
Minimum Resolvable Contrast
Encyclopedia
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
sensor
Sensor
A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. For example, a mercury-in-glass thermometer converts the measured temperature into expansion and contraction of a liquid which can be read on a calibrated...
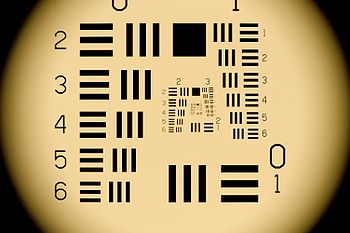
’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT (Unit Under Test) are used to determine the MRC of the UUT, i.e the visible spectrum camera or sensor. A trained observer selects the smallest target resolvable at each contrast level. Typically, specialized computer software collects the inputed data of the observer and provides a graph of contrast v.s. spatial frequency at a given luminance level. A first order polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
is fitted
Curve fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function...
to the data and an MRC curve of spatial frequency versus contrast is generated.
See also
- DistortionDistortionA distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
- Image resolutionImage resolutionImage resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
- Integrating sphereIntegrating sphereAn Integrating sphere is an optical component consisting of a hollow cavity with its interior coated for high diffuse reflectivity , having relatively small holes as needed for entrance and exit ports....
- Minimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature difference is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function....
- Optical resolutionOptical resolutionOptical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged.An imaging system may have many individual components including a lens and recording and display components...
- Signal to noise ratio (image processing)Signal to noise ratio (image processing)The Signal to Noise Ratio is used in imaging as a physical measure of the sensitivity of a imaging system. Industry standards measure SNR in decibels of power and therefore apply the 20 log rule to the "pure" SNR ratio...

