
Momentum exchange tether
Encyclopedia
Momentum Exchange Tethers is one of many applications for space tether
s. This sub-set represents an entire area of research using a spinning conductive and/or non-conductive tether to throw spacecraft up or down in orbit (like a sling), thereby transferring (or taking) its momentum.
Due to the centrifugal acceleration, the act of spinning a long tether will create a controlled force on the end-masses of the system. If the tether system is spun at a particular angular frequency then the objects on either end of the EDT system will experience continuous acceleration. This controlled gravity is manipulated by control of the angular frequency. From this, momentum exchange can occur if an endbody is released during the controlled rotation. The transfer in momentum to the released object will cause the system to lose orbital energy, and thus lose altitude. However, using electrodynamic tether
thrusting it is possible to re-boost itself again without the expenditure of consumables.
An attitude control tether has a small mass on one end, and a satellite
on the other. Tidal force
s stretch the tether between the two masses. There are two ways of explaining tidal forces: In one, the upper part of an object goes faster than its natural orbital speed, so centrifugal force
stretches the object upwards. The lower part moves slower than the orbital speed, so it pulls down. Another way to explain tidal force is that the top of a tall object weighs less than the bottom, so they are pulled by different amounts. The "extra" pull on the "bottom" of the object stretches it out. On Earth, these are small effects, but in space, nothing opposes them.
The resulting tidal forces stabilize the satellite so that its long dimension points towards the planet it is orbiting. Simple satellites have often been stabilized this way, with tethers or mass distribution. A small bottle of fluid may be mounted in the spacecraft to damp pendulum vibrations with viscous friction of the fluid motion.
such as around the Earth or Saturn
, a conducting rotovator can be configured as an electrodynamic tether
. This can either be used as a dynamo
, which slows the tether and changes the angular momentum whilst generating electrical power, or alternatively, its orbital speed and/or angular momentum can be increased electrically from solar or nuclear power by running current through a wire that goes the length of the tether. Thus the tether can be used either to accelerate or brake an orbit
ing spacecraft.
In both cases the tether pushes against the planet, and thus the momentum gained or lost ultimately comes from the planet.
One complication to these techniques is that if the tether rotates, the direction of current must reverse (such as is the case in alternating current
s).
The maximum speed is limited by stress tolerance and safety factor of the tether but the speed can be greatly increased if it is of thicker cross-section in the middle and tapers and is lighter, thinner at the tips.
A spacecraft could rendezvous with one end of the tether, latch to it, and be accelerated by the tether's rotation. The tether and spacecraft would then separate at a later point when the spacecraft's velocity has been changed by the rotovator.
The momentum imparted to the spacecraft is not free. The tether's momentum
and angular momentum
is changed, and this costs energy
that must be recouped. The idea is that the recharge could be done with some form of energy (for instance solar panel
s generating current
for electromagnetic propulsion
) that is far cheaper than multi-stage-rocket fuel.
Rotating tethers can also be used to slow down incoming spacecraft, thus increasing the rotational momentum. If the average momentum gained from inward traffic equals that imparted to outward traffic, there is no net energy cost, and thus nothing to recoup.
. Rotovators would be momentum exchange tethers, with a retrograde motion of the tip closest to their parent body relative to the center of the tether.
Because the tips have a significant speed (typically 1–3 km/s), it can be possible in some cases to cancel the orbital speed such that the tips are stationary at their lowest point with respect to a planetary surface or lunar body. As described by Moravec, this is "a satellite that rotates like a wheel." The tip of the tether moves in approximately a cycloid
, in which it is momentarily stationary with respect to the ground. In this case, a payload that is "grabbed" by a capture mechanism on the rotating tether during the moment when it is stationary would be picked up and lifted into orbit; and potentially could be released at the top of the rotation, at which point it is moving with a speed significantly greater than the escape velocity and thus could be released onto an interplanetary trajectory. (As with the bolo, discussed above, the momentum and energy given to the payload must be made up, either with a high-performance rocket engine, or with momentum gathered from payload moving the other direction.)
On bodies with an atmosphere, such as the Earth, the tether tip must stay above the dense atmosphere. On bodies with reasonably low orbital speed (such as the Moon
and possibly Mars
), a rotovator in low orbit can potentially touch the ground, thereby providing cheap surface transport as well as launching materials into cislunar space.
Therefore another trick to achieve lower stresses is that rather than picking up a cargo from the ground at zero velocity, a rotovator could pick up a moving vehicle and sling it into orbit. For example, a rotovator could pick up a Mach-12
aircraft from the upper atmosphere of the Earth and move it into orbit without using rockets, and could likewise catch such a vehicle and lower it into atmospheric flight. It is easier for a rocket to achieve the lower tip speed, so "Single Stage To Tether" has been proposed. One such is called the Hypersonic Airplane Space Tether Orbital Launch (HASTOL). Either air breathing or rocket to tether could save a great deal of fuel per flight, and would permit for both a simpler vehicle and more cargo.
 A tidal stabilized tether is called a "skyhook
A tidal stabilized tether is called a "skyhook
" since it appears to be "hooked onto the sky". This term was introduced relating to satellites and orbital mechanics by the Italian scientist Giuseppe Colombo
. Skyhooks rotate precisely once per orbit and hence are always oriented the same way to the parent body.
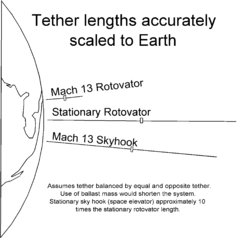
Some are called "hypersonic skyhooks" because the tip nearest the earth travels about Mach
-12 to 16 in typical designs. Longer tethers would travel more slowly. At the limit of zero ground speed, it would be re-classified as a space elevator or beanstalk.
An aircraft or sub-orbital vehicle transports cargo to one end of the skyhook.
Skyhook designs typically require climbers to transport the cargo to the other end (like a beanstalk).
Robert Raymond Boyd and Dimitri David Thomas (with Lockheed Martin Corporation)
patented the Skyhook idea in 2000 in a patent titled "Space elevator"http://www.google.com/patents?vid=USPAT6491258.
The company Tethers Unlimited Inc (founded by Dr. Robert Forward
and Dr. Robert P. Hoyt
) has called this approach "Tether Launch Assist".
) is a skyhook that is attached to planetary body. For example, on Earth, a beanstalk would go from the equator to geosynchronous orbit.
A beanstalk does not need to be powered as a rotovator does, because it gets any required angular momentum
from the planetary body. The disadvantage is that it is much longer, and for many planets a beanstalk cannot be constructed from known materials. A beanstalk on Earth would require material strengths outside current technological limits (2007). Martian and Lunar beanstalks
could be built with modern-day materials however. A space elevator on Phobos has also been proposed.
Beanstalks also have much larger amounts of potential energy than a rotovator, and if heavy parts should fail they might cause multiple impact event
s as objects hit the earth at near orbital speeds. Most anticipated cable designs would burn up before hitting the ground.
 Rotovators can thus be charged by momentum
Rotovators can thus be charged by momentum
exchange. Momentum charging uses the rotovator to move mass from a place that is "higher" in a gravity field to a place that is "lower". The technique to do this uses the Oberth effect
, where releasing the payload when the tether is moving with higher linear speed, lower in a gravitational potential gives more specific energy
, and ultimately more speed than the energy lost picking up the payload at a higher gravitational potential, even if the rotation rate is the same. For example, it is possible to use a system of two or three rotovators to implement trade between the Moon
and Earth
. The rotovators are charged by lunar mass (dirt, if exports are not available) dumped on or near the Earth, and can use the momentum so gained to boost Earth goods to the Moon. The momentum and energy exchange can be balanced with equal flows in either direction, or can increase over time.
Similar systems of rotovators could theoretically open up inexpensive transportation throughout the solar system
.
Space tether
Space tethers are cables, usually long and very strong, which can be used for propulsion, stabilization, or maintaining the formation of space systems by determining the trajectory of spacecraft and payloads...
s. This sub-set represents an entire area of research using a spinning conductive and/or non-conductive tether to throw spacecraft up or down in orbit (like a sling), thereby transferring (or taking) its momentum.
Due to the centrifugal acceleration, the act of spinning a long tether will create a controlled force on the end-masses of the system. If the tether system is spun at a particular angular frequency then the objects on either end of the EDT system will experience continuous acceleration. This controlled gravity is manipulated by control of the angular frequency. From this, momentum exchange can occur if an endbody is released during the controlled rotation. The transfer in momentum to the released object will cause the system to lose orbital energy, and thus lose altitude. However, using electrodynamic tether
Electrodynamic tether
Electrodynamic tethers are long conducting wires, such as one deployed from a tether satellite, which can operate on electromagnetic principles as generators, by converting their kinetic energy to electrical energy, or as motors, converting electrical energy to kinetic energy...
thrusting it is possible to re-boost itself again without the expenditure of consumables.
Tidal stabilization
Gravity-gradient stabilization, also called "gravity stabilization" and "tidal stabilization", is cheap and reliable. It uses no electronics, rockets or fuel.An attitude control tether has a small mass on one end, and a satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
on the other. Tidal force
Tidal force
The tidal force is a secondary effect of the force of gravity and is responsible for the tides. It arises because the gravitational force per unit mass exerted on one body by a second body is not constant across its diameter, the side nearest to the second being more attracted by it than the side...
s stretch the tether between the two masses. There are two ways of explaining tidal forces: In one, the upper part of an object goes faster than its natural orbital speed, so centrifugal force
Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force can generally be any force directed outward relative to some origin. More particularly, in classical mechanics, the centrifugal force is an outward force which arises when describing the motion of objects in a rotating reference frame...
stretches the object upwards. The lower part moves slower than the orbital speed, so it pulls down. Another way to explain tidal force is that the top of a tall object weighs less than the bottom, so they are pulled by different amounts. The "extra" pull on the "bottom" of the object stretches it out. On Earth, these are small effects, but in space, nothing opposes them.
The resulting tidal forces stabilize the satellite so that its long dimension points towards the planet it is orbiting. Simple satellites have often been stabilized this way, with tethers or mass distribution. A small bottle of fluid may be mounted in the spacecraft to damp pendulum vibrations with viscous friction of the fluid motion.

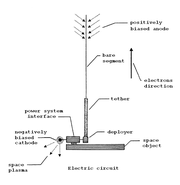
Electrodynamic tethers
In a strong planetary magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
such as around the Earth or Saturn
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,...
, a conducting rotovator can be configured as an electrodynamic tether
Electrodynamic tether
Electrodynamic tethers are long conducting wires, such as one deployed from a tether satellite, which can operate on electromagnetic principles as generators, by converting their kinetic energy to electrical energy, or as motors, converting electrical energy to kinetic energy...
. This can either be used as a dynamo
Dynamo
- Engineering :* Dynamo, a magnetic device originally used as an electric generator* Dynamo theory, a theory relating to magnetic fields of celestial bodies* Solar dynamo, the physical process that generates the Sun's magnetic field- Software :...
, which slows the tether and changes the angular momentum whilst generating electrical power, or alternatively, its orbital speed and/or angular momentum can be increased electrically from solar or nuclear power by running current through a wire that goes the length of the tether. Thus the tether can be used either to accelerate or brake an orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
ing spacecraft.
In both cases the tether pushes against the planet, and thus the momentum gained or lost ultimately comes from the planet.
One complication to these techniques is that if the tether rotates, the direction of current must reverse (such as is the case in alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
s).
Bolo
A rotating tether, or "bolo," is a high speed rotating tether, spinning so that the tips have a significant speed (~1–3 km/s).The maximum speed is limited by stress tolerance and safety factor of the tether but the speed can be greatly increased if it is of thicker cross-section in the middle and tapers and is lighter, thinner at the tips.
A spacecraft could rendezvous with one end of the tether, latch to it, and be accelerated by the tether's rotation. The tether and spacecraft would then separate at a later point when the spacecraft's velocity has been changed by the rotovator.
The momentum imparted to the spacecraft is not free. The tether's momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
and angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
is changed, and this costs energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
that must be recouped. The idea is that the recharge could be done with some form of energy (for instance solar panel
Photovoltaic module
A solar panel is a packaged, connected assembly of solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells...
s generating current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
for electromagnetic propulsion
Electromagnetic propulsion
Electromagnetic propulsion , is the principle of accelerating an object by the utilization of a flowing electrical current and magnetic fields. The electrical current is used to either create an opposing magnetic field, or to charge a fluid, which can then be repelled...
) that is far cheaper than multi-stage-rocket fuel.
Rotating tethers can also be used to slow down incoming spacecraft, thus increasing the rotational momentum. If the average momentum gained from inward traffic equals that imparted to outward traffic, there is no net energy cost, and thus nothing to recoup.
Rotovators
The word rotovator is a portmanteau derived from the words rotor and elevatorElevator
An elevator is a type of vertical transport equipment that efficiently moves people or goods between floors of a building, vessel or other structures...
. Rotovators would be momentum exchange tethers, with a retrograde motion of the tip closest to their parent body relative to the center of the tether.
Because the tips have a significant speed (typically 1–3 km/s), it can be possible in some cases to cancel the orbital speed such that the tips are stationary at their lowest point with respect to a planetary surface or lunar body. As described by Moravec, this is "a satellite that rotates like a wheel." The tip of the tether moves in approximately a cycloid
Cycloid
A cycloid is the curve traced by a point on the rim of a circular wheel as the wheel rolls along a straight line.It is an example of a roulette, a curve generated by a curve rolling on another curve....
, in which it is momentarily stationary with respect to the ground. In this case, a payload that is "grabbed" by a capture mechanism on the rotating tether during the moment when it is stationary would be picked up and lifted into orbit; and potentially could be released at the top of the rotation, at which point it is moving with a speed significantly greater than the escape velocity and thus could be released onto an interplanetary trajectory. (As with the bolo, discussed above, the momentum and energy given to the payload must be made up, either with a high-performance rocket engine, or with momentum gathered from payload moving the other direction.)
On bodies with an atmosphere, such as the Earth, the tether tip must stay above the dense atmosphere. On bodies with reasonably low orbital speed (such as the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
and possibly Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
), a rotovator in low orbit can potentially touch the ground, thereby providing cheap surface transport as well as launching materials into cislunar space.
Earth launch assist bolo
Unfortunately an Earth-to-orbit rotovator cannot be built from currently available materials since the thickness and tether mass to handle the loads on the rotovator would be uneconomically large. A "watered down" rotovator with two-thirds the rotational speed, however, would halve the centripetal acceleration stresses.Therefore another trick to achieve lower stresses is that rather than picking up a cargo from the ground at zero velocity, a rotovator could pick up a moving vehicle and sling it into orbit. For example, a rotovator could pick up a Mach-12
Mach number
Mach number is the speed of an object moving through air, or any other fluid substance, divided by the speed of sound as it is in that substance for its particular physical conditions, including those of temperature and pressure...
aircraft from the upper atmosphere of the Earth and move it into orbit without using rockets, and could likewise catch such a vehicle and lower it into atmospheric flight. It is easier for a rocket to achieve the lower tip speed, so "Single Stage To Tether" has been proposed. One such is called the Hypersonic Airplane Space Tether Orbital Launch (HASTOL). Either air breathing or rocket to tether could save a great deal of fuel per flight, and would permit for both a simpler vehicle and more cargo.
Skyhooks

Skyhook (structure)
Skyhooks are a theoretical class of cable based techniques intended to lift payloads to high altitudes and speeds. The name skyhook is a reference to an imaginary hook that hangs from the sky....
" since it appears to be "hooked onto the sky". This term was introduced relating to satellites and orbital mechanics by the Italian scientist Giuseppe Colombo
Giuseppe Colombo
Giuseppe Colombo , better known by his nickname Bepi Colombo, was an Italian scientist, mathematician and engineer at the University of Padua, Italy Giuseppe Colombo (Padua, October 2, 1920 – Padua, February 20, 1984), better known by his nickname Bepi Colombo, was an Italian scientist,...
. Skyhooks rotate precisely once per orbit and hence are always oriented the same way to the parent body.
Some are called "hypersonic skyhooks" because the tip nearest the earth travels about Mach
Mach number
Mach number is the speed of an object moving through air, or any other fluid substance, divided by the speed of sound as it is in that substance for its particular physical conditions, including those of temperature and pressure...
-12 to 16 in typical designs. Longer tethers would travel more slowly. At the limit of zero ground speed, it would be re-classified as a space elevator or beanstalk.
An aircraft or sub-orbital vehicle transports cargo to one end of the skyhook.
Skyhook designs typically require climbers to transport the cargo to the other end (like a beanstalk).
Robert Raymond Boyd and Dimitri David Thomas (with Lockheed Martin Corporation)
patented the Skyhook idea in 2000 in a patent titled "Space elevator"http://www.google.com/patents?vid=USPAT6491258.
The company Tethers Unlimited Inc (founded by Dr. Robert Forward
Robert Forward
Robert Lull Forward — known as Robert L. Forward — was an American physicist and science fiction writer...
and Dr. Robert P. Hoyt
Robert P. Hoyt
Dr. Robert P. Hoyt is a physicist and engineer who is famous for his invention of the Hoytether. He also originated the MXER Tether concept, which combines momentum-exchange techniques with electrodynamic reboost propulsion to enable a bolo tether system to serve as a fully reusable in-space upper...
) has called this approach "Tether Launch Assist".
Space elevator (beanstalk)
A beanstalk (a type of space elevatorSpace elevator
A space elevator, also known as a geostationary orbital tether or a beanstalk, is a proposed non-rocket spacelaunch structure...
) is a skyhook that is attached to planetary body. For example, on Earth, a beanstalk would go from the equator to geosynchronous orbit.
A beanstalk does not need to be powered as a rotovator does, because it gets any required angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
from the planetary body. The disadvantage is that it is much longer, and for many planets a beanstalk cannot be constructed from known materials. A beanstalk on Earth would require material strengths outside current technological limits (2007). Martian and Lunar beanstalks
Lunar space elevator
A lunar space elevator is a proposed cable running from the surface of the Moon into space.It is similar in concept to the better known Earth space elevator idea...
could be built with modern-day materials however. A space elevator on Phobos has also been proposed.
Beanstalks also have much larger amounts of potential energy than a rotovator, and if heavy parts should fail they might cause multiple impact event
Impact event
An impact event is the collision of a large meteorite, asteroid, comet, or other celestial object with the Earth or another planet. Throughout recorded history, hundreds of minor impact events have been reported, with some occurrences causing deaths, injuries, property damage or other significant...
s as objects hit the earth at near orbital speeds. Most anticipated cable designs would burn up before hitting the ground.
Cislunar transportation system
Although it might be thought that this requires constant energy input, it can in fact be shown to be energetically favourable to lift cargo off the surface of the Moon and drop it into a lower Earth orbit, and thus it can be achieved without any significant use of propellant, since the moon's surface is in a comparatively higher potential energy state.
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
exchange. Momentum charging uses the rotovator to move mass from a place that is "higher" in a gravity field to a place that is "lower". The technique to do this uses the Oberth effect
Oberth effect
In astronautics, the Oberth effect is where the use of a rocket engine when travelling at high speed generates much more useful energy than one at low speed...
, where releasing the payload when the tether is moving with higher linear speed, lower in a gravitational potential gives more specific energy
Specific energy
Specific energy is defined as the energy per unit mass. Common metric units are J/kg. It is an intensive property. Contrast this with energy, which is an extensive property. There are two main types of specific energy: potential energy and specific kinetic energy. Others are the gray and sievert,...
, and ultimately more speed than the energy lost picking up the payload at a higher gravitational potential, even if the rotation rate is the same. For example, it is possible to use a system of two or three rotovators to implement trade between the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
and Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. The rotovators are charged by lunar mass (dirt, if exports are not available) dumped on or near the Earth, and can use the momentum so gained to boost Earth goods to the Moon. The momentum and energy exchange can be balanced with equal flows in either direction, or can increase over time.
Similar systems of rotovators could theoretically open up inexpensive transportation throughout the solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
.

