
Miniature Inertial Measurement Unit (MIMU)
Encyclopedia
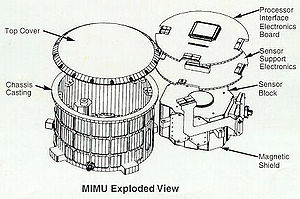
Inertial measurement unit
An inertial measurement unit, or IMU, is an electronic device that measures and reports on a craft's velocity, orientation, and gravitational forces, using a combination of accelerometers and gyroscopes. IMUs are typically used to maneuver aircraft, including UAVs, among many others, and...
(IMU) developed and built by Honeywell International to control and stabilize spacecraft
Spacecraft
A spacecraft or spaceship is a craft or machine designed for spaceflight. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, planetary exploration and transportation of humans and cargo....
during mission operations. MIMUs can also be configured to perform as an inertial reference unit
Inertial Reference Unit
An inertial reference unit is a type of inertial sensor which uses gyroscopes and accelerometers to determine a moving aircraft’s or spacecraft’s change in rotational attitude and translational position over a...
(IRU). MIMUs have been flown on GEO, Low Earth orbit
Low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit is generally defined as an orbit within the locus extending from the Earth’s surface up to an altitude of 2,000 km...
(LEO), planetary missions and deep-space-probe applications.
Planetary missions
- Mars Reconnaissance OrbiterMars Reconnaissance OrbiterMars Reconnaissance Orbiter is a NASA multipurpose spacecraft designed to conduct reconnaissance and Exploration of Mars from orbit...
– launched in 2005 on a mission to study the planetPlanetA planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
MarsMarsMars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance... - STEREOSTEREOSTEREO is a solar observation mission. Two nearly identical spacecraft were launched into orbits that cause them to respectively pull farther ahead of and fall gradually behind the Earth...
– launched in 2006 on a mission to study the SunSunThe Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields... - Lunar Reconnaissance OrbiterLunar Reconnaissance OrbiterThe Lunar Precursor Robotic Program is a program of robotic spacecraft missions which NASA will use to prepare for future human spaceflight missions to the Moon. Two LPRP missions, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite , were launched in June 2009...
– launched in 2009 on a mission to study the MoonMoonThe Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
Deep-space-probe missions
- New HorizonsNew HorizonsNew Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015...
– launched in 2006 on a mission to study the planetPlanetA planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
PlutoPlutoPluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun...

