
National Institute for Computational Sciences
Encyclopedia

National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
and managed by the University of Tennessee
University of Tennessee
The University of Tennessee is a public land-grant university headquartered at Knoxville, Tennessee, United States...
. NICS is home to Kraken, the most powerful computer in the world managed by academia and the world's fourth overall most powerful supercomputer. The NICS petascale scientific computing environment is housed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory is a multiprogram science and technology national laboratory managed for the United States Department of Energy by UT-Battelle. ORNL is the DOE's largest science and energy laboratory. ORNL is located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, near Knoxville...
(ORNL), home to the world's most powerful computing complex. The mission of NICS, a TeraGrid
TeraGrid
TeraGrid is an e-Science grid computing infrastructure combining resources at eleven partner sites. The project started in 2001 and operated from 2004 through 2011....
member, is to enable the scientific discoveries of researchers nationwide by providing leading-edge computational resources, together with support for their effective use, and leveraging extensive partnership opportunities.
Kraken

Cray XT5
The Cray XT5 is an updated version of the Cray XT4 supercomputer, launched on November 6, 2007. It includes a faster version of the XT4's SeaStar2 interconnect router called SeaStar2+, and can be configured either with XT4 compute blades, which have four dual-core AMD Opteron processor sockets, or...
system containing 16,512 compute sockets and more than 129 terabytes of memory. In November 2009, it was named the third fastest computer in the world. In its final configuration, the XT5 system will deliver in excess of 700 million CPU hours per year. The system is designed specifically for sustained application performance, scalability, reliability and will incorporate key elements of the Cray Cascade system to prepare the user community for sustained, high-productivity petascale science and engineering. The NSF computer system is co-located with the National Center for Computational Sciences
National Center for Computational Sciences
The National Center for Computational Sciences is a United States Department of Energy Leadership Computing Facility. The NCCS provides resources for calculation and simulation in fields including astrophysics, materials, and climate research...
, home of Jaguar
Jaguar (computer)
Jaguar is a petascale supercomputer built by Cray at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. The massively parallel Jaguar has a peak performance of just over 1,750 teraflops . It has 224,256 x86-based AMD Opteron processor cores, and operates with a version of Linux called the...
, and other major user facilities at the ORNL campus.
RDAV
RDAV is the University of Tennessee's Center for Data Analysis and Visualization sponsored by the National Science Foundation as part of the TeraGrid XD. Scientists and engineers are daily producing terabytes of digital data through experimentation, observation and simulation. RDAV's purpose is to aid in the significant challenge of transforming these data into knowledge and insight by providing remote visualization, analysis, and scientific workflow technologies. The hardware resources include Nautilus, an SGI shared-memory machine featuring 1024 cores and 4 terabytes of memory.RDAV is a partnership between the NICS, ORNL, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
, the University of Wisconsin, and the National Center for Supercomputing Applications
National Center for Supercomputing Applications
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications is an American state-federal partnership to develop and deploy national-scale cyberinfrastructure that advances science and engineering. NCSA operates as a unit of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign but it provides high-performance...
(NCSA) at the University of Illinois.
Verne
Verne a 5-node cluster of DellDell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
R505 quad-socket/quad-core Opteron servers dedicated to data analysis and high-end visualization was retired in September of 2010. Each node contained 16 processor cores, 128 gigabytes of memory, and 4 terabytes of local disk space. The primary purpose of Verne was to enable data analysis and visualization of simulation data generated on Kraken.
HPSS
The mass storage facility at ORNL currently consists of tape and disk storage components, IBM servers, Linux servers, and High Performance Storage System (HPSS) software. As of January 2009 it stored over 4 petabytes of data in over 11.5 million files.Tape storage is provided by robotic tape libraries. The StorageTek SL8500 libraries can each hold up to 10,000 cartridges and together house a total of thirteen 9840 drives (20 gigabyte cartridges, uncompressed), sixteen 9940B drives (200 gigabyte cartridges, uncompressed), thirty-two T10000A drives (500 gigabyte cartridges, uncompressed), and sixteen T10000B drives (1,000 gigabyte cartridges, uncompressed). The 9840 and 9940A drives read and write uncompressed data at 10 megabytes per second; the 9940B reads and writes at 30 megabytes per second. The beneficial feature of the 9840 tape technology is its fast seek time for small file access; the T10000 tape technology provides the ability to store a larger amount of data on each tape cartridge for more voluminous data sets.
Research Areas
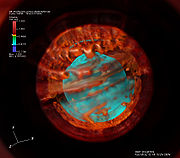
- Astrophysics - Understanding the mechanism behind supernova explosions.
- Biology - Finding a more efficient way to convert cellulose to ethanol.
- Climate - Enhancing resolution in the climate models used by policymakers.
- Seismology - Finding out where in California the ground would be most susceptible to movement in future earthquakes.
- Physics - Revealing the nature of matter from the behavior of molecules to the atoms that make up those molecules, to quarks, electrons, and other fundamental particles.

