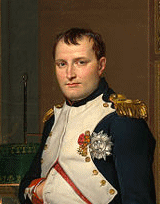
.
As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French
from 1804 to 1815. His legal reform, the Napoleonic Code
, has been a major influence on many civil law
jurisdictions worldwide, but he is best remembered for his role in the wars led against France by a series of coalitions, the so-called Napoleonic Wars
.
1795 General Napoleon Bonaparte first rises to national prominence being named to defend the French National Convention against armed counter-revolutionary rioters threatening the three year old revolutionary government.
1795 Napoleon Bonaparte first rises to national prominence with a "Whiff of Grapeshot", using cannon to suppress armed counter-revolutionary rioters threatening the French Legislature (National Convention).
1796 Napoléon Bonaparte marries his first wife, Joséphine de Beauharnais.
1796 The Armistice of Cherasco is signed by Napoleon Bonaparte and Vittorio Amedeo III, the King of Sardinia, expanding French territory along the Mediterranean coast.
1796 First Coalition: Napoleon I of France wins a decisive victory against Austrian forces at Lodi bridge over the Adda River in Italy. The Austrians lose some 2,000 men.
1796 First Coalition: Napoleon enters Milan in triumph.
1797 First Coalition: Napoleon I of France conquers Venice.
1799 Napoleon Bonaparte captures Jaffa in Palestine and his troops proceed to kill more than 2,000 Albanian captives.
1799 At Aboukir in Egypt, Napoleon I of France defeats 10,000 Ottomans under Mustafa Pasha.
1799 Napoleon leaves Egypt for France en route to seize power.

