Mu-law algorithm
Overview
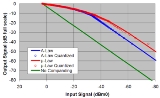
Companding
In telecommunication, signal processing, and thermodynamics, companding is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range...
algorithm, primarily used in the digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
systems of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. Companding algorithms reduce the dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
of an audio signal
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
. In analog systems, this can increase the signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
(SNR) achieved during transmission, and in the digital domain, it can reduce the quantization error (hence increasing signal to quantization noise ratio). These SNR increases can be traded instead for reduced bandwidth for equivalent SNR.
It is similar to the A-law algorithm
A-law algorithm
An A-law algorithm is a standard companding algorithm, used in European digital communications systems to optimize, i.e., modify, the dynamic range of an analog signal for digitizing.It is similar to the μ-law algorithm used in North America and Japan....
used in regions where digital telecommunication signals are carried on E-1 circuits, e.g.

