–7, 2007.
A particular characteristic of the Warko is the absence of a clutch: the engine is always connected to the wheels, and the rear drive is obtained by means of an epicyclic system
Epicyclic gearing
Epicyclic gearing or planetary gearing is a gear system consisting of one or more outer gears, or planet gears, revolving about a central, or sun gear. Typically, the planet gears are mounted on a movable arm or carrier which itself may rotate relative to the sun gear...
in output. This system, named “power split”, allows the engine to have a "neutral gear": when the engine turns (connected to the sun gear of the epicyclic system), the variator (i.e., the planetary gears) will compensate for the engine rotation, so the outer ring gear (which provides output) remains stationary.
Diagrams:
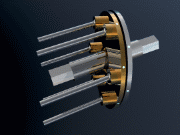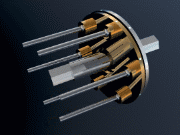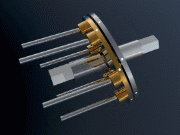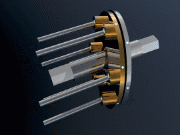
Radial roller CVT
The working principle of this CVT is similar to that of conventional oil compression engines, but, instead of compressing oil, common steel rollers are compressed.For more details see EP1688645A1
Prototype applications for wind farms Video 1
Inside mechanical parts Video 2
The motion transmission between rollers and rotors is assisted by an adapted traction fluid, which ensures the proper friction between the surfaces and slows down wearing thereof. Unlike other systems, the radial rollers do not show a tangential speed variation (delta) along the contact lines on the rotors. From this, a greater mechanical efficiency and working life are obtained.
The main advantages of this CVT are the manufacturing inexpensiveness and the high power efficiency.
History
Leonardo da VinciLeonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
, in 1490, conceptualized a stepless continuously variable transmission. The first patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
for a friction-based belt CVT was filed in Europe by Daimler and Benz in 1886, and a US Patent for a toroidal CVT was granted in 1935.
In 1910 Zenith Motorcycles
Zenith Motorcycles
Zenith Motorcycles was a British motorcycle manufacturer established in Finsbury Park, London in 1904. Zenith motorcycles used engines from various suppliers, including Precision, Villiers and JAP...
built a V2-Motorcycle with the Gradua-Gear which was a CVT. This Zenith-Gradua was so successful in hillclimb events, that it was eventually barred, so that other manufacturers had a chance to win.
1912 the British motorcycle manufacturer Rudge-Whitworth built the Rudge Multigear. The Multi was a much improved version of Zenith’s Gradua-Gear. The Rudge Multi was so successful that CVT-gears were eventually barred at the famous Tourist Trophy
Isle of Man TT
The International Isle of Man TT Race is a motorcycle racing event held on the Isle of Man and was for many years the most prestigious motorcycle race in the world...
race (which was the world's most important motorcycle race before World War I) from 1913 on.
In 1922 Browne offered a motorcycle with variable-stroke ratchet drive using a face ratchet.
An early application of CVT was in the British Clyno
Clyno
Developing from a motorcycle manufacturer, the Clyno Engineering Company Ltd, founded by Frank Smith, became the surprise success of British car manufacturing in the 1920s becoming the country's third largest car manufacturer in 1926...
car, introduced in 1923.
A CVT, called Variomatic
Variomatic
Variomatic is the stepless, fully automatic transmission of the Dutch car manufacturer DAF, originally developed by Hub van Doorne: this consists of a "V" shaped drive belt and two pulleys, each of two cones, whose effective diameter can be changed so that the "V" belt runs nearer the spindle or...
, was designed and built by Hub van Doorne
Hub van Doorne
Joseph Josephus Hubert van Doorne was the founder of Van Doorne's Aanhangwagenfabriek and of Van Doorne's Automobielfabriek known, especially to non-Dutch speakers, as DAF, together with his brother Willem van Doorne.-Early years:Van Doorne was born in America, a confusingly named small town...
, co-founder of Van Doorne's Automobiel Fabriek
DAF Trucks
DAF Trucks NV is a Dutch truck manufacturing company and a division of PACCAR. Its headquarters and main plant are in Eindhoven. Cabs and axle assemblies are produced at its Westerlo plant in Belgium...
(DAF), in the late 1950s, specifically to produce an automatic transmission for a small, affordable car. The first DAF car using van Doorne's CVT, the DAF 600
DAF 600
The DAF 600 is a small family car that was DAF's first production passenger car: it was first presented at the Amsterdam Motor Show in February 1958 and was in production by 1959, although the firm had published the first details of the car at the end of 1957...
,was produced in 1958. Van Doorne's patents were later transferred to a company called VDT (Van Doorne Transmissie B.V.) when the passenger car division was sold to Volvo
Volvo Cars
Volvo Car Corporation, or Volvo Personvagnar AB, is a Swedish automobile manufacturer founded in 1927, in Gothenburg, Sweden. It is owned by Zhejiang Geely Holding Group. Volvo was originally formed as a subsidiary company to the ball bearing maker SKF. When Volvo AB was introduced on the Swedish...
in 1975; its CVT was used in the Volvo 340.
In 1995, VDT was acquired by Robert Bosch GmbH
Robert Bosch GmbH
Robert Bosch GmbH is a multinational engineering and electronics company headquartered in Gerlingen, near Stuttgart, Germany. It is the world's largest supplier of automotive components...
.
Many snowmobiles use a rubber belt CVT. In 1974, Rokon
Rokon motorcycle
Rokon is a Rochester, New Hampshire-based motorcycle manufacturer that builds unusual 2-wheel-drive off-road motorcycles which are sometimes referred to as Moto-tractors.-History:...
offered a motorcycle with a rubber belt CVT.
CVTs are used in some ATVs. The first ATV equipped with CVT was Suzuki
Suzuki
is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Hamamatsu, Japan that specializes in manufacturing compact automobiles and 4x4 vehicles, a full range of motorcycles, all-terrain vehicles , outboard marine engines, wheelchairs and a variety of other small internal combustion engines...
's LT80 mini in 1987.
In early 1987, Subaru
Subaru
; is the automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate Fuji Heavy Industries .Subaru is internationally known for their use of the boxer engine layout popularized in cars by the Volkswagen Beetle and Porsche 911, in most of their vehicles above 1500 cc as well as...
launched the Justy in Tokyo with an electronically controlled continuously variable transmission (ECVT) developed by Fuji Heavy Industries
Fuji Heavy Industries
, or FHI, is a Japanese transportation conglomerate most known for being the manufacturer of Subaru automobiles. It traces its roots to the Nakajima Aircraft Company, a leading supplier of airplanes to the Japanese government during World War II...
, which owns Subaru. In 1989 the Justy became the first production car in the U.S. to offer CVT technology. While the Justy saw only limited success, Subaru continues to use CVT in its kei car
Kei car
Kei cars, K-cars, or , are a Japanese category of small vehicles, including passenger cars, vans, and pickup trucks. They are designed to comply with Japanese government tax and insurance regulations, and in most rural areas are exempted from the requirement to certify that adequate parking is...
s to this day, while also supplying it to other manufacturers.
In the summer of 1987 the Ford Fiesta
Ford Fiesta
The Ford Fiesta is a front wheel drive supermini/subcompact manufactured and marketed by Ford Motor Company and built in Europe, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Venezuela, China, India, Thailand and South Africa...
and Fiat Uno
Fiat Uno
The Fiat Uno is a supermini car produced by the Italian manufacturer Fiat. The Uno was launched in 1983 and built in its homeland until 1995, with production still taking place in other countries.-First series :...
became the first mainstream European cars to be equipped with steel-belted CVT (as opposed to the less robust rubber-belted DAF design). This CVT, the Ford CTX was developed by Ford, Van Doorne, and Fiat, with work on the transmission starting in 1976.
The 1992 Nissan March
Nissan March
The Nissan Micra, known in Latin America and in most of Asia as the Nissan and in North America as the Nissan Versa , is a supermini produced by the Japanese automaker Nissan since 1982.-Micra K10:...
contained Nissan's N-CVT based on the Fuji Heavy Industries ECVT. In the late 1990s, Nissan designed its own CVT that allowed for higher torque and included a torque converter
Torque converter
In modern usage, a torque converter is generally a type of hydrodynamic fluid coupling that is used to transfer rotating power from a prime mover, such as an internal combustion engine or electric motor, to a rotating driven load...
. This gearbox was used in a number of Japanese-market models. Nissan is also the only car maker to bring a roller-based CVT to the market in recent years. Their toroidal CVT, named the Extroid, was available in the Japanese market Y34 Nissan Gloria
Nissan Cedric
The Nissan Cedric is a large automobile produced by Nissan since 1960. It was developed to provide upscale transportation, competing with the Prince Skyline and Gloria which were later merged into the Nissan family...
and V35 Skyline GT-8
Nissan Skyline
The first Skyline was introduced in April 1957, by the Prince Motor Company, and was marketed as a luxury car. It featured a 1.5 L GA-30 engine producing 44 kW @ 4400 rpm. It used a de Dion tube rear suspension and was capable of 140 km/h . The car weighed around 1300 kg...
. However, the gearbox was not carried over when the Cedric/Gloria was replaced by the Nissan Fuga
Nissan Fuga
The Fuga is a full-size sedan, rear wheel drive with optional all wheel drive, produced by Nissan of Japan since October 2004 and now in its second generation. It is built on a wider, stretched wheelbase version of the Nissan FM platform. After the Nissan Cima and Nissan President were...
in 2004. The Nissan Murano
Nissan Murano
The first generation Nissan Murano was powered by a 3.5 litre 245 bhp V6 engine, also used in several other Nissan models like the Altima, Maxima, and Nissan 350Z, but specifically tuned for use in the Murano. Available with standard front-wheel-drive and optional all-wheel-drive , the Nissan...
, introduced in 2003, and the Nissan Rogue
Nissan Rogue
The Nissan Rogue is a compact crossover SUV that debuted in October 2007 for the 2008 model year, produced by the Japanese automaker Nissan. It is the North American counterpart of the X-Trail sold outside North America , as well as the Qashqai in Europe and the Dualis in Japan and Australia.The...
, introduced in 2007, also use CVT in their automatic transmission models. In a Nissan Press Release, July 12, 2006, Nissan announced a huge shift to CVT transmissions when they selected their XTronic CVT technology for all automatic versions of the Nissan Versa, Cube
Nissan Cube
The Nissan Cube is a Mini MPV produced by Nissan for the Japanese market since 1998, and now sold in export markets such as North America and Europe.-First generation:...
, Sentra
Nissan Sentra
The Nissan Sentra is a compact car produced by automaker Nissan Motors and is generally a rebadged export version of the Japanese Nissan Sunny. The name "Sentra" is not used in Japan....
, Altima
Nissan Altima
The Nissan Altima is a mid-size automobile manufactured by Nissan, and is arguably a continuation of the Nissan Bluebird line, which began in 1957. It has historically been larger, more powerful, and more luxurious than the Nissan Sentra but less so than the Nissan Maxima. The Altima is available...
and Maxima
Nissan Maxima
The first car to wear the Maxima name was introduced in 1981. It was essentially a Japanese-market Bluebird 910 with a longer nose. The car was offered as the 810 Deluxe or 810 Maxima that first year, and all 810s became Maximas for 1982...
vehicles in North America, making the CVT a mainstream transmission system. One major motivator for Nissan to make a switch to CVTs was as a part of their 'Green Program 2010' aimed at reducing CO2 emissions by 2010. To date Nissan has had the most success with producing their CVTs in high volume and on a wide range of vehicles. The CVT found in Nissan’s Maxima
Nissan Maxima
The first car to wear the Maxima name was introduced in 1981. It was essentially a Japanese-market Bluebird 910 with a longer nose. The car was offered as the 810 Deluxe or 810 Maxima that first year, and all 810s became Maximas for 1982...
, Murano
Nissan Murano
The first generation Nissan Murano was powered by a 3.5 litre 245 bhp V6 engine, also used in several other Nissan models like the Altima, Maxima, and Nissan 350Z, but specifically tuned for use in the Murano. Available with standard front-wheel-drive and optional all-wheel-drive , the Nissan...
and the V6 version of Altima is considered to be the worlds first "3.5L class" belt CVT and can hold much higher torque loads than other belt CVTs.
After studying pulley-based CVT for years, Honda also introduced their own version on the 1995 Honda Civic
Honda Civic
The Honda Civic is a line of subcompact and subsequently compact cars made and manufactured by Honda. The Civic, along with the Accord and Prelude, comprised Honda's vehicles sold in North America until the 1990s, when the model lineup was expanded...
VTi. Dubbed Honda Multi Matic, this CVT gearbox accepted higher torque than traditional pulley CVTs, and also includes a torque converter for "creep" action. The CVT is also currently employed in the Honda City ZX that is manufactured in India and Honda City Vario manufactured in Pakistan.
Toyota used a Power Split Transmission (PST) in the 1997 Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
, and all subsequent Toyota and Lexus
Lexus
is the luxury vehicle division of Japanese automaker Toyota Motor Corporation. First introduced in 1989 in the United States, Lexus is now sold globally and has become Japan's largest-selling make of premium cars. The Lexus marque is marketed in over 70 countries and territories worldwide, and has...
hybrids sold internationally continue to use the system (marketed under the Hybrid Synergy Drive
Hybrid Synergy Drive
Hybrid Synergy Drive is a set of hybrid car technologies developed by Toyota and used in the company's Auris, Prius, Highlander Hybrid, Camry Hybrid, Estima, Alphard, Lexus CT, Lexus RX 400h/RX 450h, Lexus GS 450h, Lexus LS 600h/LS 600hL, and Lexus HS 250h automobiles. Toyota also licenses its HSD...
name). The HSD is also referred to as an Electronically-controlled Continuously-variable Transmission. The PST allows either the electric motor or the internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
(ICE) or both to propel the vehicle. In ICE-only mode, part of the engine's power is mechanically coupled to the drivetrain, with the other part going through a generator and a motor. The amount of power being channeled through the electrical path determine the effective gear ratio. Toyota also offers a non-hybrid CVT called Multidrive for models such as Avensis
Toyota Avensis
The Toyota Avensis is a large family car built in Derbyshire, United Kingdom by Japanese carmaker Toyota since 1997. It is the direct successor to the Carina E and is available as a four-door saloon, five-door liftback and estate...
.
Audi
Audi
Audi AG is a German automobile manufacturer, from supermini to crossover SUVs in various body styles and price ranges that are marketed under the Audi brand , positioned as the premium brand within the Volkswagen Group....
has, since 2000, offered a chain
Roller chain
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire and tube drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and simple machines like...
-type CVT (Multitronic) as an option on some of its larger-engine models, for example the A4
Audi A4
The first generation Audi A4 debuted in 1994, with production starting November 1994. It was built on the Volkswagen Group B5 platform, which it shared with the fourth generation Volkswagen Passat . It had a front-mounted longitudinal engine and front-wheel drive...
3.0 L V6.
Fiat
Fiat
FIAT, an acronym for Fabbrica Italiana Automobili Torino , is an Italian automobile manufacturer, engine manufacturer, financial, and industrial group based in Turin in the Italian region of Piedmont. Fiat was founded in 1899 by a group of investors including Giovanni Agnelli...
in 2000 offered a Cone
Cone clutch
A cone clutch serves the same purpose as a disk or plate clutch. However, instead of mating two spinning disks, the cone clutch uses two conical surfaces to transmit torque by friction....
-type CVT as an option on its hit model Fiat Punto
Fiat Punto
The Fiat Punto is a supermini produced by the Italian manufacturer, Fiat, since 1993.-1st generation :Internally codenamed Project 176, the Punto was announced in September 1993 and launched in late 1993 as a replacement for the ageing Fiat Uno. The Fiat Punto was voted European Car of the Year...
(16v 80 PS ELX,Sporting) and Lancia Y (1.2 16V).
BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
used a belt-drive CVT (manufactured by ZF Friedrichshafen
ZF Friedrichshafen
ZF Friedrichshafen AG, also known as ZF Group, and commonly abbreviated to ZF, is a German public company headquartered in Friedrichshafen, in the south-west German region of Baden-Württemberg....
) as an option for the low- and middle-range MINI in 2001, forsaking it only on the supercharged version of the car where the increased torque levels demanded a conventional automatic gearbox. The CVT could also be manually "shifted" if desired with software-simulated shift points.
MG-Rover used an identical ZF CVT transmission on its Rover 45 and MG ZS
MG ZS
The MG ZS is a sports family car. The ZS is essentially a badge engineered Rover 45 . The 45 in turn is a facelifted version of the Rover 400 which was launched in hatchback form in 1995 and saloon form in 1996. The Rover 400 had much in common with the Honda Civic of 1995-1999...
models.
GM introduced its version of CVT known as VTi
VTi transmission
The VTi is a continuously variable transmission for automobiles. It is fully automatic, electronically controlled, and designed for transverse front-wheel drive use. The VTi is assembled at a General Motors/Fiat joint venture plant in Szentgotthard, Hungary....
in 2002. It was used in the Saturn Vue
Saturn VUE
The Saturn Vue is a compact crossover SUV that was sold by General Motors' Saturn marque, and at one time was Saturn's best-selling model. It was the first vehicle to use the GM Theta platform when it was introduced in 2002. A second generation model was launched in 2007 for the 2008 model as a...
and Saturn Ion
Saturn ION
The Saturn Ion was a compact car sold by the Saturn marque of American automaker General Motors between the 2003 and 2007 model years. It used the GM Delta platform. The Ion replaced the Saturn S-Series in 2003,...
models. This transmission was quickly withdrawn in 2005 models due to high failure rates.
Ford introduced a chain-driven CVT known as the CFT30 in their 2005 Ford Freestyle, Ford Five Hundred
Ford Five Hundred
The Ford Five Hundred is a full-size sedan that was produced by the Ford Motor Company during the 2005 to 2007 model years in North America. In North America, the name evoked the classic Fairlane 500 and Galaxie 500 models of the 1950s through 1970s.-Overview:The Five Hundred was introduced at the...
and Mercury Montego
Mercury Montego
The Mercury Montego was a mid-size vehicle in the Mercury line of Ford Motor Company from 1968 to 1976. The namplate first appeared in 1967 in Canada as part of the Mercury-derived Meteor line. After 1976, the basic design of the Montego was updated and the nameplate disappeared as the Cougar...
. The transmission was designed in cooperation with German automotive supplier ZF Friedrichshafen
ZF Friedrichshafen
ZF Friedrichshafen AG, also known as ZF Group, and commonly abbreviated to ZF, is a German public company headquartered in Friedrichshafen, in the south-west German region of Baden-Württemberg....
and was produced in Batavia, Ohio at Batavia Transmissions LLC (a subsidiary of Ford Motor Company) until March 22, 2007. The Batavia plant also produced the belt-driven CFT23 CVT which went in the Ford Focus C-MAX
Ford Focus C-MAX
The Ford C-Max is a compact MPV produced by Ford in Saarlouis for Europe since 2003 and in North America from 2011. Although C-MAX was initially available only in Europe, the first generation was partially available in New Zealand. The North American model will launch with the second generation...
. Ford also sold Escort and Orion
Ford Orion
The Ford Orion is a saloon car built by the automaker Ford for the European market from 22 July 1983 until 19 September 1993. A total of 3,534,239 Orions were sold throughout the car's 10-year life....
models in Europe with CVTs in the 1980s and 1990s.
Contract agreements were established in 2006 between MTD Products
MTD Products
MTD Products is a manufacturer of outdoor power equipment for the mass market. Based in Cleveland, Ohio, USA, the company began in 1932 and is a family-owned, private company. It originated as a tool and die maker...
and Torotrak for the first full toroidal system to be manufactured for outdoor power equipment such as jet skis, ski-mobiles and ride-on mowers.
The 2007 Dodge Caliber
Dodge Caliber
The Dodge Caliber was a compact car produced by the Dodge division of Chrysler. It replaced the Neon, and it went on sale in the spring of 2006 as a 2007 model year vehicle...
and the related Jeep Compass
Jeep Compass
The Jeep Compass is a compact crossover SUV introduced for the 2007 model year. The Jeep Compass, along with the Patriot both slot below the Jeep Wrangler as Jeep's entry-level sport utility vehicles, and is one of Jeep's first crossover SUVs....
and Jeep Patriot
Jeep Patriot
The Jeep Patriot is a compact crossover SUV introduced in early 2007 for the 2007 model year by the Jeep marque of Chrysler. It debuted publicly in April 2006 at the New York Auto Show and slots between the Compass and Liberty in the Jeep lineup...
employ a CVT using a variable pulley system as their optional automatic transmission.
The 2008 Mitsubishi Lancer
Mitsubishi Lancer
The Mitsubishi Lancer is a family car built by Mitsubishi Motors. It has been known as the Colt Lancer, Dodge/Plymouth Colt, Chrysler Valiant Lancer, Chrysler Lancer, Eagle Summit, Hindustan Lancer, Soueast Lioncel, Mitsubishi Carisma, and Mitsubishi Mirage in various countries at different times,...
model is available with CVT transmission as the automatic transmission. DE and ES models receive a standard CVT with Drive and Low gears; the GTS model is equipped with a standard Drive and also a Sportronic mode that allows the driver to use 6 different preset gear ratios (either with the shifter or steering wheel-mounted paddle shifters).
The 2009 SEAT Exeo
SEAT Exeo
The SEAT Exeo is a five-seat large family car, and flagship model, built by the Spanish car manufacturer, and Volkswagen Group subsidiary SEAT, S.A., with factory production commencing in December 2008....
is available with a CVT automatic transmission (multitronic
Multitronic
multitronic is a stepless transmission launched by AUDI AG in late 1999, jointly developed and manufactured by LuK.Based on the principles of continuously variable transmission popularised by DAF, multitronic offers a stepless automatic transmission in which the ratio between the input shaft and...
) as an option for the 2.0 TSI 200 hp petrol engine, with selectable 'six-speeds'.
Subaru
Subaru
; is the automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate Fuji Heavy Industries .Subaru is internationally known for their use of the boxer engine layout popularized in cars by the Volkswagen Beetle and Porsche 911, in most of their vehicles above 1500 cc as well as...
offers CVT on the 2010 Legacy and 2010 Outback (Lineartronic).
The US Patent Office issued patent number 7,647,768 B1 for a Torque Converter Transmission that offers a continuously variable tranmission that does not use belts or friction. This transmission can be used in any application where any automatic is currently used.
See also
- VariomaticVariomaticVariomatic is the stepless, fully automatic transmission of the Dutch car manufacturer DAF, originally developed by Hub van Doorne: this consists of a "V" shaped drive belt and two pulleys, each of two cones, whose effective diameter can be changed so that the "V" belt runs nearer the spindle or...
- Kinetic energy recovery system (in motorsport)
- List of automobiles with continuously variable transmissions
- Planetary gear
- Power bandPower bandThe power band of an engine or electric motor refers to the range of operating speeds under which an the engine or motor is able to operate efficiently...

