
NMR tube
Encyclopedia

Construction
NMR tubes are typically made of borosilicate glassBorosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with the main glass-forming constituents silica and boron oxide. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion , making them resistant to thermal shock, more so than any other common glass...
. They are available in seven and eight inch lengths; a 5 mm tube outer diameter is most common, but 3 mm and 10 mm outer diameters are available as well. Where boron NMR is desired, quartz NMR tubes containing low concentrations of boron (as opposed to borosilicate glass) are available. Specialized closures such as J. Young valves and screwcap closures are available aside from more common polyethylene caps.
Two common specifications for NMR tubes are concentricity and camber. Concentricity refers to the variation in the radial centers, measured at the inner and outer walls. Camber refers to the "straightness" of the tube. Poor values for either may cause poorer quality spectra by reducing the homogeneity of the sample. In particular, an NMR tube which has poor camber may wobble when rotated, giving rise to spinning side bands.
Sample preparation
The sample may be sonicated or agitated to aid dissolution, and solids are removed via filtering through a plug of celite in a Pasteur pipette
Pasteur pipette
Pasteur pipettes, also known as droppers or eye droppers, are used to transfer small quantities of liquids. They are usually glass tubes tapered to a narrow point, and fitted with a rubber bulb at the top. The combination of the Pasteur pipette and rubber bulb has also been referred to as a teat...
, directly into the NMR tube.
The NMR tube is then usually sealed with a polyethylene cap, but can be flame sealed or sealed with a Teflon 'Schlenk
Schlenk flask
A Schlenk flask, or Schlenk tube is a reaction vessel typically used in air sensitive chemistry, invented by Wilhelm Schlenk. It has a side arm fitted with a PTFE or ground glass stopcock which allows the vessel to be evacuated or filled with gases...
' tap or even a very small rubber septum
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
. Parafilm
Parafilm
Parafilm is a plastic paraffin film with a paper backing produced by Pechiney Plastic Packaging Company, based in Chicago, Illinois primarily used in laboratories. It is commonly used for sealing or protecting vessels...
may be wrapped around the cap to reduce solvent evaporation.
Shigemi tubes
A Shigemi tube is a microscale NMR tube used with an ordinary-size NMR tube. Shigemi tubes may be appropriate for protein NMR experiments, where only a smaller sample is available. A corresponding smaller solvent volume is desired to maintain a higher sample concentration. The reduced sample depth is compensated for by solid glass on the NMR tube beneath the level of sample, which varies for the make of spectrometer. Once air bubbles have been expelled, the plunger is secured to the tube proper by parafilm. Ideally, the tubes are matched with the deuterated solvent used to have better spectrum resolution.Cleaning

Cleaning is performed usually by rinsing with the same (non-deuterated) solvent used to dissolve the initial sample. Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a moderately sweet aroma is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is miscible with many organic solvents...
or acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
are good choices because dichloromethane is similar in polarity to chloroform, a common NMR solvent, while acetone dissolves many organic compounds. Sonication and scrubbing with a pipe cleaner
Pipe cleaner
A pipe cleaner or chenille stem is a type of brush originally intended for cleaning dottle from smoking pipes. Besides cleaning pipes, they can be used for any application that calls for cleaning out small bores or tight places. Special pipe cleaners are manufactured specifically for cleaning out...
may be helpful in removing traces of solid contaminants. If necessary, the tube may be filled with an oxidizing solution of aqua regia
Aqua regia
Aqua regia or aqua regis is a highly corrosive mixture of acids, fuming yellow or red solution, also called nitro-hydrochloric acid. The mixture is formed by freshly mixing concentrated nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, usually in a volume ratio of 1:3, respectively...
or piranha solution
Piranha solution
Piranha solution, also known as piranha etch, is a mixture of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide , used to clean organic residues off substrates...
(H2O2/H2SO4). Chromic acid
Chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the...
solutions are never used, due to traces of paramagnetic chromium left behind on the tubes causing interference with NMR experiments.
When the NMR tube is determined to be clean, it is triple-rinsed with distilled water, acetone, and left to air-dry or dry in an oven at high-temperature. It is best not to exceed 60 deg C. At higher temperatures, slight tube distortion can occur which will effect tube camber. If you wash NMR tubes, we recommend a final rinse with a solvent that easily evaporates at 60 deg C and that has no residue.
NMR tube cleaner
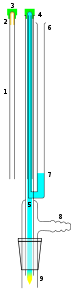
A better alternative to the use of potentially hazardous oxidizers is an NMR tube cleaner (left). It is an apparatus which uses a vacuum to flush solvent and/or a detergent solution through the entire length of the NMR tube.In this apparatus, the NMR tube 1 (with the cap 3 fixed to the base of the NMR tube), is placed upside down on the apparatus. The NMR tube fits over an inner tube 5 linked to the solvent reservoir 6. The NMR cap rests on the outer tube of the apparatus 4. A vacuum is applied (usually via a water aspirator via the vacuum inlet). The NMR tube cap forms a vacuum seal. Solvent 7 is drawn from the solvent reservoir 6 and is forced to the base of the NMR tube and flushes the NMR tube out 9 with solvent cleaning it. Note to complete the vacuum a flask is attached to the NMR tube cleaning apparatus.
This sort of apparatus is commercially available, though it is costly and easy to destroy by shattering or breaking off the cleaning tube. Equivalent designs may be assembled from ordinary labware as well.

