
Multiple working
Encyclopedia


Multiple working is a term used on the UK rail network to describe the practice of having more than one diesel or electric locomotive hauling a train under the control of one driver.
Terminology
Multiple Working is the term used in the UK where more than one operational diesel or electric locomotive are coupled together under the control of one driver. The term can also apply when diesel or electric multiple unit trains are coupled together and also under the control of one driver. 'In tandem' is the term usually used in the UK when more than one diesel or electric locomotive are hauling a single train and under the control of a driver on each locomotive.If the front locomotive of a pair in multiple has failed the driver can still control the rear locomotive for as long as air and electricity supplies are available on the failed locomotive.
Locomotives
In the early days of diesel locomotives, locomotives worked within their class (i.e. two locomotives of the same class could work together but not with other classes). Locomotives from different manufacturers had varying methods of controlling engines or braking systemsBrake (railway)
Brakes are used on the cars of railway trains to enable deceleration, control acceleration or to keep them standing when parked. While the basic principle is familiar from road vehicle usage, operational features are more complex because of the need to control multiple linked carriages and to be...
. If a train required more than one locomotive, an additional driver was needed, at extra expense.
Since then, locomotives have been built to work with other locomotives in the same code or system. Similar systems are assigned a coupling code, which is normally indicated on the front of the locomotive.
Early diesels were also fitted with communicating doors in the nose which allowed the secondman
Secondman
A Secondman or Second man is a railway employee who assists the driver of a train with his duties. For this reason the term driver's assistant is also used...
to access the train heating boiler
Steam generator (railroad)
Steam generator is the term used to describe a type of boiler used to produce steam for climate control and potable water heating in railroad passenger cars...
of the rearmost locomotive. The doors actually saw little use and, as they frequently caused draughts in the cab, many of them were later welded shut.
| Coupling code | System | Class of locomotives |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Star | Electro-pneumatic | Class 15 British Rail Class 15 The British Rail Class 15 diesel locomotives, also known as the BTH Type 1, were designed by British Thomson-Houston, and built by the Yorkshire Engine Company and the Clayton Equipment Company, between 1957 and 1961.- Design history :... , Class 17 British Rail Class 17 The British Rail Class 17 was a class of 117 Bo-Bo diesel-electric locomotives built 1962–1965 by Clayton Equipment Company and their sub-contractor Beyer, Peacock & Co., for British Railways .... (Nos D8588–8616), Class 20 British Rail Class 20 The British Rail Class 20, otherwise known as an English Electric Type 1, is a class of diesel-electric locomotive. In total, 228 locomotives in the class were built by English Electric between 1957 and 1968, the large number being in part because of the failure of other early designs in the same... , Class 24 British Rail Class 24 The British Rail Class 24 diesel locomotives, also known as the Sulzer Type 2, were built from 1958 to 1961. One hundred and fifty-one of these locomotives were built at Derby, Crewe and Darlington, the first twenty of them as part of the British Rail 1955 Modernisation Plan. This class was used as... , Class 25 British Rail Class 25 The British Rail Class 25 diesel locomotives were also known as Sulzer Type 2 and nicknamed Rats, as it was alleged they could be seen everywhere in Britain, and hence were "as common as rats"... , Class 26 British Rail Class 26 The British Rail Class 26 diesel locomotives, also known as the BRCW Type 2, were built by the Birmingham Railway Carriage & Wagon Company at Smethwick in 1958-59. Forty seven examples were built, and the last were withdrawn from service in 1993... , Class 27 British Rail Class 27 British Rail's Class 27 comprised 69 diesel locomotives built by the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company during 1961 and 1962. They were a development of the earlier Class 26; both were originally classified as the BRCW Type 2.- Usage :... , Class 31/1 British Rail Class 31 The British Rail Class 31 diesel locomotives, also known as the Brush Type 2 and originally as Class 30, were built by Brush Traction from 1957-62.- Description :... , Class 33 British Rail Class 33 The British Rail Class 33 also known as the BRCW Type 3 or Crompton is a class of Bo-Bo diesel-electric locomotives ordered in 1957 and built for the Southern Region of British Railways between 1960 and 1962.... , Class 37 British Rail Class 37 The British Rail Class 37 is a diesel-electric locomotive. Also known as the English Electric Type 3, the Class was ordered as part of the British Rail modernisation plan.... , Class 40 British Rail Class 40 The British Rail Class 40 is a type of British railway diesel locomotive. Built by English Electric between 1958 and 1962, and eventually numbering 200, they were for a time the pride of the British Rail early diesel fleet... , Class 44 British Rail Class 44 The British Rail Class 44 or Sulzer Type 4 diesel locomotives were built by British Railways' Derby Works between 1959 to 1960. They were named after British mountains, and consequently nicknamed Peaks.-Description:... , Class 45 British Rail Class 45 The British Rail Class 45 also known as the Sulzer Type 4 diesel locomotives were built by British Rail at their Derby and Crewe Works between 1960 and 1962... and Class 46 British Rail Class 46 The British Rail Class 46 is a class of diesel locomotive. They were built from 1961-1963 at British Railways' Derby Works and were initially numbered D138-D193. With the arrival of TOPS they were renumbered to Class 46. Fifty-six locomotives were built... , Class 73 British Rail Class 73 The British Rail Class 73 is a United Kingdom model of electro-diesel locomotive. The type is unusual in that it can operate from a 750 V DC third-rail or an on-board diesel engine to allow it to operate on non-electrified routes... (under diesel power only). |
| ● Red Circle | Electro-magnetic | Class 16 British Rail Class 16 The North British Type 1 was a type of diesel locomotive ordered under British Railways' 1955 Modernisation Plan. Like other Type 1 designs, they were relatively small locomotives intended primarily for local freight traffic.... , Class 21 British Rail Class 21 The British Rail Class 21 was a type of Type 2 diesel-electric locomotive built by the North British Locomotive Company in Glasgow for British Railways in 1958-1960.... , Class 28 British Rail Class 28 The British Rail Class 28 diesel locomotives, or 'Metrovicks' as they were popularly known, were built as part of the British Railways 1955 Modernisation Plan. The locomotives had a Co-Bo wheel arrangement – unique in British Railways practice though not uncommon in other countries, notably Japan... , Class 29 British Rail Class 29 The British Rail Class 29 were a class of 20 diesel-electric Bo'Bo' locomotives produced by the re-engining of the British Rail Class 21 units. The units were designed for both passenger and freight trains... , Class 31/0 British Rail Class 31 The British Rail Class 31 diesel locomotives, also known as the Brush Type 2 and originally as Class 30, were built by Brush Traction from 1957-62.- Description :... . |
| ● Green Circle | Some Class 47 British Rail Class 47 The British Rail Class 47, is a class of British railway diesel-electric locomotive that was developed in the 1960s by Brush Traction. A total of 512 Class 47s were built at Crewe Works and Brush's Falcon Works, Loughborough between 1962 and 1968, which made them the most numerous class of British... . |
|
| ■ Orange Square | Class 50 British Rail Class 50 The British Rail Class 50 is a diesel locomotive built from 1967-68 by English Electric at their Vulcan Foundry Works in Newton-le-Willows. Fifty of these locomotives were built to haul express passenger trains on the, then non-electrified, section of the West Coast Main Line between Crewe,... . |
|
| Red Diamond | Symbol re-used for different systems Class D16/1 British Rail Class D16/1 British Railways Class D16/1 or 10000 and 10001 were the first mainline diesel locomotives in Great Britain. They were built by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway at its Derby Works, using the EE16SVT 1600 hp diesel engine with electric transmission, in association with English Electric and... (nos 10000/10001) Class 17 British Rail Class 17 The British Rail Class 17 was a class of 117 Bo-Bo diesel-electric locomotives built 1962–1965 by Clayton Equipment Company and their sub-contractor Beyer, Peacock & Co., for British Railways .... (D8500–D8587) Class 56 British Rail Class 56 The British Rail Class 56 is a type of diesel locomotive designed for heavy freight work. It is a Type 5 locomotive, with a Ruston-Paxman power unit developing 3,250 bhp , and has a Co-Co wheel arrangement... , Class 58 British Rail Class 58 The British Rail Class 58 is a class of Co-Co diesel locomotive designed for heavy freight. Introduced in 1983, they followed American practice of modularisation. From new they were painted in grey Railfreight Sector livery, instead of BR blue... , |
|
| Diesel hydraulics | Class 22 British Rail Class 22 The British Rail Class 22 or "Baby Warship" was a class of diesel-hydraulic locomotives designed for the Western Region of British Railways and built by the North British Locomotive Company. They were very similar in appearance to the Class 21 diesel-electrics... , Class 41 British Rail Class 41 (Warship Class) The British Railways Class D600 diesel-hydraulic locomotives were built by the North British Locomotive Company in Glasgow during 1957 and 1958. Although never assigned a TOPS class as they were withdrawn before TOPS was introduced British Loco enthusiasts coined the term "Class 41"... , Class 42 British Rail Class 42 British Railways' Type 4 Warship class diesel-hydraulic locomotives were introduced in 1958. It was apparent at that time that the largest centre of expertise on diesel-hydraulic locomotives was in Germany... , Class 43 British Rail Class 43 (Warship Class) The British Rail Class 43 diesel-hydraulic locomotives were built by the North British Locomotive Company from 1960–1962.-Classification:... |
|
| Diesel hydraulics | Class 35 British Rail Class 35 The British Rail Class 35 is a class of mixed-traffic B-B diesel locomotive with hydraulic transmission. Because of their Mekydro-design hydraulic transmission units, the locomotives became known as the Hymeks.... |
|
| SR EMU System | Class 33/1 British Rail Class 33 The British Rail Class 33 also known as the BRCW Type 3 or Crompton is a class of Bo-Bo diesel-electric locomotives ordered in 1957 and built for the Southern Region of British Railways between 1960 and 1962.... , Class 73 British Rail Class 73 The British Rail Class 73 is a United Kingdom model of electro-diesel locomotive. The type is unusual in that it can operate from a 750 V DC third-rail or an on-board diesel engine to allow it to operate on non-electrified routes... , Mark One Electric Multiple Units Electric multiple unit An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages, using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number of the carriages... . |
|
| Class 87 British Rail Class 87 The British Rail Class 87 is a type of electric locomotive built from 1973-75 by British Rail Engineering Limited . 36 of these locomotives were built to work passenger services over the West Coast Main Line . They were the flagships of British Rail's electric locomotive fleet until the late 1980s,... , some Class 86 British Rail Class 86 The British Rail Class 86 was the standard electric locomotive built during the 1960s, developed as a result of testing with the earlier Classes 81, 82, 83, 84 and 85. One hundred of these locomotives were built from 1965-1966 by either English Electric at Vulcan Foundry, Newton-le-Willows, or... s. |
||
| Class 43 (InterCity 125) British Rail Class 43 (HST) The British Rail Class 43 is the TOPS classification used for the InterCity 125 High Speed Train power cars, built by BREL from 1975 to 1982.... Class 60 British Rail Class 60 The British Rail Class 60 is a class of Co-Co heavy freight diesel-electric locomotives built by Brush Traction. They are nicknamed Tugs by Rail Enthusiasts.-History:... . |
||
| TDM System Time-division multiplexing Time-division multiplexing is a type of digital multiplexing in which two or more bit streams or signals are transferred apparently simultaneously as sub-channels in one communication channel, but are physically taking turns on the channel. The time domain is divided into several recurrent... |
Class 86 British Rail Class 86 The British Rail Class 86 was the standard electric locomotive built during the 1960s, developed as a result of testing with the earlier Classes 81, 82, 83, 84 and 85. One hundred of these locomotives were built from 1965-1966 by either English Electric at Vulcan Foundry, Newton-le-Willows, or... , Class 87 British Rail Class 87 The British Rail Class 87 is a type of electric locomotive built from 1973-75 by British Rail Engineering Limited . 36 of these locomotives were built to work passenger services over the West Coast Main Line . They were the flagships of British Rail's electric locomotive fleet until the late 1980s,... , Class 89 British Rail Class 89 The Class 89 is a prototype design for an electric locomotive. Only one unit was built, no. 89001, which was officially named Avocet by the then Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher on 16 January 1989 at Sandy, Bedfordshire - the home of the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds... , Class 90 British Rail Class 90 The British Rail Class 90 electric locomotives were built by BREL at Crewe from 1987-1990. Each locomotive weighs 84.5 tonnes and has a top speed of . They operate from 25 kV AC overhead wires and produce... , Class 91 British Rail Class 91 The British Rail Class 91 is a class of , electric locomotives ordered as a component of the East Coast Main Line modernisation and electrification programme of the late 1980s. The Class 91s were given the auxiliary name of InterCity 225 to indicate their envisaged top speed of... , DBSO Driving Brake Standard Open A Driving Brake Standard Open or DBSO is a type of railway carriage, converted to operate as a control car. Fourteen such vehicles, numbered 9701 to 9714, were converted from Mk. 2F Brake Standard Open carriages. Modifications included adding a driving cab and TDM equipment to allow a locomotive... , DVT Driving Van Trailer A Driving Van Trailer is a purpose-built railway vehicle that allows the driver to operate a locomotive at the opposite end of a train. Trains operating with a DVT therefore do not require the locomotive to be moved around to the other end of the train at terminal stations... . |
|
| AAR Association of American Railroads The Association of American Railroads is an industry trade group representing primarily the major freight railroads of North America . Amtrak and some regional commuter railroads are also members... System |
Class 59 British Rail Class 59 The Class 59 Co-Co diesel locomotives were built and introduced between 1985 and 1995 by Electro-Motive Division of General Motors for private British companies, initially Foster Yeoman... , Class 66 British Rail Class 66 The Class 66 is a six axle diesel electric freight locomotive developed in part from the British Rail Class 59, for use on the railways of the UK. Since its introduction the class has been successful and has been sold to British and other European railway companies... and Class 67 British Rail Class 67 The Class 67 locomotives are a class of Bo'Bo' diesel electric mainline locomotives which were built for the English, Welsh and Scottish Railway between 1999 to 2000 by Alstom at Meinfesa in Valencia, Spain with drive components from General Motors Diesel.Rail enthusiasts have nicknamed the class... , some DVT Driving Van Trailer A Driving Van Trailer is a purpose-built railway vehicle that allows the driver to operate a locomotive at the opposite end of a train. Trains operating with a DVT therefore do not require the locomotive to be moved around to the other end of the train at terminal stations... (Wrexham Shropshire). |
|
First-generation

Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
. For instance, a Class 127
British Rail Class 127
The British Rail Class 127 diesel multiple units were built by BR Derby in 1959. Thirty 4-car units were built, formed of two outer driving motor vehicles, sandwiching two intermediate trailers which were classified class 186...
unit (hydraulic transmission
Hydraulic transmission
Hydraulic transmission may refer to:* Hydrostatic transmission, see Hydraulic drive system and Hydraulic machinery* Hydrokinetic transmission, see Torque converter...
) could be required to work in multiple with a Class 112
British Rail Class 112
The Class 112 and Class 113 DMUs utilised the standard Cravens body used on Class 105s but had a single Rolls-Royce engine rated at per car, all of which formed into 'power twins'- two car sets with both vehicles powered....
unit (mechanical transmission). For this reason, the drive selector on the Class 127 was fitted with positions marked "D, 3, 2, 1" to change the gears when working in formation with vehicles with mechanical transmission.
First-generation DMU coupling codes:
| Coupling code | Class |
|---|---|
| ■ Blue Square | Most units with mechanical transmission |
| Orange Star | Most units with hydraulic transmission |
| Yellow Diamond | Derby Lightweight British Rail Derby Lightweight The British Rail Derby Lightweight diesel multiple units, were the first such trains to be built en-masse for British Railways. The units were built at BR's Derby Works from 1954 to 1955. The units were built in various formations, including 12 power-twin 2-car units, 84 power-trailer 2-car units,... (mechanical transmission) |
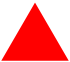 Red Triangle Red Triangle |
Derby Lightweight (hydraulic transmission) |
| O White Circle | Class 126 British Rail Class 126 The British Rail Class 126 diesel multiple unit was built by BR Swindon Works in 1959/60 to work services from Glasgow to Ayrshire and comprised 22 Motor Second vehicles , 22 Motor Brake Second , 10 Kitchen Trailer First and 11 Trailer Composite vehicles formed into 22 3-car sets formed Motor... |
Second-generation
Most second-generation units built by British Rail were designed to use the BSI multiple working system, including members of the 14x PacerPacer (train)
Pacer is the operational name of the British Rail Classes 140, 141, 142, 143 and 144 diesel multiple unit railbuses, built between 1984 and 1987...
and 15x Sprinter
Sprinter (train)
The Sprinter is a family of diesel multiple unit trains in use on the UK railway system. They were built in the 1980s and early 1990s by BREL, Metro Cammell and Leyland. Most are based around a Cummins engine with Voith hydraulic transmission, although some class 158s have a Perkins engine...
families. Later units, post-privatisation ones in particular, saw a number of different, incompatible systems re-emerge. Examples include the Dellner-coupled Class 220
British Rail Class 220
The Class 220 Voyager are a class of diesel-electric high-speed multiple-unit trains built by Bombardier Transportation in 2000 and 2001....
, 221
British Rail Class 221
The Class 221 Super Voyager is a class of British diesel-electric multiple-unit express trains built by Bombardier Transportation between 2001 and 2002, entering service on 12 April 2002....
and 390
British Rail Class 390
The Class 390 Pendolino is a type of train used in Great Britain. They are electric multiple units using Fiat's tilting train pendolino technology and built by Alstom. Fifty-three 9-car units were originally built for Virgin Trains from 2001 to 2004 for operation on the West Coast Main Line , with...
, originally used by Virgin Trains
Virgin Trains
Virgin Trains is a train operating company in the United Kingdom. It operates long-distance passenger services on the West Coast Main Line between London, the West Midlands, North West England, North Wales and Scotland...
, and the Scharfenberg-coupled Class 175
British Rail Class 175
The Class 175 Coradia is a type of diesel multiple unit passenger train used in the United Kingdom. The fleet of 27 sets were built from 1999 to 2001 by Alstom at Washwood Heath in Birmingham. They are part of the Coradia family of trains along with the Class 180.The entire fleet is owned by the...
and 180
British Rail Class 180
The Class 180 is a type of British diesel multiple unit train built by Alstom between 2000 and 2001 for use on then-new express services by First Great Western . They were built at Washwood Heath in Birmingham and are part of the Coradia 1000 family along with the Class 175. FGW stopped using the...
, originally used by First North Western
First North Western
First North Western was a train operating company in the United Kingdom serving North West England. It operated from 1997 to 2004.The company when first privatised was known as North Western Trains and was owned by Great Western Holdings, a partnership between Great Western's management, First...
and First Great Western
First Great Western
First Great Western is the operating name of First Greater Western Ltd, a British train operating company owned by FirstGroup that serves Greater London, the South East, South West and West Midlands regions of England, and South Wales....
respectively. Franchise changes and stock reallocation means that many Train Operating Companies
Train operating company
The term train operating company is used in the United Kingdom to describe the various businesses operating passenger trains on the railway system of Great Britain under the collective National Rail brand...
use fleets with a number of incompatible multiple working systems.

