
Multifactor productivity
Encyclopedia
Multifactor productivity (MFP) measures the changes in output per unit of combined inputs. In the United States, Indices of MFP are produced for the private business, private nonfarm business, and manufacturing sectors of the economy. MFP is also developed for 2-and 3-digit Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) through 1987, and NAICS (North Atlantic Industrial Classification System) through 2005 for manufacturing industries, the railroad transportation industry, the air transportation industry, and the utility and gas industry.
Multifactor productivity measures reflect output per unit of some combined set of inputs. A change in multifactor productivity reflects the change in output that cannot be accounted for by the change in combined inputs. As a result, multifactor productivity measures reflect the joint effects of many factors including new technologies, economies of scale, managerial skill, and changes in the organization of production.
Whereas labor productivity
measures the output per unit of labor input, multifactor productivity looks at a combination of production inputs (or factors): labor, materials, and capital. In theory, it’s a more comprehensive measure than labor productivity, but it’s also more difficult to calculate.
(1)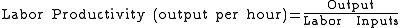
(2)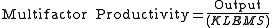
Multi-factor productivity is the same as total factor productivity
, a certain type of Solow residual
.
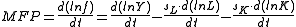
where:
Multifactor productivity measures reflect output per unit of some combined set of inputs. A change in multifactor productivity reflects the change in output that cannot be accounted for by the change in combined inputs. As a result, multifactor productivity measures reflect the joint effects of many factors including new technologies, economies of scale, managerial skill, and changes in the organization of production.
Whereas labor productivity
Labor productivity
Workforce productivity is the amount of goods and services that a worker produces in a given amount of time. It is one of several types of productivity that economists measure. Workforce productivity can be measured for a firm, a process, an industry, or a country...
measures the output per unit of labor input, multifactor productivity looks at a combination of production inputs (or factors): labor, materials, and capital. In theory, it’s a more comprehensive measure than labor productivity, but it’s also more difficult to calculate.
(1)
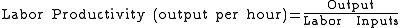
(2)
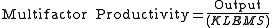
Multi-factor productivity is the same as total factor productivity
Total factor productivity
In economics, total-factor productivity is a variable which accounts for effects in total output not caused by inputs. If all inputs are accounted for, then total factor productivity can be taken as a measure of an economy’s long-term technological change or technological dynamism.If all inputs...
, a certain type of Solow residual
Solow residual
The Solow residual is a number describing empirical productivity growth in an economy from year to year and decade to decade. Robert Solow defined rising productivity as rising output with constant capital and labor input...
.
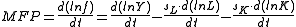
where:
-
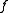 is the global production function;
is the global production function; -
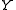 is output;
is output; -
 is time;
is time; -
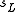 is the share of input costs attributable to labor expenses;
is the share of input costs attributable to labor expenses; -
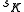 is the share of input costs attributable to capital expenses;
is the share of input costs attributable to capital expenses; -
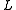 is a dollar quantity of labor
is a dollar quantity of labor -
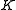 is a dollar quantity of capital
is a dollar quantity of capital -
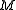 is a dollar quantity of materials
is a dollar quantity of materials -
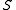 is a dollar quantity of [business] services
is a dollar quantity of [business] services

