
Miracidium
Encyclopedia
Trematodes
are small parasitic flatworms that use vertebrate
s as their definitive host
, and molluscs as their intermediate host. In order to accomplish this, they have several varied lifecyle stages.
The lifecycle
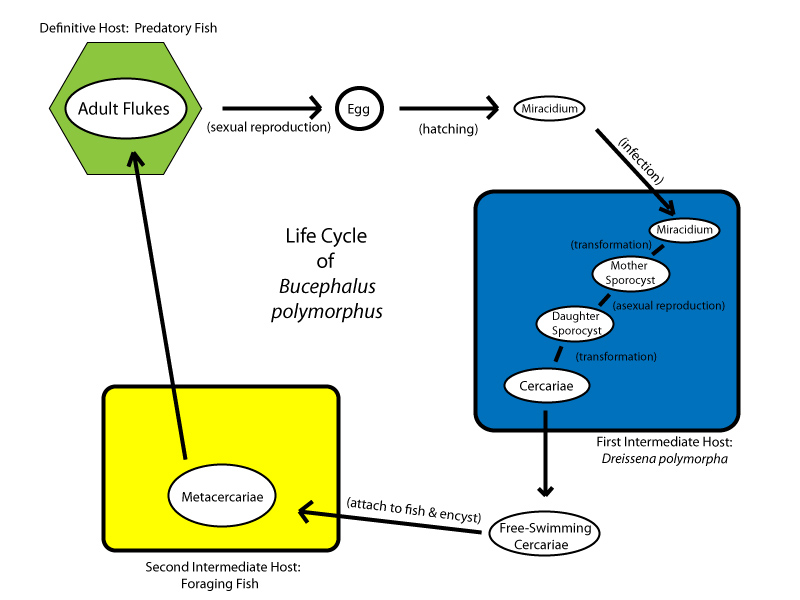
of a typical digenean trematode can be thought to begin when its egg is immersed in water. Following this a miracidium hatches, which swims to find a mollusc host. The miracidia go through several stages in the mollusc host, eventually emerging as motile cercaria larvae. The cercaria infect vertebrates either through the skin or are ingested. In its vertebrate host, the cercaria matures to an adult form, and lays eggs that are discharged with the host faeces or urine
. In the presence of open water, the eggs will hatch and the miracidium stage of life is reached again.
, the general lifecycle stages are as follows:
Many digenean trematodes require two hosts, one (typically a snail) where asexual reproduction occurs in sporocysts, the other a vertebrate (typically a fish) where the adult form engages in sexual reproduction to produce eggs. In some species (for example Ribeiroia
) the cercaria encysts, and waits until the host is eaten by a third host, in whose gut it emerges and develops into an adult.
Most trematodes are hermaphroditic, but members of the family Schistosomatidae
are dioecious
. Males are shorter and stouter than the females.
Trematoda
Trematoda is a class within the phylum Platyhelminthes that contains two groups of parasitic flatworms, commonly referred to as "flukes".-Taxonomy and biodiversity:...
are small parasitic flatworms that use vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s as their definitive host
Host (biology)
In biology, a host is an organism that harbors a parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. In botany, a host plant is one that supplies food resources and substrate for certain insects or other fauna...
, and molluscs as their intermediate host. In order to accomplish this, they have several varied lifecyle stages.
The lifecycle
Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
of a typical digenean trematode can be thought to begin when its egg is immersed in water. Following this a miracidium hatches, which swims to find a mollusc host. The miracidia go through several stages in the mollusc host, eventually emerging as motile cercaria larvae. The cercaria infect vertebrates either through the skin or are ingested. In its vertebrate host, the cercaria matures to an adult form, and lays eggs that are discharged with the host faeces or urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
. In the presence of open water, the eggs will hatch and the miracidium stage of life is reached again.
Typical lifecyle stages
While the details vary with each speciesSpecies
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
, the general lifecycle stages are as follows:
- Egg – discharged either in open water or in mollusc intestine.
- Miracidia – free-living motile form, covered with cilia, which settles in the mollusc to become a sporocyst.
- Sporocyst – an elongated sac that produces either rediae or more sporocysts.
- Redia (plural rediae) – a larval form with an oral sucker, it will produce either more rediae, or cercariae.
- Cercaria (plural cercariae) – the larval form of the parasite, developed within the germinal cells of the sporocyst or redia. A cercaria has a tapering head with large penetration glands. It may or may not have a long swimming "tail", depending on the species. The motile cercaria finds and settles in a host where it will become either an adult, or a mesocercaria, or a metacercaria, according to species.
- Mesocercaria – a cercaria little modified but resting.
- Metacercaria – a cercaria encystedCystA cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
and resting.
- Adult – the fully developed mature stage, capable of sexual reproduction.
Deviations from the typical lifecycle
The typical sequence (eggs, miracidia, sporocysts, rediae, ceracariae, and adults) is by no means the rule for all trematode species. In some species the redia stage is omitted and sporocysts produce cercariae. In some species, the cercaria develops into an adult within the same host.Many digenean trematodes require two hosts, one (typically a snail) where asexual reproduction occurs in sporocysts, the other a vertebrate (typically a fish) where the adult form engages in sexual reproduction to produce eggs. In some species (for example Ribeiroia
Ribeiroia
Ribeiroia is a group of trematode parasites that sequentially infect freshwater snails in the family Planorbidae as first intermediate hosts, fish and larval amphibians as second intermediate hosts, and birds and mammals as definitive hosts...
) the cercaria encysts, and waits until the host is eaten by a third host, in whose gut it emerges and develops into an adult.
Most trematodes are hermaphroditic, but members of the family Schistosomatidae
Schistosomatidae
Schistosomatidae is a family of digenetic trematodes with complex parasitic life cycles. Immature developmental stages of schistosomes are found in molluscs and adults occur in vertebrates. The best studied group, the blood flukes of the genus Schistosoma, infect and cause disease in humans...
are dioecious
Dioecious
Dioecy is the property of a group of biological organisms that have males and females, but not members that have organs of both sexes at the same time. I.e., those whose individual members can usually produce only one type of gamete; each individual organism is thus distinctly female or male...
. Males are shorter and stouter than the females.
Representations of lifecycles of several different trematode species

See also
- Bucephalus polymorphusBucephalus polymorphusBucephalus polymorphus is a species of the Bucephalidae family of Digenea, a subclass of Trematodes within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It is characterized by having a mouth near middle of body along with a sac-like gut. The adults occur in the centre of the ventral surface. The adults occur in the...
- Trematode infection
- Apicomplexa lifecycle stages

