
Natural process variation
Encyclopedia
Natural process variation, sometimes just called process variation, is the statistical
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
description of natural fluctuations in process outputs.
Equations
The following equations are used for an x-bar-control chartControl chart
Control charts, also known as Shewhart charts or process-behaviour charts, in statistical process control are tools used to determine whether or not a manufacturing or business process is in a state of statistical control.- Overview :...
:
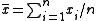
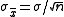
In the example, with n = 10 samples, the targeted mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
,
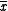 , and standard error
, and standard errorStandard error (statistics)
The standard error is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic. The term may also be used to refer to an estimate of that standard deviation, derived from a particular sample used to compute the estimate....
of the mean,
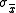 are:
are: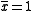
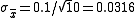
That is, independent 10-sample means should themselves have a standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of 0.0316. It is natural that the means vary this much, for by the central limit theorem
Central limit theorem
In probability theory, the central limit theorem states conditions under which the mean of a sufficiently large number of independent random variables, each with finite mean and variance, will be approximately normally distributed. The central limit theorem has a number of variants. In its common...
the means should have a normal distribution, regardless of the distribution of the samples themselves.
The importance of knowing the natural process variation becomes clear when we apply statistical process control
Statistical process control
Statistical process control is the application of statistical methods to the monitoring and control of a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential to produce conforming product. Under SPC, a process behaves predictably to produce as much conforming product as possible with the least...
. In a stable process, the mean is on target; in the example, the target is the filling, set to 1 litre. The variation within the upper and lower control limits (UCL and LCL) is considered the natural variation of the process.
Usage
When a sample average (size n = 10 in this case) is located outside the control limits, then this is an indication that the process is out of (statistical) control. To be more specific:- The Western ElectricWestern ElectricWestern Electric Company was an American electrical engineering company, the manufacturing arm of AT&T from 1881 to 1995. It was the scene of a number of technological innovations and also some seminal developments in industrial management...
rules conclude that the process is out of control if:- One point plots outside the 3σ-limits (the UCL and LCL).
- Two out of three consecutive points plot beyond a 2σ-limit.
- Four out of five consecutive points plot at a distance of 1σ or beyond from the centerline.
- Eight consecutive points plot on one side of the center line.
Goal
The most important goal of understanding the principle of natural process variation is to consider the natural variance in the output before we make any changes to the process. Since SPCStatistical process control
Statistical process control is the application of statistical methods to the monitoring and control of a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential to produce conforming product. Under SPC, a process behaves predictably to produce as much conforming product as possible with the least...
tends to minimize the process variations in time, as we better understand the process and have more experience with running it, we try to reduce the variation of it. The knowledge of the principle of natural variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
helps us avoid making any unnecessary changes to the process, which might add variance to the process, instead of removing it.

