Mucorales
Encyclopedia
The Mucorales is the largest and best studied order
of Zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds.
, 56 genera
and approximately 300 species. Mucoralean classification has traditionally been based on morphological, developmental, and ecological characters. Recently, molecular data have revealed that some aspects of traditional classification are quite artificial. For example, the Mucoraceae
is believed to be polyphyletic, as are the Thamnidiaceae
, Chaetocladiaceae
and Radiomycetaceae
. Some of the genera, (including Mucor
, Absidia
and Backusella) appear to be polyphyletic. Today, the traditional system is still largely in use, as further studies are needed to reconcile morphological and molecular concepts of families and genera.
lack septa
(multiperforate septa are present only in sporangiophores and gametangia
). The hyphae grow mostly within the substrate
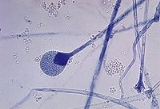
. Sporangiophores are upright (simple or ramified) hyphae that support sac-like sporangia filled with asexual sporangiospores.
Many are known by the damage they do to stored food. Others can can cause a mycosis
(infection), generally in patients already infected with other diseases.
) that are produced inside sporangia
(thousands of spores) or sporangiole
s (single or few spores). They are released when mature by the disintegration of the sporangium wall, or as a whole sporangiole that separates from the sporangiophore.
The sporangiospores germinate
to form the haploid hyphae of a new mycelium. Asexual reproduction
often occurs continuously.
Sexual reproduction
occurs when opposite mating types (designated + and -) come into close proximity, inducing the formation of specialized hyphae called gametangia. The gametangia grow toward each other, then fuse, forming a diploid zygote
at the point of fusion. The zygote develops a resistant cell wall
, forming a single-celled zygospore, the characteristic that gives its name to this group of fungi. Meiosis
occurs within the zygospore, and one of the resulting recombinant nuclei survives. Upon germination, a new haploid mycelium or sporangium is formed. Some species are homothallic
.
or pathogen
s of animals, plants and fungi. A few species cause human and animal disease zygomycosis, as well as allergic reactions.
Order (biology)
In scientific classification used in biology, the order is# a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, family, genus, and species, with order fitting in between class and family...
of Zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds.
Systematics
The order includes 12-13 familiesFamily (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
, 56 genera
Genera
Genera is a commercial operating system and development environment for Lisp machines developed by Symbolics. It is essentially a fork of an earlier operating system originating on the MIT AI Lab's Lisp machines which Symbolics had used in common with LMI and Texas Instruments...
and approximately 300 species. Mucoralean classification has traditionally been based on morphological, developmental, and ecological characters. Recently, molecular data have revealed that some aspects of traditional classification are quite artificial. For example, the Mucoraceae
Mucoraceae
The Mucoraceae are a family of fungi of the order Mucorales, characterized by having the thallus not segmented or ramified. Pathogenic genera include Absidia, Apophysomyces, Mucor, Rhizomucor, and Rhizopus. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 25 genera and 129...
is believed to be polyphyletic, as are the Thamnidiaceae
Thamnidiaceae
The Thamnidiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales....
, Chaetocladiaceae
Chaetocladiaceae
The Chaetocladiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales....
and Radiomycetaceae
Radiomycetaceae
The Radiomycetaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. Members of this family have a widespread distribution, but are more commonly found in warm climates.-Description:...
. Some of the genera, (including Mucor
Mucor
Mucor is a microbial genus of about 3000 species of moulds commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, and rotten vegetable matter.-Description:...
, Absidia
Absidia
Absidia is a genus of fungi in the family Mucoraceae. The best known species is the pathogenic Absidia corymbifera, which causes zygomycosis, especially in the form of mycotic spontaneous abortion in cows. It can also cause mucormycosis in humans. It is an allergenic that could cause mucorosis in...
and Backusella) appear to be polyphyletic. Today, the traditional system is still largely in use, as further studies are needed to reconcile morphological and molecular concepts of families and genera.
Characteristics
Mucoralean fungi are typically fast-growing, and their wide hyphaeHypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
lack septa
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
(multiperforate septa are present only in sporangiophores and gametangia
Gametangia
A gametangium is an organ or cell in which gametes are produced that is found in many multicellular protists, algae, fungi, and the gametophytes of plants...
). The hyphae grow mostly within the substrate
Substrate (biology)
In biology a substrate is the surface a plant or animal lives upon and grows on. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock can be substrate for another animal that lives on top of the algae. See also substrate .-External...
. Sporangiophores are upright (simple or ramified) hyphae that support sac-like sporangia filled with asexual sporangiospores.
Many are known by the damage they do to stored food. Others can can cause a mycosis
Mycosis
A mycosis is a fungal infection of animals, including humans. Mycoses are common, and a variety of environmental and physiological conditions can contribute to the development of fungal diseases...
(infection), generally in patients already infected with other diseases.
Life cycle
The sporangiospores are asexual mitospores (formed via mitosisMitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
) that are produced inside sporangia
Sporangium
A sporangium is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. All plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle...
(thousands of spores) or sporangiole
Sporangiole
A sporangiole is a specialised spherical spore produced by some species of fungi, which is not enclosed in sporangium....
s (single or few spores). They are released when mature by the disintegration of the sporangium wall, or as a whole sporangiole that separates from the sporangiophore.
The sporangiospores germinate
Germination
Germination is the process in which a plant or fungus emerges from a seed or spore, respectively, and begins growth. The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However the growth of a sporeling from a spore, for example the...
to form the haploid hyphae of a new mycelium. Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
often occurs continuously.
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
occurs when opposite mating types (designated + and -) come into close proximity, inducing the formation of specialized hyphae called gametangia. The gametangia grow toward each other, then fuse, forming a diploid zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
at the point of fusion. The zygote develops a resistant cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
, forming a single-celled zygospore, the characteristic that gives its name to this group of fungi. Meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
occurs within the zygospore, and one of the resulting recombinant nuclei survives. Upon germination, a new haploid mycelium or sporangium is formed. Some species are homothallic
Homothallic
Homothallic refers to the possession, within a single organism, of the resources to reproduce sexually.It can be contrasted to heterothallic.It is often used to categorize fungi. In yeast, heterothallic cells have mating types a and α...
.
Ecology
Most Mucoralean species are saprotrophic, and grow on organic substrates (such as fruit, soil, and dung). Some species are parasitesParasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
or pathogen
Pathogen
A pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
s of animals, plants and fungi. A few species cause human and animal disease zygomycosis, as well as allergic reactions.

