NGC 3079
Encyclopedia
NGC 3079 is a barred spiral galaxy
about 50 million
light-years away, and located in the constellation
Ursa Major
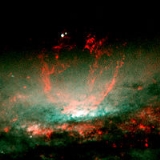
. A prominent feature of this galaxy is the "bubble" forming in the very center (see picture at right).
. This current bubble is thought to have been created about one million years ago, and computer modeling suggests that there is an ongoing cycle of forming bubbles, with a new bubble forming approximately every 10 million years.
Barred spiral galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies...
about 50 million
1 E23 m
To help compare different orders of magnitude, this page lists distances starting at 100 Zm .Distances shorter than 100 Zm* 140 Zm — 15 million light years — Distance to Centaurus A galaxy...
light-years away, and located in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Ursa Major
Ursa Major
Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April...
. A prominent feature of this galaxy is the "bubble" forming in the very center (see picture at right).
Center Bubble
The bubble forming in the center of NGC 3079 is believed to be about 3000 light-years wide and to rise more than 3500 light-years above the disc of the galaxy. It is speculated that the bubble is being formed by particles streaming at high speeds, which were in turn caused by a large burst of star formationStar formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
. This current bubble is thought to have been created about one million years ago, and computer modeling suggests that there is an ongoing cycle of forming bubbles, with a new bubble forming approximately every 10 million years.
External links
- HST: Burst of Star Formation Drives Bubble in Galaxy's Core
- Superwind Sculpts Filamentary Features - Chandra Space Telescope
- Astronomy Picture of the Day for August 22, 2001

