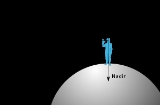
Nadir
Encyclopedia

Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface there. Since the concept of being below is itself somewhat vague, scientists define the nadir in more rigorous terms. Specifically, in astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, geophysics
Geophysics
Geophysics is the physics of the Earth and its environment in space; also the study of the Earth using quantitative physical methods. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and...
and related sciences (e.g., meteorology
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
), the nadir at a given point is the local vertical direction
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
pointing in the direction of the force of gravity
Gravitation
Gravitation, or gravity, is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract with a force proportional to their mass. Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped...
at that location. The direction opposite of the nadir is the zenith
Zenith
The zenith is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the imaginary celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the apparent gravitational force at that location. The opposite direction, i.e...
.
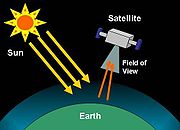
Nadir also refers to the downward-facing viewing geometry of an orbiting satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
, such as is employed during remote sensing of the atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
, as well as when an astronaut
Astronaut
An astronaut or cosmonaut is a person trained by a human spaceflight program to command, pilot, or serve as a crew member of a spacecraft....
faces the Earth while performing an EVA
Extra-vehicular activity
Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon...
.
The term nadir can also be used to represent the lowest point reached by a celestial body during its apparent orbit around a given point of observation. This can be used to describe the location of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, but it is only technically accurate for one latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
at a time and only possible at the low latitudes. The sun is said to be at the nadir at a location when it is at the zenith
Zenith
The zenith is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the imaginary celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the apparent gravitational force at that location. The opposite direction, i.e...
at the location's antipode
Antipodes
In geography, the antipodes of any place on Earth is the point on the Earth's surface which is diametrically opposite to it. Two points that are antipodal to one another are connected by a straight line running through the centre of the Earth....
.

