
Mixed model
Encyclopedia
A mixed model is a statistical model containing both fixed effects and random effects, that is mixed effects. These models are useful in a wide variety of disciplines in the physical, biological and social sciences.
They are particularly useful in settings where repeated measurements are made on the same statistical unit
s, or where measurements are made on clusters of related statistical units.
introduced random effects models to study the correlations of trait values between relatives. In the 1950s, Charles Roy Henderson
provided best linear unbiased estimates
(BLUE) of fixed effects and best linear unbiased prediction
s (BLUP) of random effects. Subsequently, mixed modeling has become a major area of statistical research, including work on computation of maximum likelihood estimates, non-linear mixed effect models, missing data in mixed effects models, and Bayesian
estimation of mixed effects models. Mixed models are applied in many disciplines where multiple correlated measurements are made on each unit of interest. They are prominently used in research involving human and animal subjects in fields ranging from genetics to marketing, and have also been used in industrial statistics.
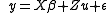
where
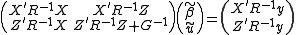
The solutions to the MME,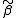 and
and 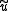 are best linear unbiased estimates (BLUE) and predictors for
are best linear unbiased estimates (BLUE) and predictors for 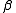 and
and  , respectively. This is a consequence of the Gauss-Markov theorem when the conditional variance of the outcome is not scalable to the identity matrix. When the conditional variance is known, then the inverse variance weighted least squares estimate is BLUE. However, the conditional variance is rarely, if ever, known. So it is desirable to jointly estimate the variance and weighted parameter estimates when solving MMEs.
, respectively. This is a consequence of the Gauss-Markov theorem when the conditional variance of the outcome is not scalable to the identity matrix. When the conditional variance is known, then the inverse variance weighted least squares estimate is BLUE. However, the conditional variance is rarely, if ever, known. So it is desirable to jointly estimate the variance and weighted parameter estimates when solving MMEs.
One method used to fit such mixed models is that of the EM algorithm where the variance components are treated as unobserved nuisance parameters in the joint likelihood. Currently, this is the implemented method for the major statistical software packages R
(lme in the nlme library) and SAS
(proc mixed). The solution to the mixed model equations is a maximum likelihood estimate when the distribution of the errors is normal.
They are particularly useful in settings where repeated measurements are made on the same statistical unit
Statistical unit
A unit in a statistical analysis refers to one member of a set of entities being studied. It is the material source for the mathematical abstraction of a "random variable"...
s, or where measurements are made on clusters of related statistical units.
History and current status
Ronald FisherRonald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher FRS was an English statistician, evolutionary biologist, eugenicist and geneticist. Among other things, Fisher is well known for his contributions to statistics by creating Fisher's exact test and Fisher's equation...
introduced random effects models to study the correlations of trait values between relatives. In the 1950s, Charles Roy Henderson
Charles Roy Henderson
Charles Roy Henderson was a statistician and a pioneer in animal breeding — the application of quantitative methods for the genetic evaluation of domestic livestock. He developed mixed model equations to obtain best linear unbiased predictions of breeding values and, in general, any random effect...
provided best linear unbiased estimates
Gauss–Markov theorem
In statistics, the Gauss–Markov theorem, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss and Andrey Markov, states that in a linear regression model in which the errors have expectation zero and are uncorrelated and have equal variances, the best linear unbiased estimator of the coefficients is given by the...
(BLUE) of fixed effects and best linear unbiased prediction
Best linear unbiased prediction
In statistics, best linear unbiased prediction is used in linear mixed models for the estimation of random effects. BLUP was derived by Charles Roy Henderson in 1950 but the term "best linear unbiased predictor" seems not to have been used until 1962...
s (BLUP) of random effects. Subsequently, mixed modeling has become a major area of statistical research, including work on computation of maximum likelihood estimates, non-linear mixed effect models, missing data in mixed effects models, and Bayesian
Bayesian statistics
Bayesian statistics is that subset of the entire field of statistics in which the evidence about the true state of the world is expressed in terms of degrees of belief or, more specifically, Bayesian probabilities...
estimation of mixed effects models. Mixed models are applied in many disciplines where multiple correlated measurements are made on each unit of interest. They are prominently used in research involving human and animal subjects in fields ranging from genetics to marketing, and have also been used in industrial statistics.
Definition
In matrix notation a mixed model can be represented as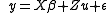
where
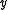 is a vector of observations, with mean
is a vector of observations, with mean 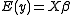
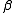 is a vector of fixed effects
is a vector of fixed effects
 is a vector of independent and identically-distributed (IID) random effects with mean
is a vector of independent and identically-distributed (IID) random effects with mean 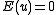 and variance-covariance matrix
and variance-covariance matrix 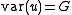
 is a vector of IID random error terms with mean
is a vector of IID random error terms with mean 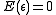 and variance
and variance 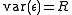
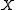 and
and 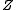 are matrices of regressors relating the observations
are matrices of regressors relating the observations 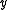 to
to 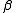 and
and 
Estimation
Henderson's "mixed model equations" (MME) are: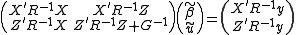
The solutions to the MME,
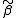 and
and 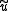 are best linear unbiased estimates (BLUE) and predictors for
are best linear unbiased estimates (BLUE) and predictors for 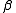 and
and  , respectively. This is a consequence of the Gauss-Markov theorem when the conditional variance of the outcome is not scalable to the identity matrix. When the conditional variance is known, then the inverse variance weighted least squares estimate is BLUE. However, the conditional variance is rarely, if ever, known. So it is desirable to jointly estimate the variance and weighted parameter estimates when solving MMEs.
, respectively. This is a consequence of the Gauss-Markov theorem when the conditional variance of the outcome is not scalable to the identity matrix. When the conditional variance is known, then the inverse variance weighted least squares estimate is BLUE. However, the conditional variance is rarely, if ever, known. So it is desirable to jointly estimate the variance and weighted parameter estimates when solving MMEs.One method used to fit such mixed models is that of the EM algorithm where the variance components are treated as unobserved nuisance parameters in the joint likelihood. Currently, this is the implemented method for the major statistical software packages R
R (programming language)
R is a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. The R language is widely used among statisticians for developing statistical software, and R is widely used for statistical software development and data analysis....
(lme in the nlme library) and SAS
SAS
- Special forces :* Special Air Service, a special forces unit of the British Army* Australian Special Air Service Regiment * New Zealand Special Air Service * Rhodesian Special Air Service...
(proc mixed). The solution to the mixed model equations is a maximum likelihood estimate when the distribution of the errors is normal.
See also
- Linear regressionLinear regressionIn statistics, linear regression is an approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar variable y and one or more explanatory variables denoted X. The case of one explanatory variable is called simple regression...
- Fixed effects model
- Random effects model
- Multilevel modelMultilevel modelMultilevel models are statistical models of parameters that vary at more than one level...
- Mixed-design analysis of varianceMixed-design analysis of varianceIn statistics, a mixed-design analysis of variance model is used to test for differences between two or more independent groups whilst subjecting participants to repeated measures...
Further reading
- Milliken, G. A., & Johnson, D. E. (1992). Analysis of messy data: Vol. I. Designed experiments. New York: Chapman & Hall.
- West, B. T., Welch, K. B., & Galecki, A. T. (2007). Linear mixed models: A practical guide to using statistical software. New York: Chapman & Hall/CRC.

