
Nanoshell
Encyclopedia
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
). These nanoshells involve a quasiparticle
Quasiparticle
In physics, quasiparticles are emergent phenomena that occur when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in free space...
called plasmon
Plasmon
In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. The plasmon is a quasiparticle resulting from the quantization of plasma oscillations just as photons and phonons are quantizations of light and mechanical vibrations, respectively...
which is a collective excitation or quantum plasma oscillation where the electrons simultaneously oscillate with respect to all the ions.
The simultaneous oscillation can be called plasmon hybridization where the tunability of the oscillation is associated with mixture of the inner and outer shell where they hybridize to give a lower energy or higher energy. This lower energy couples strongly to incident light whereas, the higher energy is an anti-bonding and weakly combines to incident light. The hybridization interaction is stronger for thinner shell layers, hence, the thickness of the shell and overall particle radius determines which wavelength of light it couples with. Nanoshells can be varied across a broad range of the light spectrum that spans the visible and near infrared regions. The interaction of light and nanoparticles affects the placements of charges which affects the coupling strength. Incident light polarized parallel to the substrate gives a s-polarization (Figure 1b), hence the charges are further from the substrate surface which gives a stronger interaction between the shell and core. Otherwise, a p-polarization is formed which gives a more strongly shifted plasmon energy causing a weaker interaction and coupling.
Synthesis
A nanoshell is synthesized in a multistep process :- Obtain gold nanoparticles in a solution (usually tetrachloroauric acidChloroauric acidChloroauric acid is a inorganic compound with the formula HAuCl4. This pale yellow compound is a common precursor to gold in a variety of purposes. The term chloroauric acid is also sometimes used to describe other gold chlorides....
and a reducing agent)- This solution phase synthesis of the gold nanoparticles uses a reduction using tetrachloroauric acid by a reducing agent. There are several different reducing agents used and all can greatly affect the uniformity of the nanoparticle.
- Attach a very small seed colloid onto the dielectric nanoparticles (such as: zinc selenideZinc selenideZinc selenide , is a light yellow binary solid compound. It is an intrinsic semiconductor with a band gap of about 2.70 eV at 25 °C. ZnSe rarely occurs in nature...
, sapphireSapphireSapphire is a gemstone variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide , when it is a color other than red or dark pink; in which case the gem would instead be called a ruby, considered to be a different gemstone. Trace amounts of other elements such as iron, titanium, or chromium can give...
, and glassGlassGlass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
) giving a discontinuous shell - Grow a continuous shell by using a chemical reduction of the metal attached to the dielectric nanoparticles
If a uniform shell is not obtained then it can greatly affect the optical properties of the nanoshell. A good example of this is a nanoegg, which is a metallic nanoshell that has a nonuniform thickness. This characteristic nonuniformity causes additional hybridized plasmon resonances in the spectrum making the coupling not as effective.
Applications
Since nanoshells possess highly favorable optical and chemical properties it is often used for biomedical imaging, therapeutic applications, fluorescence enhancement of weak molecular emitters, surface enhanced Raman spectroscopySurface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy or surface enhanced Raman scattering is a surface-sensitive technique that enhances Raman scattering by molecules adsorbed on rough metal surfaces...
and surface enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy.
Cancer Treatment
Gold nanoshells are shuttled into tumors by the use of phagocytosis where phagocytes engulf the nanoshells through the cell membrane to form an internal phagosome, or macrophage. After this it is shuttled into a cell and enzymes are usually used to metabolize it and shuttle it back out of the cell. These nanoshells are not metabolized so for them to be effective they just need to be within the tumor cells and photoinduced cell death is used to terminate the tumor cells. This scheme is shown in Figure 2.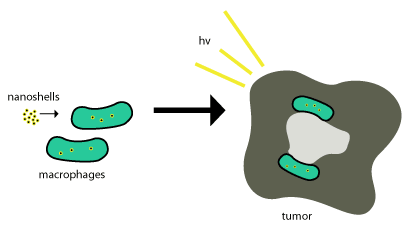
This process works so well since tumors are about ¾ macrophages and once monocytes are brought into the tumor, it differentiates into macrophages which would also be need to maintain the cargo nanoparticles. Once the nanoshells are at the necrotic center, near-infrared illumination is used to destroy the tumor associated macrophages.

