Mollaret's meningitis
Encyclopedia
Mollaret's meningitis is a recurrent inflammation
of the protective membranes covering the brain
and spinal cord
, known collectively as the meninges
. It is a recurrent, benign, aseptic meningitis
.
It is named for Pierre Mollaret.
infection. Some patients also report frequent shingles
outbreaks. The chickenpox virus is part of the herpes family. CNS epidermoid cyst
s can give rise to Mollaret's meningitis especially with surgical manipulation of cyst contents.
s (electrolytes, liver and kidney function, inflammatory markers and a complete blood count
) and usually X-ray
examination of the chest. The most important test in identifying or ruling out meningitis is analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid (fluid that envelops the brain and the spinal cord) through lumbar puncture
(LP). However, if the patient is at risk for a cerebral mass lesion or elevated intracranial pressure
(recent head injury, a known immune system problem, localizing neurological signs, or evidence on examination of a raised ICP), a lumbar puncture may be contraindicated because of the possibility of fatal brain herniation
. In such cases, a CT
or MRI
scan is generally performed prior to the lumbar puncture to exclude this possibility. Otherwise, the CT or MRI should be performed after the LP, with MRI preferred over CT due to its superiority in demonstrating areas of cerebral edema, ischemia, and meningeal inflammation.
During the lumbar puncture procedure, the opening pressure is measured. A pressure of over 180 mm H2O is suggestive of bacterial meningitis.
Mollaret's meningitis is suspected based on clinical criteria and confirmed by HSV 1 or HSV 2 on PCR of CSF, although not all cases test positive.
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
of the protective membranes covering the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
and spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
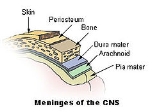
, known collectively as the meninges
Meninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
. It is a recurrent, benign, aseptic meningitis
Aseptic meningitis
Aseptic meningitis, or sterile meningitis, is a condition in which the layers lining the brain, meninges, become inflamed and a pyogenic bacterial source is not to blame. Meningitis is diagnosed on a history of characteristic symptoms and certain examination findings...
.
It is named for Pierre Mollaret.
Signs and symptoms
Mollaret's meningitis is characterized by recurrent episodes of severe headache, meningismus, and fever; cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pleocytosis with large "endothelial" cells, neutrophils, and lymphocytes; and attacks separated by symptom-free periods of weeks to months; and spontaneous remission of symptoms and signs. Many people have side effects between bouts that vary from chronic daily headaches to after-effects from meningitis such as hearing loss. Some patients report short bouts of 3–7 days of being sick while others have cases that can last for weeks or months. Many references talk about brief acute cases but support groups of people with Mollaret's show a wide variety of lengths of each bout. Although historically Mollaret's meningitis did not have a causative agent, it is now believed to be mostly from herpeticHerpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 , also known as Human herpes virus 1 and 2 , are two members of the herpes virus family, Herpesviridae, that infect humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are ubiquitous and contagious...
infection. Some patients also report frequent shingles
Herpes zoster
Herpes zoster , commonly known as shingles and also known as zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a limited area on one side of the body, often in a stripe...
outbreaks. The chickenpox virus is part of the herpes family. CNS epidermoid cyst
Epidermoid cyst
An epidermoid cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.-Terminology:...
s can give rise to Mollaret's meningitis especially with surgical manipulation of cyst contents.
Diagnosis
Investigations include blood testBlood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a needle, or via fingerprick....
s (electrolytes, liver and kidney function, inflammatory markers and a complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count , also known as full blood count or full blood exam or blood panel, is a test panel requested by a doctor or other medical professional that gives information about the cells in a patient's blood...
) and usually X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
examination of the chest. The most important test in identifying or ruling out meningitis is analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid (fluid that envelops the brain and the spinal cord) through lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture
A lumbar puncture is a diagnostic and at times therapeutic procedure that is performed in order to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid for biochemical, microbiological, and cytological analysis, or very rarely as a treatment to relieve increased intracranial pressure.-Indications:The...
(LP). However, if the patient is at risk for a cerebral mass lesion or elevated intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
(recent head injury, a known immune system problem, localizing neurological signs, or evidence on examination of a raised ICP), a lumbar puncture may be contraindicated because of the possibility of fatal brain herniation
Brain herniation
Brain herniation, also known as cistern obliteration, is a deadly side effect of very high intracranial pressure that occurs when the brain shifts across structures within the skull...
. In such cases, a CT
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
scan is generally performed prior to the lumbar puncture to exclude this possibility. Otherwise, the CT or MRI should be performed after the LP, with MRI preferred over CT due to its superiority in demonstrating areas of cerebral edema, ischemia, and meningeal inflammation.
During the lumbar puncture procedure, the opening pressure is measured. A pressure of over 180 mm H2O is suggestive of bacterial meningitis.
Mollaret's meningitis is suspected based on clinical criteria and confirmed by HSV 1 or HSV 2 on PCR of CSF, although not all cases test positive.

