
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
Encyclopedia

United States Department of Transportation
The United States Department of Transportation is a federal Cabinet department of the United States government concerned with transportation. It was established by an act of Congress on October 15, 1966, and began operation on April 1, 1967...
. It describes its mission as “Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes.”
As part of its activities, NHTSA is charged with writing and enforcing safety, theft-resistance, and fuel economy
Fuel economy in automobiles
Fuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
standards for motor vehicle
Motor vehicle
A motor vehicle or road vehicle is a self-propelled wheeled vehicle that does not operate on rails, such as trains or trolleys. The vehicle propulsion is provided by an engine or motor, usually by an internal combustion engine, or an electric motor, or some combination of the two, such as hybrid...
s, the latter under the rubric of the Corporate Average Fuel Economy
Corporate Average Fuel Economy
The Corporate Average Fuel Economy are regulations in the United States, first enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1975, and intended to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks sold in the US in the wake of the 1973 Arab Oil Embargo...
(CAFE) system. NHTSA also licenses vehicle manufacturers and importers, allows or blocks the import of vehicles and safety-regulated vehicle parts, administers the vehicle identification number
Vehicle identification number
A Vehicle Identification Number, commonly abbreviated to VIN, is a unique serial number used by the automotive industry to identify individual motor vehicles. VINs were first used in 1954...
(VIN) system, develops the anthropomorphic dummies
Crash test dummy
Crash test dummies are full-scale anthropomorphic test devices that simulate the dimensions, weight proportions and articulation of the human body, and are usually instrumented to record data about the dynamic behavior of the ATD in simulated vehicle impacts...
used in safety testing, as well as the test protocols themselves, and provides vehicle insurance
Insurance
In law and economics, insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from one entity to another, in exchange for payment. An insurer is a company selling the...
cost information. The agency has asserted preemptive regulatory authority over greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions, but this has been disputed by such state regulatory agencies as the California Air Resources Board
California Air Resources Board
The California Air Resources Board, also known as CARB or ARB, is the "clean air agency" in the government of California. Established in 1967 in the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Motor Vehicle Pollution Control Board, CARB is a department within the...
.
Another of NHTSA’s major activities is the creation and maintenance of the data files maintained by the National Center for Statistics and Analysis. In particular, the Fatality Analysis Reporting System
Fatality Analysis Reporting System
Fatality Analysis Reporting System was created in the United States by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to provide an overall measure of highway safety, to help suggest solutions, and to help provide an objective basis to evaluate the effectiveness of motor vehicle safety...
(FARS), has become a resource for traffic safety research not only in the United States, but throughout the world. Research contributions using FARS by researchers from many countries appear in many non-U.S. technical publications, and provide a significant database and knowledge bank on the subject. Even with this database, conclusive analysis of crash causes often remains difficult and controversial, with experts debating the veracity and statistical validity of results.
History
In 1965 and 1966, public pressure grew in the U.S. to increase the safety of carsCar safety
Automobile safety is the study and practice of vehicle design, construction, and equipment to minimize the occurrence and consequences of automobile accidents. Automobile safety is the study and practice of vehicle design, construction, and equipment to minimize the occurrence and consequences of...
, culminating with the publishing of Unsafe at Any Speed
Unsafe at Any Speed
Unsafe at Any Speed: The Designed-In Dangers of the American Automobile by Ralph Nader, published in 1965, is a book detailing resistance by car manufacturers to the introduction of safety features, like seat belts, and their general reluctance to spend money on improving safety...
, by Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader is an American political activist, as well as an author, lecturer, and attorney. Areas of particular concern to Nader include consumer protection, humanitarianism, environmentalism, and democratic government....
, an activist lawyer, and the National Academy of Sciences
United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences is a corporation in the United States whose members serve pro bono as "advisers to the nation on science, engineering, and medicine." As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and...
' "Accidental Death and Disability—The Neglected Disease of Modern Society".
In 1966, Congress held a series of highly publicized hearings regarding highway safety, passed legislation to make installation of seat belts mandatory, and enacted Public Law 89-563, Public Law 89-564, and Public Law 89-670 which created the U.S. Department of Transportation on October 15, 1966). This legislation created several predecessor agencies which would eventually become NHTSA, including the National Traffic Safety Agency, the National Highway Safety Agency, and the National Highway Safety Bureau. Once the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) came into effect, vehicles not certified by the maker or importer as compliant with US safety standards were no longer legal to import into the United States.
NHTSA was officially established in 1970 by the Highway Safety Act of 1970. In 1972, the Motor Vehicle Information and Cost Savings Act expanded NHTSA's scope to include consumer information programs. Since then, automobiles have become far better in protecting their occupants in vehicle impacts. The number of deaths on American highways hovers around 40,000 annually, a lower death rate per vehicle-mile travelled than in the 1960s.
NHTSA has conducted numerous high-profile investigations of automotive safety issues, including the Audi 5000/60 Minutes
Audi 100
The restyled C2 Audi 100 was launched in 1976, with an in-line five-cylinder engine...
affair, the Ford Explorer
Ford Explorer
The Ford Explorer is a sport-utility vehicle sold in North America and built by the Ford Motor Company since 1990, as a replacement for the smaller but related Ford Bronco II. It is manufactured in Chicago, Illinois...
rollover
Rollover
A rollover is a type of vehicle accident in which a vehicle tips over onto its side or roof. The most common cause of a rollover is traveling too fast while turning.- Dynamics :Vehicles can roll over in several ways...
problem and the Toyota: Sticky accelerator pedal problem. The agency has introduced a proposal to mandate Electronic Stability Control
Electronic Stability Control
Electronic stability control is a computerized technology that may potentially improve the safety of a vehicle's stability by detecting and minimizing skids. When ESC detects loss of steering control, it automatically applies the brakes to help "steer" the vehicle where the driver intends to go...
on all passenger vehicles by the 2012 model year. This technology was first brought to public attention in 1997, with the Swedish moose test
Moose test
A moose test or elk test is a test to determine how a certain vehicle acts when the driver evades a suddenly appearing obstacle...
.
Consumers today have a far greater amount of auto safety information available, due to the efforts of NHTSA and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety is a U.S. non-profit organization funded by auto insurers, established in 1959 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It works to reduce the number of motor vehicle crashes, and the rate of injuries and amount of property damage in the crashes that...
.
Versus international consensus
In 1958, under the auspices of the United NationsUnited Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
, a consortium called the Economic Commission for Europe had been established to commonize vehicle regulations across Europe so as to standardize best practices in vehicle design and equipment and minimize technical barriers to pan-European vehicle trade and traffic. This eventually became the World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
, which began to promulgate what would eventually become the UN's ECE Regulations on vehicle design, construction, and safety performance. Although most of the world's countries accept or require ECE-compliant vehicles—either as official signatories to ECE regulations or by national regulations effectively identical to ECE—the United States, virtually alone in the world, has declined to join the forum or accept ECE regulations, and blocks the importation of vehicles built to international ECE Regulations rather than the U.S. safety regulations.
Because of the unavailability in America of certain vehicle models, a grey market
Grey import vehicles
Grey import vehicles are new or used motor vehicles and motorcycles legally imported from another country through channels other than the maker's official distribution system...
arose in the late 1970s. This provided an alternate, legal method to acquire vehicles only sold overseas. The success of the grey market, however, ate into the business of Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz is a German manufacturer of automobiles, buses, coaches, and trucks. Mercedes-Benz is a division of its parent company, Daimler AG...
of North America Inc., which launched a successful congressional
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
lobbying
Lobbying
Lobbying is the act of attempting to influence decisions made by officials in the government, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying is done by various people or groups, from private-sector individuals or corporations, fellow legislators or government officials, or...
effort to eliminate this alternative for consumers in 1988, despite the lack of any evidence suggesting grey-market vehicles were less safe than those built to comply with U.S. regulations. As a result, it is no longer possible to import foreign vehicles into the United States as a personal import, with few exceptions—primarily Canadian cars with safety regulations substantially similar to the United States, and vehicles imported temporarily for display or research purposes. In practice the gray market involved a few thousand luxury cars annually,before its virtual elimination in 1988.
In 1998, NHTSA exempted vehicles older than 25 years from the rules it administers, since these are presumed to be collector vehicles. In 1999, certain very low production volume specialist vehicles were also exempt for "Show and Display
Show and Display
The "Show and Display" rule, introduced by the United States federal National Highway Traffic Safety Administration in 1999, made it legal for car collectors to import cars for use in their private collections that would otherwise not be street legal in the United States...
" purposes. However, the ban on newer vehicles considered safe in countries with lower vehicle-related death rates has led some to claim that the main effect of NHTSA's regulatory activity is to protect the U.S. market for a modified oligopoly consisting of the three U.S.-based automakers and the American operations of foreign-brand producers. It has been suggested that the impetus for NHTSA's seeming preoccupation with market control rather than vehicular safety performance is a result of overt market protections such as tariffs and local-content laws having become politically unpopular due to the increasing popularity of free trade
Free trade
Under a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
. This has driven U.S. industry to adopt less visible forms of trade restrictions
Non-tariff barriers to trade
Non-tariff barriers to trade are trade barriers that restrict imports but are not in the usual form of a tariff. Some common examples of NTB's are anti-dumping measures and countervailing duties, which, although they are called "non-tariff" barriers, have the effect of tariffs once they are...
in the form of technical regulations different but demonstrably not superior to those outside the United States.
An example of the market-control effects of NHTSA's regulatory protocol is found in the agency's 1974 banning
Criminalization
Criminalization or criminalisation, in criminology, is "the process by which behaviors and individuals are transformed into crime and criminals". Previously legal acts may be transformed into crimes by legislation or judicial decision...
of the Citroën SM automobile, which contemporary journalists noted was one of the safest vehicles available at the time. NHTSA disapproved the SM due to its high-performance, low-glare, steerable headlamps which were not of the outmoded sealed beam
Sealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
design mandatory in the U.S., and its height adjustable suspension
Height adjustable suspension
Height adjustable suspension is a feature of certain automobile suspension systems that allow the motorist to vary the ride height or ground clearance. This can be done for various reasons including giving better ground clearance over rough terrain, a lower ground clearance to improve fuel economy...
, which made compliance with the 1973 bumper requirements impossible; the bumper regulation was intended to control the costs resulting from low speed collisions, not enhance occupant safety.
Regulatory performance
In the mid 1960s when the framework was established for US vehicle safety regulations, the US auto market was an oligopolyOligopoly
An oligopoly is a market form in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of sellers . The word is derived, by analogy with "monopoly", from the Greek ὀλίγοι "few" + πόλειν "to sell". Because there are few sellers, each oligopolist is likely to be aware of the actions of the others...
, with just three companies (GM
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
, Ford
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
, and Chrysler) controlling 85% of the market. At that time, the United States had safer traffic than any country in the world, whether measured by the number of traffic deaths per thousand vehicles, or the number of traffic deaths per 100 million miles.
The Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards are contained in the United States Code of Federal Regulations
Code of Federal Regulations
The Code of Federal Regulations is the codification of the general and permanent rules and regulations published in the Federal Register by the executive departments and agencies of the Federal Government of the United States.The CFR is published by the Office of the Federal Register, an agency...
, Title 49, Part 571. This is commonly referred to as 49CFR571, with any particular FMVSS appended after a period, as for example 49CFR571.301—the location of FMVSS 301. Additional federal vehicle standards are contained elsewhere in the CFR. For instance, 49CFR564 contains the specifications and requirements for the various types of replaceable headlamp
Headlamp
A headlamp is a lamp, usually attached to the front of a vehicle such as a car or a motorcycle, with the purpose of illuminating the road ahead during periods of low visibility, such as darkness or precipitation. Headlamp performance has steadily improved throughout the automobile age, spurred by...
"light source" (bulb). FMVSS 209 was the first standard to become effective on March 1, 1967.
Although a system of uniform auto safety performance and equipment regulations (ECE Regulations) had been in place in Europe since 1958, the United States did not seek to adopt or harmonize with these ECE regulations, which have since been adopted by virtually all industrialized countries outside North America. Compared to the ECE regulations, American regulations are fundamentally different in philosophy, content, emphasis, and enforcement protocol. Vehicles conforming to the internationalized (originally European) ECE regulations are allowed or required throughout the entire rest of the world, but such vehicles are illegal in the United States.
Despite the evolution of the North American auto market to include most of the world's major automakers, and the ongoing proliferation of U.S. safety regulations, the previously-existing market oligopoly still exerts strong influence: American vehicle equipment and construction regulations are based almost entirely on Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standards, which were written almost entirely by U.S. automakers.
In a 2004 book by former General Motors safety researcher Leonard Evans, government data (FARS for the U.S.) showed other countries achieving safety performance improvements over time greater than those achieved by the United States:
1979 Fatalities
2002 Fatalities
Percent Change
United States
51,093
42,815
-16.2%
Great Britain
6,352
3,431
-46.0%
Canada
5,863
2,936
-49.9%
Australia
3,508
1,715
-51.1%
Research on the trends in use of heavy vehicles indicate that a significant difference between the U.S. and other countries is the relatively high prevalence of pickup trucks and SUVs in the U.S. A 2003 study by the U.S. Transportation Research Board
Transportation Research Board
The Transportation Research Board is a division of the National Research Council, which serves as an independent adviser to the President, the Congress and federal agencies on scientific and technical questions of national importance...
found that SUVs and pickup trucks are significantly less safe than passenger cars, that imported-brand vehicles tend to be safer than American-brand vehicles, and that the size and weight of a vehicle has a significantly smaller effect on safety than the quality of the vehicle's engineering. Comparisons of past data with the present in the U.S. can result in distortions, due to a significant population increase
Demographics of the United States
As of today's date, the United States has a total resident population of , making it the third most populous country in the world. It is a very urbanized population, with 82% residing in cities and suburbs as of 2008 . This leaves vast expanses of the country nearly uninhabited...
and since the level of large commercial truck traffic has substantially increased from the 1960s while highway capacity has not kept pace with the increase in large commercial truck traffic on U.S. highways. However, other factors exert significant influence; Canada has lower roadway death and injury rates despite a vehicle mix comparable to that of the U.S. Nevertheless, the widespread use of truck-based vehicles as passenger carriers is correlated with roadway deaths and injuries not only directly by dint of vehicular safety performance per se, but also indirectly through the relatively low fuel costs that facilitate the use of such vehicles in North America. Motor vehicle fatalities decline as gasoline prices increase. NHTSA has issued few regulations in the past 25 years.
Most of the reduction in vehicle fatality rates during the last third of the 20th Century were gained from the initial NHTSA safety standards during 1968–1984 and subsequent voluntary changes in vehicle crashworthiness by vehicle manufacturers.
Cost/benefit requirements
There are nominally strict cost-benefit ratio requirements for every safety device, system, or design feature NHTSA mandates for installation on vehicles. That is, the device, system, or design feature may not be made mandatory unless it will save more money (in property damage, health care, etc.) than it costs, or must cost no more than a specified amount of money per life saved. Such requirements may be subject to manipulation of estimated costs and estimated benefits to justify or reject almost any standard; FMVSS #208 effectively mandates the installation of frontal airbags in all new vehicles in the United States, for it is written such that no other technology can meet the stipulated requirements. It has been argued that even using conservative cost figures and optimistic benefit figures, airbags' cost-benefit ratio so extreme that it may fall outside of the cost-benefit requirements for mandatory safety devices. These same cost-benefit requirements have been used as the basis for Lighting-relatedAutomotive lighting
The lighting system of a motor vehicle consists of lighting and signalling devices mounted or integrated to the front, sides, rear, and in some cases the top of the motor vehicle...
lags in American regulations; for example, virtually every country in the world has since at least the early 1970s required rear turn signals to emit amber light so they can immediately be discerned from adjacent red brake lamps. U.S. regulations still permit rear turn signals to emit red light on grounds of cost-effectiveness despite NHTSA research showing amber rear turn signals instead of red ones give a larger crash-avoidance benefit than the 3rd brake light.
Regulations
NHTSA also administers the controversial Corporate Average Fuel EconomyCorporate Average Fuel Economy
The Corporate Average Fuel Economy are regulations in the United States, first enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1975, and intended to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks sold in the US in the wake of the 1973 Arab Oil Embargo...
(CAFE), which is intended to incentivize the production of fuel-efficient vehicles by dint of fuel economy requirements measured against the sales-weighted average of each manufacturer's range of vehicles. The Wall Street Journal
The Wall Street Journal
The Wall Street Journal is an American English-language international daily newspaper. It is published in New York City by Dow Jones & Company, a division of News Corporation, along with the Asian and European editions of the Journal....
and others argue this program forces people to buy smaller, lighter, less-safe vehicles. CAFE may be a driving factor behind the explosion in demand for SUV
Sport utility vehicle
A sport utility vehicle is a generic marketing term for a vehicle similar to a station wagon, but built on a light-truck chassis. It is usually equipped with four-wheel drive for on- or off-road ability, and with some pretension or ability to be used as an off-road vehicle. Not all four-wheel...
s, which are considered "light trucks" for CAFE purposes and therefore are not required to meet the stricter standards for vehicles classified as "cars." Many governments outside North America regulate fuel economy by heavily taxing motor fuel and/or by including a vehicle's engine size or fuel economy in calculating vehicle registration taxes. It is argued that such regulations are not politically feasible, and that doing so would hurt the struggling U.S. auto industry. Another putative problem with CAFE is that fuel economy is negatively correlated to vehicle weight—lighter vehicles giving better fuel economy—while vehicle weight is positively correlated to safety—larger and heavier vehicles better protect their occupants. Thus, NHTSA must accomplish two potentially contradictory regulatory goals at the same time. However, Transportation Research Board
Transportation Research Board
The Transportation Research Board is a division of the National Research Council, which serves as an independent adviser to the President, the Congress and federal agencies on scientific and technical questions of national importance...
studies show safety disparities may exist among vehicles of differing price, country of origin, and quality not just among vehicles of different size and weight alone. Some other researchers dispute the incompatibility of reduction in vehicle weight and increased fuel economy.
Performance
NHTSA's Summary of Fuel Economy Performance, ranks automakers according to their CAFE:- LotusLotus CarsLotus Cars is a British manufacturer of sports and racing cars based at the former site of RAF Hethel, a World War II airfield in Norfolk. The company designs and builds race and production automobiles of light weight and fine handling characteristics...
: 30.2 mpgus - Toyota: 29.69 mpgus
- HondaHondais a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
: 29.47 mpgus - HyundaiHyundaiHyundai ) is a global conglomerate company, part of the Korean chaebol, that was founded in South Korea by one of the most famous businessmen in Korean history: Chung Ju-yung...
: 29.39 mpgus - KiaKia MotorsKia Motors , headquartered in Seoul, is South Korea's second-largest automobile manufacturer, following the Hyundai Motor Company, with sales of over 1.4 million vehicles in 2010...
: 28.44 mpgus - SubaruSubaru; is the automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate Fuji Heavy Industries .Subaru is internationally known for their use of the boxer engine layout popularized in cars by the Volkswagen Beetle and Porsche 911, in most of their vehicles above 1500 cc as well as...
: 28.11 mpgus - Nissan: 27.64 mpgus
- VW: 27.38 mpgus
- SuzukiSuzukiis a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Hamamatsu, Japan that specializes in manufacturing compact automobiles and 4x4 vehicles, a full range of motorcycles, all-terrain vehicles , outboard marine engines, wheelchairs and a variety of other small internal combustion engines...
: 27.08 mpgus - BMWBMWBayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
: 26.76 mpgus - MitsubishiMitsubishiThe Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy...
: 26.67 mpgus - GMGeneral MotorsGeneral Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
: 25.16 mpgus - Ford: 25.15 mpgus
- Daimler Chrysler: 23.97 mpgus
Aerodynamics brings change to NHTSA
Automakers faced an inherent conflict between NHTSA's stringent headlight legislation, which froze U.S. headlight technology in 1940, and the Corporate Average Fuel EconomyCorporate Average Fuel Economy
The Corporate Average Fuel Economy are regulations in the United States, first enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1975, and intended to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks sold in the US in the wake of the 1973 Arab Oil Embargo...
standard, which effectively mandated that automakers develop ways to improve the ability of the car to cleave the air. As a result, in the early 1980s, automakers lobbied for a modification of the mandate for fixed shape sealed-beam headlamp
Headlamp
A headlamp is a lamp, usually attached to the front of a vehicle such as a car or a motorcycle, with the purpose of illuminating the road ahead during periods of low visibility, such as darkness or precipitation. Headlamp performance has steadily improved throughout the automobile age, spurred by...
s.
NHTSA adopted Ford's
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
proposal for low-cost aerodynamic headlamps with polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
lenses and transverse-filament bulbs.
For the 1984 model year
Model year
The model year of a product is a number used worldwide, but with a high level of prominence in North America, to describe approximately when a product was produced, and indicates the coinciding base specification of that product....
, Ford introduced the Lincoln Mark VII, the first car since 1939 to be sold in the U.S. market with architectural headlamps as part of its aerodynamic design. These composite headlamps, when new to the American market, were commonly but improperly referred to as "Euro" headlamps, since aerodynamic headlamps were already common in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Though conceptually similar to European headlamps with nonstandardized shape and replaceable-bulb construction, these headlamps conform to the SAE headlamp design standards contained in U.S. Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
, and not to the international safety standards used worldwide outside North America.
Consistent with allowing automobile designers appropriate levels of freedom to do their work, the minimum allowed performance and materials durability requirements of this new headlamp system were actually lower than those of the old sealed beam
Sealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
system.
NCAP

The first standardized, 35 mph front crash test was May 21, 1979, and the first results were released October 15 that year.
The agency established a frontal impact test protocol based on Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208 (“Occupant Crash Protection”), except that the frontal 4 NCAP test is conducted at 56 km/h (35 mph), rather than 48 km/h (30 mph) as required by FMVSS No. 208.
More recently, in an effort to improve the dissemination of NCAP ratings and as a result of the Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users (SAFETEA–LU) the agency has issued a Final Rule requiring manufacturers to place NCAP star ratings on the Monroney sticker
Monroney sticker
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. Since the mid-seventies the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency provides fuel economy metrics in the label...
(automobile price sticker). The rule has a September 1, 2007 compliance date.
Administration
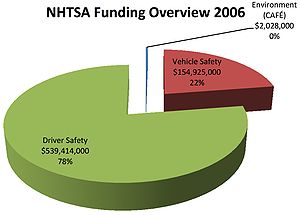
On April 9, 2009, President Barack Obama nominated Chuck Hurly, Chief Executive Officer of Mothers Against Drunk Driving, to be the next NHTSA Administrator. In addition to drunk driving, his areas of expertise include air bag, seat belt, teen driving, and child safety. David Strickland is the Administrator, appointed in 2010.
See also
- The Century CouncilThe Century CouncilThe Century Council is a Virginia-based American not-for-profit organization founded in 1991 and funded by a group of distillers that aims to fight to eliminate drunk driving and underage drinking and promotes responsible decision-making regarding alcohol use....
- Crash testCrash testA crash test is a form of destructive testing usually performed in order to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness and crash compatibility for various modes of transportation or related systems and components.- Types :...
- Euro NCAP
- Fatality Analysis Reporting SystemFatality Analysis Reporting SystemFatality Analysis Reporting System was created in the United States by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to provide an overall measure of highway safety, to help suggest solutions, and to help provide an objective basis to evaluate the effectiveness of motor vehicle safety...
- Fuel economy in automobilesFuel economy in automobilesFuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
- Insurance Institute for Highway SafetyInsurance Institute for Highway SafetyThe Insurance Institute for Highway Safety is a U.S. non-profit organization funded by auto insurers, established in 1959 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It works to reduce the number of motor vehicle crashes, and the rate of injuries and amount of property damage in the crashes that...
- Intelligent Transportation Systems InstituteIntelligent Transportation Systems InstituteThe Intelligent Transportation Systems Institute is a national University Transportation Center headquartered at the University of Minnesota. The ITS Institute researches activities to enhance the safety and mobility of road-based and transit-based transportation, particularly in a northern...
- National Transportation Safety BoardNational Transportation Safety BoardThe National Transportation Safety Board is an independent U.S. government investigative agency responsible for civil transportation accident investigation. In this role, the NTSB investigates and reports on aviation accidents and incidents, certain types of highway crashes, ship and marine...
- Not Invented HereNot Invented HereNot invented here is a term used to describe persistent social, corporate, or institutional culture that avoids using or buying already existing products, research, standards, or knowledge because of their external origins. It is normally used in a pejorative sense, and may be considered an...
syndrome - Road-traffic safetyRoad-traffic safetyThe term road traffic safety is about the risk of a person being killed or seriously injured while using the road network as a pedestrian, cyclist, motorist or user of on road public transport...
- UNECE
- Vehicle inspectionVehicle inspectionVehicle inspection is a procedure mandated by national or subnational governments in many countries, in which a vehicle is inspected to ensure that it conforms to regulations governing safety, emissions, or both. Inspection can be required at various times, e.g., periodically or on transfer of...
- World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle RegulationsWorld Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle RegulationsThe World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
Further reading
- Kevin M. McDonald, "Shifting Out of Park: Moving Auto Safety from Recalls to Reason" (Lawyers & Judges Publishing, 2006).
- The Century CouncilThe Century CouncilThe Century Council is a Virginia-based American not-for-profit organization founded in 1991 and funded by a group of distillers that aims to fight to eliminate drunk driving and underage drinking and promotes responsible decision-making regarding alcohol use....
's Report on Alcohol-Related Traffic Fatalities in the United States (2006)
External links
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration website, U.S. Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, Definitions
- safercar.gov—Official ratings, tips, and recalls
- Regulations regarding vehicle importation into the U.S.
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS)
- Definitions
- http://www.nhtsa.dot.gov/portal/site/nhtsa/template.MAXIMIZE/menuitem.4759a5f928566706e93305d546108a0c/?javax.portlet.tpst=4427b997caacf504a8bdba101891ef9a_ws_MX&javax.portlet.prp_4427b997caacf504a8bdba101891ef9a_viewID=detail_view&javax.portlet.begCacheTok=com.vignette.cachetoken&javax.portlet.endCacheTok=com.vignette.cachetoken&itemID=4aedfb9a5afd0110VgnVCM1000002c567798RCRD&viewType=standardSafety testing]
- U.S. Appeals Court Orders New Fuel Economy Standards
- UNECE vehicle safety regulations
- Peltzman, Sam. "The Effects of Automobile Safety Regulation." The Journal of Political Economy 83, no. 4 (August 1975): 677-725. JSTOR link

