
Mir Environmental Effects Payload
Encyclopedia

Space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing...
Mir
Mir
Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the...
from 1996 to 1997 to study the effects of space debris impacts and exposure to the space environment on a variety of materials. The materials used in the experiments were being considered for use on the International Space Station
International Space Station
The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes...
, and by exposing them at a similar orbital altitude to that flown by the ISS, the experiments provided an assessment of the performance of those materials in a similar space environment. MEEP also fulfilled the need to examine the occurrence and effects of man-made debris and natural micrometeoroid
Micrometeoroid
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid; a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeor or micrometeorite is such a particle that enters the Earth's atmosphere or falls to Earth.-Scientific interest:...
s through capture and impact studies. The experiments were installed on the Mir docking module
Mir Docking Module
The Stykovochnyy Otsek , GRAU index 316GK, otherwise known as the Mir docking module or SO, was the sixth module of the Russian space station Mir, launched in November 1995 aboard the...
during STS-76
STS-76
STS-76 was NASA's 76th Space Shuttle mission, and the 16th mission for Atlantis. STS-76 launched on 22 March 1996 at 3:13 am EST from Kennedy Space Center launch pad 39B...
, and retrieved during STS-86
STS-86
STS-86 was a Space Shuttle Atlantis mission to the Mir space station. This was the last Atlantis mission before it was taken out of service temporarily for maintenance and upgrades, including the glass cockpit.-Crew:-Crew notes:...
.
Components
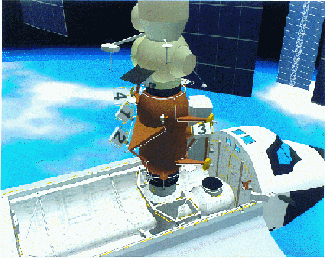
Mir Docking Module
The Stykovochnyy Otsek , GRAU index 316GK, otherwise known as the Mir docking module or SO, was the sixth module of the Russian space station Mir, launched in November 1995 aboard the...
. Each PEC consisted of three components; the experiment carrier, which contained the experiment itself, the sidewall carrier, which kept the PEC secure in the payload bay of the space shuttle during launch and return, and the handrail clamp, which was used to attach the PEC to the docking module.
The first experiment, Polished Plate Micrometeoroid and Debris (PPMD), consisted of gold, aluminium, and zinc plates and studied how often space debris hit the station, the sizes and sources of the debris, and the damage the debris might do on hitting a space station. The second, the Orbital Debris Collector (ODC), captured orbital debris
Space debris
Space debris, also known as orbital debris, space junk, and space waste, is the collection of objects in orbit around Earth that were created by humans but no longer serve any useful purpose. These objects consist of everything from spent rocket stages and defunct satellites to erosion, explosion...
in aerogel
Aerogel
Aerogel is a synthetic porous material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component of the gel has been replaced with a gas. The result is a solid with extremely low density and thermal conductivity...
cells for return to Earth to determine the possible origins and components of that debris. The last two experiments, Passive Optical Sample Assemblies I (POSA I) and II (POSA II), tested various materials
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
intended for use on the International Space Station including paint samples, glass coatings, multilayer insulation, and a variety of metallic samples.
History

Langley Research Center
Langley Research Center is the oldest of NASA's field centers, located in Hampton, Virginia, United States. It directly borders Poquoson, Virginia and Langley Air Force Base...
had overall responsibility for MEEP as well as the development of the Passive Equipment Carriers as well as the PPMD experiment. Johnson Space Center
Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's center for human spaceflight training, research and flight control. The center consists of a complex of 100 buildings constructed on 1,620 acres in Houston, Texas, USA...
was responsible for the ODC, Marshall Space Flight Center
Marshall Space Flight Center
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. The largest center of NASA, MSFC's first mission was developing the Saturn launch vehicles for the Apollo moon program...
for POSA I and Boeing
Boeing
The Boeing Company is an American multinational aerospace and defense corporation, founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington. Boeing has expanded over the years, merging with McDonnell Douglas in 1997. Boeing Corporate headquarters has been in Chicago, Illinois since 2001...
's Defence and Space Group for POSA II.
The MEEP experiment hardware was launched to Mir aboard on STS-76
STS-76
STS-76 was NASA's 76th Space Shuttle mission, and the 16th mission for Atlantis. STS-76 launched on 22 March 1996 at 3:13 am EST from Kennedy Space Center launch pad 39B...
. The four experiments installed on the docking module during the only EVA of the mission, carried out by Michael Clifford
Michael R. Clifford
Michael Richard Uram "Rich" Clifford , is a former U.S. Army officer and NASA astronaut. Michael Clifford was born in San Bernardino, California, but considers Ogden, Utah to be his hometown. Clifford is married and has two sons...
and Linda Godwin
Linda M. Godwin
Linda Maxine Godwin is an American scientist and a NASA astronaut. Godwin is the Assistant to the Director for Exploration, Flight Crew Operations Directorate at the Johnson Space Center.-Background:...
on flight day six, 27 March 1996. MEEP remained attached to Mir for 18 months until 1 October 1997, when, during flight day seven of STS-86
STS-86
STS-86 was a Space Shuttle Atlantis mission to the Mir space station. This was the last Atlantis mission before it was taken out of service temporarily for maintenance and upgrades, including the glass cockpit.-Crew:-Crew notes:...
, the experiments were retrieved in an EVA by Vladimir Titov
Vladimir Titov
Vladimir Georgiyevich Titov , Colonel, Russian Air Force, Ret., and former Russian cosmonaut was born January 1, 1947, in Sretensk, in the Zabaykalsky Krai region of Russia. He is married to the former Alexandra Kozlova of Ivanovo Region, Russia...
and Scott Parazynski
Scott E. Parazynski
Scott Edward Parazynski, M.D. is an American physician and a former NASA astronaut. A veteran of five Space Shuttle flights and seven spacewalks, Parazynski's latest mission was STS-120 in October, 2007 --- highlighted by a dramatic, unplanned EVA to repair a live solar array...
. In addition to the MEEP experiments, a solar array which had been exposed to the space environment for more than ten years was was removed from the core module
Mir Core Module
Mir , DOS-7, was the first module of the Soviet/Russian Mir space station complex, in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. Generally referred to as either the core module or base block, the module was launched on 20 February 1986 on a Proton-K rocket from LC-200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome...
of Mir in November 1997, and returned to Earth in January 1998 on STS-89
STS-89
STS-89 was a space shuttle mission to the Mir space station flown by Space Shuttle Endeavour, and launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on 22 January 1998.-Crew:-Crew notes:...
. The experiments were then inspected and studied by teams of space environmental effects investigators for micrometeoroid and space debris effects, space exposure effects on materials, and electrical performance.
Also MEEPS can trace their inception to the Passive Optical Sample Array (POSA) sample trays flown on STS-1
STS-1
STS-1 was the first orbital flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program. Space Shuttle Columbia launched on 12 April 1981, and returned to Earth on 14 April, having orbited the Earth 37 times during the 54.5-hour mission. It was the first American manned space flight since the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project...
and STS-2
STS-2
STS-2 was a Space Shuttle mission conducted by NASA, using the Space Shuttle Columbia. The mission launched on 12 November 1981. It was the second shuttle mission overall, and was also the second mission for Columbia...
, and their successor Effects of Oxygen Interaction with Materials (EOIM) on STS-3
STS-3
STS-3 was NASA's third Space Shuttle mission, and was the third mission for the Space Shuttle Columbia. It was the first shuttle launch with an unpainted external tank, and the only mission to land at the White Sands Space Harbor near Las Cruces, New Mexico.-Crew:-Backup crew:-Mission...
and STS-5
STS-5
STS-5 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission, the fifth shuttle mission overall and the fifth flight of the Space Shuttle Columbia. It was the first shuttle mission to deploy communications satellites into orbit...
.
See also
- Long Duration Exposure FacilityLong Duration Exposure FacilityNASA's Long Duration Exposure Facility, or LDEF, was a school bus-sized cylindrical space experiment rack that exposed various material samples to outer space for about 5.7 years, completing 32,422 Earth orbits.- Construction :...
- Materials International Space Station ExperimentMaterials International Space Station ExperimentThe Materials International Space Station Experiment , is a series of experiments mounted externally on the International Space Station that investigates the effects of long-term exposure of materials to the harsh space environment....

