
Moneyness
Encyclopedia
- "In the money" redirects here; for the poker term, see In the money (poker).
In finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, moneyness is a measure of the degree to which a derivative
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
is likely to have positive monetary value at its expiration
Expiration
Expiration is an independent feature film written, directed and starring Gavin Heffernan. It was the winner of the Grand Jury Prize and Best Film at the Canadian Filmmakers' Festival....
, in the risk-neutral measure
Risk-neutral measure
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure, is a prototypical case of an equivalent martingale measure. It is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market a derivative's price is the discounted...
. It can be measured in percentage probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
, or in standard deviations.
Intrinsic value and time value
The intrinsic value (or "monetary value") of an option is the value of exercising it now. Thus if the current (spotSpot price
The spot price or spot rate of a commodity, a security or a currency is the price that is quoted for immediate settlement . Spot settlement is normally one or two business days from trade date...
) price of the underlying security is above the agreed (strike
Strike price
In options, the strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price of the underlying instrument at that time.Formally, the strike...
) price, a call
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
has positive intrinsic value (and is called "in the money"), while a put
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
has zero intrinsic value.
The time value
Option time value
In finance, the time value of an option is the premium a rational investor would pay over its current exercise value , based on its potential to increase in value before expiring. This probability is always greater than zero, thus an option is always worth more than its current exercise value...
of an option is a function of the option value less the intrinsic value. It equates to uncertainty in the form of investor hope. It is also viewed as the value of not exercising the option immediately. In the case of a European option, you cannot choose to exercise it at any time, so the time value can be negative; for an American option if the time value is ever negative, you exercise it: this yields a boundary condition.
ATM: At-the-money
An optionOption (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
is at-the-money if the strike price
Strike price
In options, the strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price of the underlying instrument at that time.Formally, the strike...
is the same as the spot price of the underlying security on which the option is written. An at-the-money option has no intrinsic value, only time value.
ITM: In-the-money
An in-the-money option has positive intrinsic value as well as time value. A call option is in-the-money when the strike price is below the spot price. A put option is in-the-money when the strike price is above the spot price.OTM: Out-of-the-money
An out-of-the-money option has no intrinsic value. A call option is out-of-the-money when the strike price is above the spot price of the underlying security. A put option is out-of-the-money when the strike price is below the spot price.Spot versus forward
Assets can have a forward price (a price for delivery in future) as well as a spot price. One can also talk about moneyness with respect to the forward price: thus one talks about ATMF, "ATM Forward", and so forth. For instance, if the spot price for USD/JPY is 120, and the forward price one year hence is 110, then a call struck at 110 is ATMF but not ATM.Which are used?
Buying an ITM option is effectively lending money in the amount of the intrinsic value. Further, an ITM call can be replicated by entering a forward and buying an OTM put (and conversely). Consequently, ATM and OTM options are the main traded ones.Example
Suppose the current stock price of IBMIBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
is $100. A call
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
or put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
with a strike of $100 is at-the-money. A call option
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
with a strike of $80 is in-the-money (100 – 80 = 20 > 0). A put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
with a strike at $80 is out-of-the-money (80 – 100 = –20 < 0). Conversely, a call option with a $120 strike is out-of-the-money and a put option with a $120 strike is in-the-money.
When one uses the Black–Scholes model to value the option, one may define moneyness quantitatively. If we define the moneyness (of a call) as
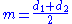
where d1 and d2 are the standard Black–Scholes parameters then

where T is the time to expiry.
In other words, it is the number of standard deviations the current price is above the ATMF price.
This choice of parameterisation means that the moneyness is zero when the forward price of the underlying, discounted at the risk-free rate, equals the strike price
Strike price
In options, the strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price of the underlying instrument at that time.Formally, the strike...
. Such an option is often referred to as at-the-money-forward. Moneyness is measured in standard deviations from this point, with a positive value meaning an in-the-money call option and a negative value meaning an out-of-the-money call option (with signs reversed for a put option).
One can also measure it as a percent, via
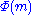 , where
, where 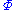 is the standard normal cumulative distribution function
is the standard normal cumulative distribution functionCumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
; thus a moneyness of 0 yields a 50% probability of expiring ITM, while a moneyness of 1 yields an approximately 84% probability of expiring ITM.
Beware that (percentage) moneyness is close to but different from Delta:
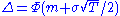
instead of
 , for a call (conversely for a put).
, for a call (conversely for a put).Thus a 25 Delta call option has approximately (but not exactly) 25% moneyness.
Note that
 is the risk-free rate, not the expected return on the underlying.
is the risk-free rate, not the expected return on the underlying.

