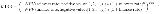
Modified Internal Rate of Return
Encyclopedia
The modified internal rate of return (MIRR) is a financial
measure of an investment
's attractiveness. It is used in capital budgeting
to rank alternative investments of equal size. As the name implies, MIRR is a modification of the internal rate of return
(IRR) and as such aims to resolve some problems with the IRR.
First, IRR assumes that interim positive cash flows are reinvested at the same rate of return as that of the project that generated them. This is usually an unrealistic scenario and a more likely situation is that the funds will be reinvested at a rate closer to the firm's cost of capital. The IRR therefore often gives an unduly optimistic picture of the projects under study. Generally for comparing projects more fairly, the weighted average cost of capital
should be used for reinvesting the interim cash flows.
Second, more than one IRR can be found for projects with alternating positive and negative cash flows, which leads to confusion and ambiguity. MIRR finds only one value.
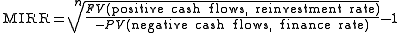 ,
,
where n is the number of equal periods at the end of which the cash flows occur (not the number of cash flows), PV is present value
(at the beginning of the first period), FV is future value
(at the end of the last period).
The formula adds up the negative cash flows after discounting them to time zero using the external cost of capital, adds up the positive cash flows including the proceeds of reinvestment at the external reinvestment rate to the final period, and then works out what rate of return would cause the magnitude of the discounted negative cash flows at time zero to be equivalent to the future value of the positive cash flows at the final time period.
Spreadsheet applications
, such as Microsoft Excel
, have inbuilt functions to calculate the MIRR. In Microsoft Excel this function is "=MIRR".
then the IRR is given by
is given by
 .
.
In this case, the answer is 25.48% (the other solutions to this equation are -593.16% and -132.32%, but they will not be considered meaningful IRRs).
To calculate the MIRR, we will assume a finance rate of 10% and a reinvestment rate of 12%. First, we calculate the present value of the negative cash flows (discounted at the finance rate):
 .
.
Second, we calculate the future value of the positive cash flows (reinvested at the reinvestment rate):
 .
.
Third, we find the MIRR:
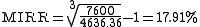 .
.
The calculated MIRR (17.91%) is significantly different from the IRR (25.48%).
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
measure of an investment
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
's attractiveness. It is used in capital budgeting
Capital budgeting
Capital budgeting is the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term investments such as new machinery, replacement machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects are worth pursuing...
to rank alternative investments of equal size. As the name implies, MIRR is a modification of the internal rate of return
Internal rate of return
The internal rate of return is a rate of return used in capital budgeting to measure and compare the profitability of investments. It is also called the discounted cash flow rate of return or the rate of return . In the context of savings and loans the IRR is also called the effective interest rate...
(IRR) and as such aims to resolve some problems with the IRR.
Problems with the IRR
While there are several problems with the IRR, MIRR resolves two of them.First, IRR assumes that interim positive cash flows are reinvested at the same rate of return as that of the project that generated them. This is usually an unrealistic scenario and a more likely situation is that the funds will be reinvested at a rate closer to the firm's cost of capital. The IRR therefore often gives an unduly optimistic picture of the projects under study. Generally for comparing projects more fairly, the weighted average cost of capital
Weighted average cost of capital
The weighted average cost of capital is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets....
should be used for reinvesting the interim cash flows.
Second, more than one IRR can be found for projects with alternating positive and negative cash flows, which leads to confusion and ambiguity. MIRR finds only one value.
Calculation of the MIRR
MIRR is calculated as follows: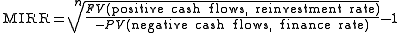 ,
,where n is the number of equal periods at the end of which the cash flows occur (not the number of cash flows), PV is present value
Present value
Present value, also known as present discounted value, is the value on a given date of a future payment or series of future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money and other factors such as investment risk...
(at the beginning of the first period), FV is future value
Future value
Future value is the value of an asset at a specific date. It measures the nominal future sum of money that a given sum of money is "worth" at a specified time in the future assuming a certain interest rate, or more generally, rate of return; it is the present value multiplied by the accumulation...
(at the end of the last period).
The formula adds up the negative cash flows after discounting them to time zero using the external cost of capital, adds up the positive cash flows including the proceeds of reinvestment at the external reinvestment rate to the final period, and then works out what rate of return would cause the magnitude of the discounted negative cash flows at time zero to be equivalent to the future value of the positive cash flows at the final time period.
Spreadsheet applications
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application that simulates a paper accounting worksheet. It displays multiple cells usually in a two-dimensional matrix or grid consisting of rows and columns. Each cell contains alphanumeric text, numeric values or formulas...
, such as Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a proprietary commercial spreadsheet application written and distributed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. It features calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications...
, have inbuilt functions to calculate the MIRR. In Microsoft Excel this function is "=MIRR".
Example
If an investment project is described by the sequence of cash flows:| Year | Cash flow |
|---|---|
| 0 | -1000 |
| 1 | -4000 |
| 2 | 5000 |
| 3 | 2000 |
then the IRR
 is given by
is given by .
.In this case, the answer is 25.48% (the other solutions to this equation are -593.16% and -132.32%, but they will not be considered meaningful IRRs).
To calculate the MIRR, we will assume a finance rate of 10% and a reinvestment rate of 12%. First, we calculate the present value of the negative cash flows (discounted at the finance rate):
 .
.Second, we calculate the future value of the positive cash flows (reinvested at the reinvestment rate):
 .
.Third, we find the MIRR:
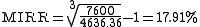 .
.The calculated MIRR (17.91%) is significantly different from the IRR (25.48%).

