
Mydriasis
Encyclopedia
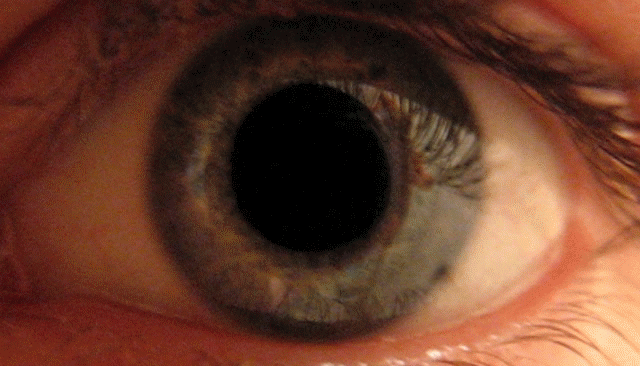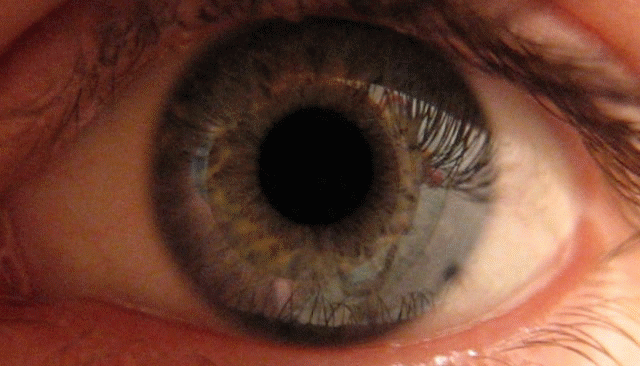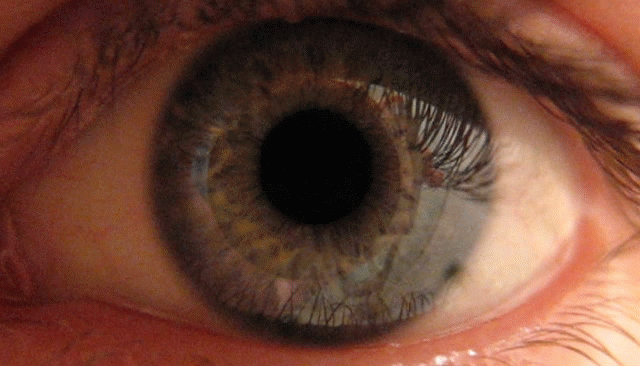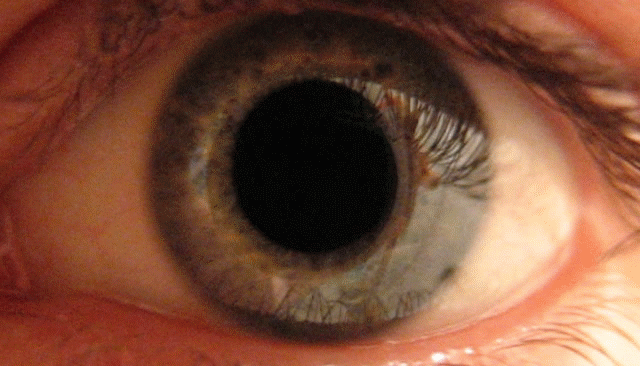
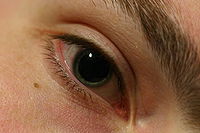
Mydriasis icon is a dilation of the pupil
due to disease
, trauma
or the use of drug
s. Normally, the pupil dilates in the dark
and constricts
in the light
to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina
from sunlight damage during the day. A mydriatic pupil will remain excessively large even in a bright environment and is sometimes colloquially referred to as a "blown pupil
". More generally, mydriasis refers to the dilation of pupils, for instance in low light conditions or under sympathetic stimulation. The excitation of the radial fibres of the iris which increases the pupillary aperature is referred to as a mydriasis.
The opposite, constriction of the pupil, is referred to as miosis
. Both mydriasis and miosis can be physiological.
that control the size of the iris
: circular
muscle and radial
muscle. The former is innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system
, the latter by the sympathetic nervous system
. Sympathetic stimulation of α1 adrenergic receptors causes the contraction
of the radial muscle, and subsequent dilation of the pupil. Conversely, parasympathetic stimulation cause contraction of the circular muscle and constriction of the pupil.
The mechanism of mydriasis depends on the agent being used. It usually involves either a disruption of the parasympathetic nerve supply to the eye (which causes contraction of the pupil), or overactivity of the sympathetic nervous system
(SNS).
can cause mild to moderate mydriasis. Strong sexual arousal can often lead to very enlarged pupils, rather than the minor dilation observed during sexual affection. Orgasm
has been reported to lead to pupillary block in a single case in combination with an ocular precondition. Here the parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation lead to sphincter muscle stimulation during pupillary dilation in the dark, while ciliary contraction caused zonular relaxation leading to pupillary block and angle-closure in combination with pre-existing narrow chamber angle
.
, is supplied by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor nerve
. Damage to this nerve typically manifests itself as mydriasis, because the sympathetic
supply to the pupil, which causes mydriasis, remains unaffected, and therefore unopposed.
Multiple central nervous system
disorders e.g. epilepsy, stroke are known to lead to temporal mydriasis as well.
 In cases of head injury
In cases of head injury
or orbit trauma (eye injury)
, the iris sphincter
(the muscle responsible for closing the pupil) or the nerves controlling it can be damaged, reducing or eliminating consensual reactivity to light.
s such as atropine
, hyoscyamine
, and scopolamine
antagonize the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
s in the eye. By blocking these receptors, the pupils are no longer capable of constriction and dilation results. Such alkaloids present in many plants of the family Solanaceae
may also induce mydriasis when used recreationally.
Most hallucinogens such as LSD
, psilocybin
, and mescaline
, in addition to some other phenethylamines and tryptamines, all produce mydriasis by agonizing the serotonergic 5-HT2A receptor
s in the brain. Dissociatives such as ketamine
, DXM
, and PCP
do so as well via antagonism of the NMDA glutamate receptors. There have also been reports that the atypical psychedelic herb Salvia divinorum
and its active constituent salvinorin A
causes mydriasis. It works via agonism of the κ-Opioid receptors in the brain. How the neurological changes induced by these drugs ultimately causes pupil dilation is unknown.
Drugs that increase overall serotonin
levels in general are capable of causing mydriasis in the same way as the 5-HT2A-mediated psychedelics. This is because serotonin itself is naturally responsible for normal 5-HT2A stimulation. Hence, in sufficient quantities serotonin is mydriatic and can even be mildly psychedelic, though the potentially fatal serotonin syndrome
usually ensues before the psychedelia becomes overly-pronounced. Examples of such drugs include MDMA (as well as other MDxx compounds), fenfluramine
, chlorphentermine
, stimulants (including cocaine
and amphetamines), and some antidepressants (such as SSRIs, SNRI
s, and MAOIs). Natural serotonin-boosting supplements such as L-Tryptophan and 5-HTP are also capable of this, but usually only in excessive doses.
The neurotransmitter
norepinephrine
regulates many physiological processes in the body and brain. One of them is the autonomic constriction and contraction of certain muscles. The psychoactive drug cocaine
potently inhibits the normal reuptake of norepinephrine
into presynaptic nerve terminals
resulting in an increased level of extracellular
norepinephrine. Amphetamines also potently release and prevent the reuptake of norepinephrine. The released norepinephrine then proceeds to bind to adrenergic
receptors, and the biological effects of norepinephrine finally occur. When a solution of cocaine is dropped into the eye, this process takes place, and the end result is dilation of the pupil. Cocaine itself is not typically used for this task however. Any potent norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor or release agent should be capable of such an effect.
Opioids such as morphine
and heroin cause miosis
. Subsequently, mydriasis occasionally occurs during opioid rebound and withdrawal.
 A mydriatic is an agent that induces dilation of the pupil
A mydriatic is an agent that induces dilation of the pupil
. Drugs such as tropicamide
are used in medicine
to permit examination of the retina
and other deep structures of the eye, and also to reduce painful ciliary muscle
spasm (see cycloplegia
). Phenylephrine
(e.g. Cyclomydril) is used if strong mydriasis is needed for a surgical intervention. One effect of administration of a mydriatic is intolerance to bright light (Photophobia
). Purposely-induced mydriasis via mydriatics is also used as a diagnostic test for Horner's Syndrome
.
Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In humans the pupil is round, but other species, such as some cats, have slit pupils. In...
due to disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
, trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
or the use of drug
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
s. Normally, the pupil dilates in the dark
Dark
Dark commonly refers to darkness, the absence of light.Dark may also refer to:*Evil, sinister or malign*Dark , a term used to describe a broadcasting service that has ceased transmission...
and constricts
Constriction
Constriction is a method used by various snake species to kill their prey. Although some species of venomous and mildly-venomous snakes do use constriction to subdue their prey, most snakes which use constriction lack venom. The snake initially strikes at its prey and holds on, pulling the prey...
in the light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
from sunlight damage during the day. A mydriatic pupil will remain excessively large even in a bright environment and is sometimes colloquially referred to as a "blown pupil
Blown pupil
Blown pupil is an informal medical term used by medical providers to refer to sudden pupillary dilation and loss of ability to constrict in response to light...
". More generally, mydriasis refers to the dilation of pupils, for instance in low light conditions or under sympathetic stimulation. The excitation of the radial fibres of the iris which increases the pupillary aperature is referred to as a mydriasis.
The opposite, constriction of the pupil, is referred to as miosis
Miosis
Miosis is the constriction of the pupil of the eye to two millimeters or less...
. Both mydriasis and miosis can be physiological.
Mechanism
There are two types of muscleMuscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
that control the size of the iris
Iris (anatomy)
The iris is a thin, circular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupils and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. "Eye color" is the color of the iris, which can be green, blue, or brown. In some cases it can be hazel , grey, violet, or even pink...
: circular
Iris sphincter muscle
The iris sphincter muscle is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris...
muscle and radial
Iris dilator muscle
The iris dilator muscle , is a smooth muscle of the eye, running radially in the iris and therefore fit as a dilator. It has its origin from the anterior epithelium. It is innervated by the sympathetic system, which acts by releasing noradrenaline, which acts on α1-receptors...
muscle. The former is innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system . The ANS is responsible for regulation of internal organs and glands, which occurs unconsciously...
, the latter by the sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three parts of the autonomic nervous system, along with the enteric and parasympathetic systems. Its general action is to mobilize the body's nervous system fight-or-flight response...
. Sympathetic stimulation of α1 adrenergic receptors causes the contraction
Muscle contraction
Muscle fiber generates tension through the action of actin and myosin cross-bridge cycling. While under tension, the muscle may lengthen, shorten, or remain the same...
of the radial muscle, and subsequent dilation of the pupil. Conversely, parasympathetic stimulation cause contraction of the circular muscle and constriction of the pupil.
The mechanism of mydriasis depends on the agent being used. It usually involves either a disruption of the parasympathetic nerve supply to the eye (which causes contraction of the pupil), or overactivity of the sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three parts of the autonomic nervous system, along with the enteric and parasympathetic systems. Its general action is to mobilize the body's nervous system fight-or-flight response...
(SNS).
Effects
Natural release of the hormone oxytocinOxytocin
Oxytocin is a mammalian hormone that acts primarily as a neuromodulator in the brain.Oxytocin is best known for its roles in sexual reproduction, in particular during and after childbirth...
can cause mild to moderate mydriasis. Strong sexual arousal can often lead to very enlarged pupils, rather than the minor dilation observed during sexual affection. Orgasm
Orgasm
Orgasm is the peak of the plateau phase of the sexual response cycle, characterized by an intense sensation of pleasure...
has been reported to lead to pupillary block in a single case in combination with an ocular precondition. Here the parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation lead to sphincter muscle stimulation during pupillary dilation in the dark, while ciliary contraction caused zonular relaxation leading to pupillary block and angle-closure in combination with pre-existing narrow chamber angle
Anterior chamber
The anterior chamber is the fluid-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Aqueous humor is the fluid that fills the anterior chamber. Hyphema and glaucoma are two main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, blood fills the anterior chamber...
.
Autonomic neuropathy
The parasympathetic nervous supply, which causes constriction of the pupil, or miosisMiosis
Miosis is the constriction of the pupil of the eye to two millimeters or less...
, is supplied by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor nerve
Oculomotor nerve
The oculomotor nerve is the 3rd of 12 paired cranial nerves. It enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure and controls most of the eye's movements, including constriction of the pupil and maintaining an open eyelid by innervating the Levator palpebrae superiors muscle. The optic nerve is...
. Damage to this nerve typically manifests itself as mydriasis, because the sympathetic
Sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three parts of the autonomic nervous system, along with the enteric and parasympathetic systems. Its general action is to mobilize the body's nervous system fight-or-flight response...
supply to the pupil, which causes mydriasis, remains unaffected, and therefore unopposed.
Multiple central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
disorders e.g. epilepsy, stroke are known to lead to temporal mydriasis as well.
Traumatic

Head injury
Head injury refers to trauma of the head. This may or may not include injury to the brain. However, the terms traumatic brain injury and head injury are often used interchangeably in medical literature....
or orbit trauma (eye injury)
Eye injury
Physical or chemical injuries of the eye can be a serious threat to vision if not treated appropriately and in a timely fashion. The most obvious presentation of ocular injuries is redness and pain of the affected eyes. This is not, however, universally true, as tiny metallic projectiles may cause...
, the iris sphincter
Iris sphincter muscle
The iris sphincter muscle is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris...
(the muscle responsible for closing the pupil) or the nerves controlling it can be damaged, reducing or eliminating consensual reactivity to light.
Drugs
AnticholinergicAnticholinergic
An anticholinergic agent is a substance that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and the peripheral nervous system. An example of an anticholinergic is dicycloverine, and the classic example is atropine....
s such as atropine
Atropine
Atropine is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid extracted from deadly nightshade , Jimson weed , mandrake and other plants of the family Solanaceae. It is a secondary metabolite of these plants and serves as a drug with a wide variety of effects...
, hyoscyamine
Hyoscyamine
Hyoscyamine is a tropane alkaloid. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the Solanaceae family, including henbane , mandrake , jimsonweed , tomato and deadly nightshade...
, and scopolamine
Scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as levo-duboisine, and hyoscine, is a tropane alkaloid drug with muscarinic antagonist effects. It is among the secondary metabolites of plants from Solanaceae family of plants, such as henbane, jimson weed and Angel's Trumpets , and corkwood...
antagonize the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Muscarinic receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled in the plasma membranes of certain neurons and other cells...
s in the eye. By blocking these receptors, the pupils are no longer capable of constriction and dilation results. Such alkaloids present in many plants of the family Solanaceae
Solanaceae
Solanaceae are a family of flowering plants that include a number of important agricultural crops as well as many toxic plants. The name of the family comes from the Latin Solanum "the nightshade plant", but the further etymology of that word is unclear...
may also induce mydriasis when used recreationally.
Most hallucinogens such as LSD
LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide, abbreviated LSD or LSD-25, also known as lysergide and colloquially as acid, is a semisynthetic psychedelic drug of the ergoline family, well known for its psychological effects which can include altered thinking processes, closed and open eye visuals, synaesthesia, an...
, psilocybin
Psilocybin
Psilocybin is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug, with mind-altering effects similar to those of LSD and mescaline, after it is converted to psilocin. The effects can include altered thinking processes, perceptual distortions, an altered sense of time, and spiritual experiences, as well as...
, and mescaline
Mescaline
Mescaline or 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine is a naturally occurring psychedelic alkaloid of the phenethylamine class used mainly as an entheogen....
, in addition to some other phenethylamines and tryptamines, all produce mydriasis by agonizing the serotonergic 5-HT2A receptor
5-HT2A receptor
The mammalian 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor . This is the main excitatory receptor subtype among the GPCRs for serotonin , although 5-HT2A may also have an inhibitory effect on certain areas such...
s in the brain. Dissociatives such as ketamine
Ketamine
Ketamine is a drug used in human and veterinary medicine. Its hydrochloride salt is sold as Ketanest, Ketaset, and Ketalar. Pharmacologically, ketamine is classified as an NMDA receptor antagonist...
, DXM
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan is an antitussive drug. It is one of the active ingredients in many over-the-counter cold and cough medicines, such as Robitussin, NyQuil, Dimetapp, Vicks, Coricidin, Delsym, and others, including generic labels. Dextromethorphan has also found other uses in medicine, ranging...
, and PCP
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine , commonly initialized as PCP and known colloquially as angel dust, is a recreational dissociative drug...
do so as well via antagonism of the NMDA glutamate receptors. There have also been reports that the atypical psychedelic herb Salvia divinorum
Salvia divinorum
Salvia divinorum is a psychoactive plant which can induce dissociative effects and is a potent producer of "visions" and other hallucinatory experiences...
and its active constituent salvinorin A
Salvinorin A
Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in Salvia divinorum, a Mexican plant which has a long history of use as an entheogen by indigenous Mazatec shamans...
causes mydriasis. It works via agonism of the κ-Opioid receptors in the brain. How the neurological changes induced by these drugs ultimately causes pupil dilation is unknown.
Drugs that increase overall serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
levels in general are capable of causing mydriasis in the same way as the 5-HT2A-mediated psychedelics. This is because serotonin itself is naturally responsible for normal 5-HT2A stimulation. Hence, in sufficient quantities serotonin is mydriatic and can even be mildly psychedelic, though the potentially fatal serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening adverse drug reaction that may occur following therapeutic drug use, inadvertent interactions between drugs, overdose of particular drugs, or the recreational use of certain drugs...
usually ensues before the psychedelia becomes overly-pronounced. Examples of such drugs include MDMA (as well as other MDxx compounds), fenfluramine
Fenfluramine
Fenfluramine is a drug that was part of the Fen-Phen anti-obesity medication . Fenfluramine was introduced on the U.S. market in 1973. It is the racemic mixture of two enantiomers, dextrofenfluramine and levofenfluramine...
, chlorphentermine
Chlorphentermine
Chlorphentermine is an appetite suppressant of the phenethylamine class. Developed in 1962, it is the 4-chloro derivative of the better known appetite suppressant phentermine, which is still in current use.Chlorphentermine itself is a relatively weak stimulant with little abuse potential, but is...
, stimulants (including cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. The name comes from "coca" in addition to the alkaloid suffix -ine, forming cocaine. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic...
and amphetamines), and some antidepressants (such as SSRIs, SNRI
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs used in the treatment of major depression and other mood disorders...
s, and MAOIs). Natural serotonin-boosting supplements such as L-Tryptophan and 5-HTP are also capable of this, but usually only in excessive doses.
The neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
regulates many physiological processes in the body and brain. One of them is the autonomic constriction and contraction of certain muscles. The psychoactive drug cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. The name comes from "coca" in addition to the alkaloid suffix -ine, forming cocaine. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic...
potently inhibits the normal reuptake of norepinephrine
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
A norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor or adrenergic reuptake inhibitor , is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter...
into presynaptic nerve terminals
Chemical synapse
Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie...
resulting in an increased level of extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
norepinephrine. Amphetamines also potently release and prevent the reuptake of norepinephrine. The released norepinephrine then proceeds to bind to adrenergic
Adrenergic receptor
The adrenergic receptors are a class of metabotropic G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of the catecholamines, especially noradrenaline and adrenaline ....
receptors, and the biological effects of norepinephrine finally occur. When a solution of cocaine is dropped into the eye, this process takes place, and the end result is dilation of the pupil. Cocaine itself is not typically used for this task however. Any potent norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor or release agent should be capable of such an effect.
Opioids such as morphine
Morphine
Morphine is a potent opiate analgesic medication and is considered to be the prototypical opioid. It was first isolated in 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner, first distributed by same in 1817, and first commercially sold by Merck in 1827, which at the time was a single small chemists' shop. It was more...
and heroin cause miosis
Miosis
Miosis is the constriction of the pupil of the eye to two millimeters or less...
. Subsequently, mydriasis occasionally occurs during opioid rebound and withdrawal.
Mydriatics

Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In humans the pupil is round, but other species, such as some cats, have slit pupils. In...
. Drugs such as tropicamide
Tropicamide
Tropicamide is an anticholinergic used as a mydriatic. In Russia, it is used to some degree as an inexpensive recreational drug...
are used in medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
to permit examination of the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
and other deep structures of the eye, and also to reduce painful ciliary muscle
Ciliary muscle
The ciliary muscle is a ring of striated smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer that controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humour into Schlemm's canal. It changes the shape of the lens within the eye not the size of the pupil which is...
spasm (see cycloplegia
Cycloplegia
Cycloplegia is paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the eye, resulting in a loss of accommodation.-Anatomy:The iris is the heavily pigmented colored part of the eye. It has a contractile diaphragm in front of the lens with a central opening called the pupil...
). Phenylephrine
Phenylephrine
Phenylephrine is a selective α1-adrenergic receptor agonist used primarily as a decongestant, as an agent to dilate the pupil, and to increase blood pressure...
(e.g. Cyclomydril) is used if strong mydriasis is needed for a surgical intervention. One effect of administration of a mydriatic is intolerance to bright light (Photophobia
Photophobia
Photophobia is a symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical photosensitivity of the eyes, though the term...
). Purposely-induced mydriasis via mydriatics is also used as a diagnostic test for Horner's Syndrome
Horner's syndrome
Horner's syndrome is the combination of drooping of the eyelid and constriction of the pupil , sometimes accompanied by decreased sweating of the face on the same side; redness of the conjunctiva of the eye is often also present...
.

