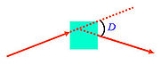
Minimum deviation
Encyclopedia
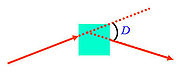
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
or a water drop
Drop (liquid)
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant drop...
. The angle is also referred to as "the angle of minimum deviation". The direction of the incident beam and the orientation of the object can be varied. The value of D can be larger than 90 degree
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
s. One of the factors that rainbow
Rainbow
A rainbow is an optical and meteorological phenomenon that causes a spectrum of light to appear in the sky when the Sun shines on to droplets of moisture in the Earth's atmosphere. It takes the form of a multicoloured arc...
can be observed is due to bunching of light rays at the minimum deviation that is close to the rainbow angle.
The angle of minimum deviation depends upon:-
♣ Wavelength of the light ray (λ):-The angle of minimum deviation is smaller for shorter wavelengths and larger for longer wavelengths, so the "red" end of the spectrum deviates less than the "violet" end.
♣Material of the prism (μ):-The larger the refractive index of the material, the larger the angle of minimum deviation.
♣Angle of prism(A):-The larger the angle of prism, the larger the angle of minimum deviation.
♣Angle of incidence(A):-The angle of deviation is dependant on the angle of incidence in the form of a U shaped curve
If a line is drawn parallel to the angle of incidence axis (X-axis), it cuts the graph at two points, showing that there are two values of angle of incidence for an angle of deviation. However, at the point of angle of minimum deviation, the line will be tangent to the curve showing that for minimum angle of deviation there is only one angle of incidence.

