
Mixed inhibition
Encyclopedia
Mixed inhibition refers to a combination of two different types of reversible enzyme inhibition – competitive inhibition
and uncompetitive inhibition. The term 'mixed' is used when the inhibitor can bind to either the free enzyme
or the enzyme-substrate complex. In mixed inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a site different from the active site
where the substrate
binds. Mixed inhibition results in a decrease in the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate (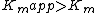 ) and a decrease in the apparent maximum enzyme reaction rate (
) and a decrease in the apparent maximum enzyme reaction rate (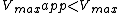 ).
).
Mathematically
, mixed inhibition occurs when the factors α and α’ (introduced into the Michaelis-Menten equation
to account for competitive and uncompetitive inhibition, respectively) are both greater than 1.
In the special case where α = α’, noncompetitive inhibition occurs, in which case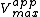 is reduced but
is reduced but 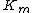 is unaffected. This is very unusual in practice
is unaffected. This is very unusual in practice
Competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibition is a form of enzyme inhibition where binding of the inhibitor to the active site on the enzyme prevents binding of the substrate and vice versa.-Mechanism:...
and uncompetitive inhibition. The term 'mixed' is used when the inhibitor can bind to either the free enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
or the enzyme-substrate complex. In mixed inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a site different from the active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
where the substrate
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
binds. Mixed inhibition results in a decrease in the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate (
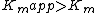 ) and a decrease in the apparent maximum enzyme reaction rate (
) and a decrease in the apparent maximum enzyme reaction rate (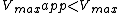 ).
).Mathematically
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, mixed inhibition occurs when the factors α and α’ (introduced into the Michaelis-Menten equation
Michaelis-Menten kinetics
In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics is one of the simplest and best-known models of enzyme kinetics. It is named after German biochemist Leonor Michaelis and Canadian physician Maud Menten. The model takes the form of an equation describing the rate of enzymatic reactions, by relating...
to account for competitive and uncompetitive inhibition, respectively) are both greater than 1.
In the special case where α = α’, noncompetitive inhibition occurs, in which case
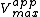 is reduced but
is reduced but 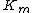 is unaffected. This is very unusual in practice
is unaffected. This is very unusual in practice

