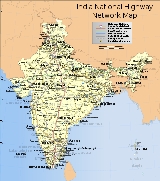
National Highways Development Project
Encyclopedia
The National Highways Development Project is a project to upgrade, rehabilitate and widen major highways in India
to a higher standard. The project was implemented in 1998. "National Highways
" account for only about 2% of the total length of roads, but carry about 40% of the total traffic across the length and breadth of the country. This project is managed by the National Highways Authority of India
under the Ministry of Road, Transport and Highways. The NHAI has implemented US$ 71 billion for this project, as of 2006.
Note: 1 crore= 10 million
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
to a higher standard. The project was implemented in 1998. "National Highways
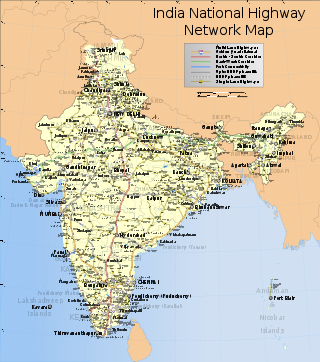
Indian highways
The National Highways Network of India, is a network of highways that is managed and maintained by agencies of the Government of India. These highways measured over as of 2010, including over of limited-access Expressways....
" account for only about 2% of the total length of roads, but carry about 40% of the total traffic across the length and breadth of the country. This project is managed by the National Highways Authority of India
National Highways Authority of India
The National Highways Authority of India is an autonomous agency of the Government of India, responsible for management of a network of over 60,000 km of National Highways in India...
under the Ministry of Road, Transport and Highways. The NHAI has implemented US$ 71 billion for this project, as of 2006.

Phases
The project is composed of the following phases:- Phase I: The Golden QuadrilateralGolden QuadrilateralThe Golden Quadrilateral is a highway network connecting India's four largest metropolises: Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata, thus forming a quadrilateral of sorts. Four other top ten metropolises: Bangalore, Pune, Ahmedabad, and Surat, are also served by the network...
(GQ; 5,846 km) connecting the four major cities of DelhiDelhiDelhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
, MumbaiMumbaiMumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
, ChennaiChennaiChennai , formerly known as Madras or Madarasapatinam , is the capital city of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, located on the Coromandel Coast off the Bay of Bengal. Chennai is the fourth most populous metropolitan area and the sixth most populous city in India...
and KolkataKolkataKolkata , formerly known as Calcutta, is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located on the east bank of the Hooghly River, it was the commercial capital of East India...
. This project connecting four metro cities, would be 5846 km (3,632.5 mi). Total cost of the project is Rs.300 billion (US$6.8 billion), funded largely by the government’s special petroleum product tax revenues and government borrowing. As of February 2011 the project is almost complete, with 5821 km (3,617 mi) of the intended 5846 km (3,632.5 mi) having been 4 laned.
- Phase II: North-South and East-West corridors comprising national highways connecting four extreme points of the country. The North-South and East-West CorridorNorth-South and East-West CorridorThe North-South–East-West Corridor is the largest ongoing highway project in India. It is the second phase of the National Highways Development Project , and consists of building 7300 kilometers of four/six lane expressways connecting Srinagar, Kanyakumari, Porbandar and Silchar, at a cost of...
(NS-EW; 7,300 km) connecting SrinagarSrinagarSrinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
in the north to Kanyakumari in the south, including spur from Salem to KanyakumariKanyakumariKanyakumari is a town in the state of Tamil Nadu in India. It is also sometimes referred to as Cape Comorin. Located at the southernmost tip of the Indian Peninsula, it is the geographical end of the Indian mainland. The district in Tamil Nadu where the town is located is called Kanyakumari...
(Via CoimbatoreCoimbatoreCoimbatore , also known as Kovai , is the second largest city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is a major commercial centre in Tamil Nadu and is known as the "Manchester of South India"....
and KochiKochi-Places:* Kochi, a city in the state of Kerala, India, formerly known as Cochin* Kingdom of Cochin, a former feudal city-state on Malabar Coast, India** Fort Kochi, one of the three main urban components which constitute the present day city of Kochi, Kerala, India...
) and SilcharSilcharSilchar is the headquarters of Cachar district in the state of Assam in India. It is the economic gateway to the state of Mizoram and part of Manipur. It is south east of Guwahati. The city of Silchar has tremendous commercial importance and is the second largest city in the state of Assam...
in the east to PorbandarPorbandarPorbandar is a coastal city in the Indian state of Gujarat, perhaps best known for being the birthplace of Mahatma Gandhi and Sudama...
in the west. Total length of the network is 7300 km (4,536 mi). As of August 2011, 79.4% of the project had been completed and 12.7% of the project work is currently at progress. It also includes Port connectivity and other projects — 1157 km (718.9 mi). The final completion date to February 28, 2009 at a cost of Rs.350 billion (US$8 billion), with funding similar to Phase I.
- Phase III: The government recently approved NHDP-III to upgrade 12109 km (7,524.2 mi)of national highways on a Build, Operate and Transfer (BOT) basis, which takes into account high-density traffic, connectivity of state capitals via NHDP Phase I and II, and connectivity to centres of economic importance. contracts have been awarded for a 2075 km (1,289.3 mi).
- Phase IV: The government is considering widening 20000 km (12,427.5 mi) of highway that were not part of Phase I, II, or III. Phase IV will convert existing single lane highways into two lanes with paved shoulders. The plan will soon be presented to the government for approval.
- Phase V: As road traffic increases over time, a number of four lane highways will need to be upgraded/expanded to six lanes. The current plan calls for upgrade of about 5000 km (3,106.9 mi) of four-lane roads, although the government has not yet identified the stretches.
- Phase VI: The government is working on constructing expressways that would connect major commercial and industrial townships. It has already identified 400 km (248.5 mi) of Vadodara (earlier Baroda)-Mumbai section that would connect to the existing Vadodara (earlier Baroda)-Ahmedabad section. The World BankWorld BankThe World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
is studying this project. The project will be funded on BOT basis. The 334 km (207.5 mi) Expressway between ChennaiChennaiChennai , formerly known as Madras or Madarasapatinam , is the capital city of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, located on the Coromandel Coast off the Bay of Bengal. Chennai is the fourth most populous metropolitan area and the sixth most populous city in India...
—BangaloreBangaloreBengaluru , formerly called Bengaluru is the capital of the Indian state of Karnataka. Bangalore is nicknamed the Garden City and was once called a pensioner's paradise. Located on the Deccan Plateau in the south-eastern part of Karnataka, Bangalore is India's third most populous city and...
and 277 km (172.1 mi) Expressway between KolkataKolkataKolkata , formerly known as Calcutta, is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located on the east bank of the Hooghly River, it was the commercial capital of East India...
—DhanbadDhanbadDhanbad features climate that is transitional between a humid subtropical climate and a tropical wet and dry climate. Summer starts from last week of March and ends in mid-June. Peak temperature in summer can reach 47oC. Dhanbad also receives heavy rainfall...
has been identified and feasibility study and DPR contract has been awarded by NHAI.
- Phase VII: This phase calls for improvements to city road networks by adding ring roads to enable easier connectivity with national highways to important cities. In addition, improvements will be made to stretches of national highways that require additional flyovers and bypasses given population and housing growth along the highways and increasing traffic. The government has not yet identified a firm investment plan for this phase. The 19 km (11.8 mi) long Chennai PortChennai PortChennai Port , formerly known as Madras Port, is the second largest port of India, behind the Mumbai Port, and the largest port in the Bay of Bengal. Being the third oldest port among the 12 major ports of India, it is over 125 years old, although maritime trade started way back in 1639 on the sea...
—MaduravoyalMaduravoyalMaduravoyal is a suburb of Chennai in Thiruvallur district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located 2 miles west of Chennai corporation limits. It is on the Chennai-Bangalore National highway. The second phase of Chennai Bypass cuts through Maduravoyal to reach the northern borders of...
Elevated Expressway is being executed under this phase.
| NHDP Phase | Particulars | Length | Indicative Cost ₹ ( in cr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NHDP-I & II | Balance work of GQ and EW-NS corridors | 13000 km (8,077.8 mi) | 42,000 |
| NHDP-III | 4-laning | 10000 km (6,213.7 mi) | 55,000 |
| NHDP-IV | 2-laning | 20000 km (12,427.5 mi) | 25,000 |
| NHDP-V | 6-laning of selected stretches | 5000 km (3,106.9 mi) | 17,500 |
| NHDP-VI | Development of expressways | 1000 km (621.4 mi) | 15,000 |
| NHDP-VII | Ring Roads, Bypasses, Grade Separators, Service Roads etc. | 700 km (435 mi) | 15,000 |
| Total | 45000 km (27,961.8 mi) | 1,69,500 (Revised to 2,20,000) |
Note: 1 crore= 10 million
| Priority | NHDP Phase | Length (km) | Status | Approval | Completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phase I | 5846 km (3,632.5 mi) | Fully awarded | December 2000 | December 2006 |
| 2 | Phase II | 7300 km (4,536 mi) | Award in progress | December 2003 | December 2009 |
| 3 | Phase III A | 4000 km (2,485.5 mi) | Already identified | March 2005 | December 2009 |
| 4 | Phase V | 6500 km (4,038.9 mi) | 5700 km of GQ + 800 km to be identified | November 2005 | December 2012 |
| 5 | Phase III B | 6000 km (3,728.2 mi) | Already identified | March 2006 | December 2012 |
| 6 | Phase VII A | 700 km (435 mi) | Ring roads to be identified | December 2006 | December 2012 |
| 7 | Phase IV A | 5000 km (3,106.9 mi) | To be identified | December 2006 | December 2012 |
| 8 | Phase VII B | Ring roads to be identified | December 2007 | December 2013 | |
| 9 | Phase IV B | 5000 km (3,106.9 mi) | To be identified | December 2007 | December 2013 |
| 10 | Phase VI A | 400 km (248.5 mi) | Already identified | December 2007 | December 2014 |
| 11 | Phase VII C | Ring roads to be identified | December 2008 | December 2014 | |
| 12 | Phase IV C | 5000 km (3,106.9 mi) | To be identified | December 2008 | December 2014 |
| 13 | Phase VI B | 600 km (372.8 mi) | To be identified | December 2008 | December 2015 |
| 14 | Phase IV D | 5000 km (3,106.9 mi) | To be identified | December 2009 | December 2015 |
Future plans
The Indian Government has set ambitious plans for upgrading of the National Highways in a phased manner in the years to come. The details are as follows:- 4-laning of 10000 km (6,213.7 mi) (NHDP Phase- III) including 4000 km (2,485.5 mi) that has been already approved. An accelerated road development programme for the North Eastern region.
- 2-laning with paved shoulders of 20000 km (12,427.5 mi) of National Highways under NHDP Phase-IV.
- 6-laning of GQ and some other selected stretches covering 6500 km (4,038.9 mi) under NHDP Phase-V.
- Development of 1000 km (621.4 mi) of express ways under NHDP Phase-VI.
- Development of ring roads, bypasses, grade separators, service roads, etc. under NHDP Phase-VII.
See also
- National Highways Authority of IndiaNational Highways Authority of IndiaThe National Highways Authority of India is an autonomous agency of the Government of India, responsible for management of a network of over 60,000 km of National Highways in India...
- Expressways of India
- Golden QuadrilateralGolden QuadrilateralThe Golden Quadrilateral is a highway network connecting India's four largest metropolises: Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata, thus forming a quadrilateral of sorts. Four other top ten metropolises: Bangalore, Pune, Ahmedabad, and Surat, are also served by the network...
(GQ) - North-South and East-West CorridorNorth-South and East-West CorridorThe North-South–East-West Corridor is the largest ongoing highway project in India. It is the second phase of the National Highways Development Project , and consists of building 7300 kilometers of four/six lane expressways connecting Srinagar, Kanyakumari, Porbandar and Silchar, at a cost of...
- List of National Highways in India
External links
- "Rs. 3.2 trillion for infrastructure in 11th plan" - India e-News article, dated 6 July 2006.
- NHAI Project Photographs
- National Highway Authority of India
- NH in Kerala
- Highway Photographs
- Map of NSEW progress, on the NHAI website.
- India Highways Group with lots of Pictures
- 'Mile by Mile, India Paves a Smoother Future' — extremely detailed New York Times article, dated December 4, 2005 (free registration required)

