Muscularis externa
Encyclopedia
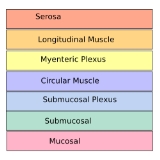
The muscular coat is a region of muscle
in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa membrane. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis
.
It usually has two distinct layers of smooth muscle
:
However, there are some exceptions to this pattern.
The inner layer of the muscularis externa forms a sphincter
at two locations of the alimentary canal:
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa membrane. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis
Peristalsis
Peristalsis is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles which propagates in a wave down the muscular tube, in an anterograde fashion. In humans, peristalsis is found in the contraction of smooth muscles to propel contents through the digestive tract. Earthworms use a similar...
.
It usually has two distinct layers of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two sub-groups; the single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit smooth muscle tissues, the autonomic nervous system innervates a single cell within a sheet or bundle and the action potential is propagated by...
:
- inner and "circular"
- outer and "longitudinal"
However, there are some exceptions to this pattern.
- In the stomach and colon, there are three layers to the muscularis externa.
- In the upper esophagusEsophagusThe esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
, part of the externa is skeletal muscleSkeletal muscleSkeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue existing under control of the somatic nervous system- i.e. it is voluntarily controlled. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac and smooth muscle...
, rather than smooth muscle.
The inner layer of the muscularis externa forms a sphincter
Sphincter
A sphincter is an anatomical structure, or a circular muscle, that normally maintains constriction of a natural body passage or orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning...
at two locations of the alimentary canal:
- in the pyloric stomach, it forms the pyloric sphincter
- in the anal canalAnal canalThe anal canal is the terminal part of the large intestine.It is situated between the rectum and anus, below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It lies in the anal triangle of perineum in between the right and left ischioanal fossa....
, it forms the anal sphincter
External links
- Histology at nhmccd.edu - "Duodenum" - "Mammal, whole system (LM, Low)" - "Muscle Tissue: smooth muscle, muscularis externa" - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal - esophagus "

