
Nabu
Encyclopedia

Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
and Babylonian god of wisdom
Wisdom
Wisdom is a deep understanding and realization of people, things, events or situations, resulting in the ability to apply perceptions, judgements and actions in keeping with this understanding. It often requires control of one's emotional reactions so that universal principles, reason and...
and writing
Writing
Writing is the representation of language in a textual medium through the use of a set of signs or symbols . It is distinguished from illustration, such as cave drawing and painting, and non-symbolic preservation of language via non-textual media, such as magnetic tape audio.Writing most likely...
, worshipped by Babylonians as the son of Marduk
Marduk
Marduk was the Babylonian name of a late-generation god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of the city of Babylon, who, when Babylon became the political center of the Euphrates valley in the time of Hammurabi , started to...
and his consort, Sarpanitum, and as the grandson of Ea. Nabu's consort was Tashmetum
Tashmetum
Tashmetum is an Akkadian goddess, the consort of the god Nabu....
.
Originally, Nabu was a West Semitic deity
Deity
A deity is a recognized preternatural or supernatural immortal being, who may be thought of as holy, divine, or sacred, held in high regard, and respected by believers....
introduced by the Amorites into Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, probably at the same time as Marduk shortly after 2000 BC. While Marduk became Babylon's main deity, Nabu resided in nearby Borsippa
Borsippa
Borsippa was an important ancient city of Sumer, built on both sides of a lake about southwest of Babylon on the east bank of the Euphrates. The site of Borsippa is in Babil Governorate, Iraq and now called Birs Nimrud, identifying the site with Nimrod...
in his temple E-zida. He was first called the "scribe and minister of Marduk", later assimilated as Marduk's beloved son from Sarpanitum. During the Babylonian New Year Festival, the cult statue of Nabu was transported from Borsippa to Babylon in order to commune with his father Marduk.
Nabu later became one of the principal gods in Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
and Assyrians addressed many prayers and inscriptions to Nabu and named children after him. Nabu was the god of writing and scribes and was the keeper of the Tablets of Destiny, in which the fate of humankind was recorded. He was also sometimes worshiped as a fertility god and as a god of water.
Nabu is accorded the office of patron of the scribes, taking over from the Sumerian goddess Nisaba. His symbols are the clay writing tablet with the writing stylus. He wears a horned cap, and stands with hands clasped, in the ancient gesture of priesthood. He rides on a winged dragon
Dragon
A dragon is a legendary creature, typically with serpentine or reptilian traits, that feature in the myths of many cultures. There are two distinct cultural traditions of dragons: the European dragon, derived from European folk traditions and ultimately related to Greek and Middle Eastern...
(mušhuššu, also known as Sirrush
Sirrush
The mušḫuššu is a creature depicted on the reconstructed Ishtar Gate of the city of Babylon, originally dating to the 6th century B.C. It is a mythological hybrid, a scaly dragon with hind legs like an eagle's talons and feline forelegs...
) that is initially Marduk's.
Triliteral
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or "radicals"...
nb´ for "to call or announce", meaning something like "He who has called".
His power over human existence is immense, because Nabu engraves the destiny
Destiny
Destiny or fate refers to a predetermined course of events. It may be conceived as a predetermined future, whether in general or of an individual...
of each person, as the gods have decided, on the tablets of sacred record. Thus, He has the power to increase or diminish, at will, the length of human life
Life
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes objects that have signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased , or else because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate...
.
Nabu is mentioned in the Nevi'im of the Tanakh as Nebo in .
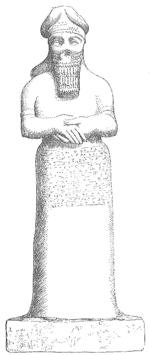
A statue of Nabu from Calah, erected during the reign of the Assyrian
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
king, Tiglath-pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III was a prominent king of Assyria in the eighth century BC and is widely regarded as the founder of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Tiglath-Pileser III seized the Assyrian throne during a civil war and killed the royal family...
is on display in the British Museum
British Museum
The British Museum is a museum of human history and culture in London. Its collections, which number more than seven million objects, are amongst the largest and most comprehensive in the world and originate from all continents, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its...
.
In late Babylonian astrology, Nabu was connected with the planet Mercury
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
. As the god of wisdom and writing, he was equated by the Greeks to either Apollo
Apollo
Apollo is one of the most important and complex of the Olympian deities in Greek and Roman mythology...
or Hermes
Hermes
Hermes is the great messenger of the gods in Greek mythology and a guide to the Underworld. Hermes was born on Mount Kyllini in Arcadia. An Olympian god, he is also the patron of boundaries and of the travelers who cross them, of shepherds and cowherds, of the cunning of thieves, of orators and...
, the latter identified by the Romans with their own god Mercury
Mercury (mythology)
Mercury was a messenger who wore winged sandals, and a god of trade, the son of Maia Maiestas and Jupiter in Roman mythology. His name is related to the Latin word merx , mercari , and merces...
.
In popular culture
- The DC Comics mystical character Doctor FateDoctor FateDoctor Fate is the name of a succession of fictional sorcerers who appear in books published by DC Comics. The original version was created by writer Gardner Fox and artist Howard Sherman, and first appeared in More Fun Comics #55...
receives his powers from a god-like being claiming to be the mythical "Nabu". - Nabu was the inspiration for the name of NabooNabooNaboo is a fictitious planet in the fictional Star Wars universe with a mostly green terrain and which is the homeworld of two societies: the Gungans who dwell in underwater cities and the humans who live in colonies on the surface...
in the Star WarsStar WarsStar Wars is an American epic space opera film series created by George Lucas. The first film in the series was originally released on May 25, 1977, under the title Star Wars, by 20th Century Fox, and became a worldwide pop culture phenomenon, followed by two sequels, released at three-year...
universe.

