
Nazi symbolism
Encyclopedia

Symbol
A symbol is something which represents an idea, a physical entity or a process but is distinct from it. The purpose of a symbol is to communicate meaning. For example, a red octagon may be a symbol for "STOP". On a map, a picture of a tent might represent a campsite. Numerals are symbols for...
ism, most notably the Hakenkreuz (swastika
Swastika
The swastika is an equilateral cross with its arms bent at right angles, in either right-facing form in counter clock motion or its mirrored left-facing form in clock motion. Earliest archaeological evidence of swastika-shaped ornaments dates back to the Indus Valley Civilization of Ancient...
), which it used as its principal symbol, and, in the form of the swastika flag, became the state flag of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
.
Other symbols employed by the Nazis include:
- the eagle atop swastika, the formal symbol of the Nazi Party
- the SS bolts (), the symbol of the Schutzstaffel
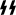 SchutzstaffelThe Schutzstaffel |Sig runes]]) was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party. Built upon the Nazi ideology, the SS under Heinrich Himmler's command was responsible for many of the crimes against humanity during World War II...
SchutzstaffelThe Schutzstaffel |Sig runes]]) was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party. Built upon the Nazi ideology, the SS under Heinrich Himmler's command was responsible for many of the crimes against humanity during World War II... - various runes from the runic alphabetRunic alphabetThe runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
, such as the odal rune, and rune-like symbols and the WolfsangelWolfsangelThe Wolfsangel is a symbol. It is also known as the Wolf's Hook or Doppelhaken. The upright variant is also known as "thunderbolt" and the horizontal variant as "werewolf".... - the black SS uniformUniforms and insignia of the SchutzstaffelThe uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel were paramilitary ranks and uniforms used by the SS between 1925 and 1945 to differentiate that organization from the regular German armed forces, the German state, and the Nazi Party....
- the brown shirts of the SturmabteilungSturmabteilungThe Sturmabteilung functioned as a paramilitary organization of the National Socialist German Workers' Party . It played a key role in Adolf Hitler's rise to power in the 1920s and 1930s...
- the death's headTotenkopfThe Totenkopf is the German word for the death's head and an old symbol for death or the dead. It consists usually of the skull and the mandible of the human skeleton...
insignia of the SS-TotenkopfverbändeSS-TotenkopfverbändeSS-Totenkopfverbände , meaning "Death's-Head Units", was the SS organization responsible for administering the Nazi concentration camps for the Third Reich....
and concentration camp units - Adolf Hitler's personal standard
Nazi flag

Black
Black is the color of objects that do not emit or reflect light in any part of the visible spectrum; they absorb all such frequencies of light...
-white
White
White is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light that stimulates all three types of color sensitive cone cells in the human eye in nearly equal amounts and with high brightness compared to the surroundings. A white visual stimulation will be void of hue and grayness.White light can be...
-red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
colour scheme is based upon the colours of the flag of the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, the black-white-red colours were commonly associated with anti-Weimar Republic German nationalists
German nationalism
German nationalism refers to the nationalism of Germans or of German culture. The origins of the beginning of a sense of German identity began with the Protestant Reformation begun by Martin Luther that resulted in the spread of a standardized common German language and literature...
after the fall of the German Empire. The Nazis denounced the black-red-yellow
Yellow
Yellow is the color evoked by light that stimulates both the L and M cone cells of the retina about equally, with no significant stimulation of the S cone cells. Light with a wavelength of 570–590 nm is yellow, as is light with a suitable mixture of red and green...
/gold
Gold (color)
Gold, also called golden, is one of a variety of orange-yellow color blends used to give the impression of the color of the element gold....
flag of the Weimar Republic - which now is the flag of Germany
Flag of Germany
The flag of Germany is a tricolour consisting of three equal horizontal bands displaying the national colours of Germany: black, red, and gold....
. In Mein Kampf
Mein Kampf
Mein Kampf is a book written by Nazi leader Adolf Hitler. It combines elements of autobiography with an exposition of Hitler's political ideology. Volume 1 of Mein Kampf was published in 1925 and Volume 2 in 1926...
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
defined the symbolism of the swastika flag: the red represents the social idea of the Nazi movement, the white disk represents the national idea, and the black swastika represents "the mission of the struggle for the victory of the Aryan
Aryan race
The Aryan race is a concept historically influential in Western culture in the period of the late 19th century and early 20th century. It derives from the idea that the original speakers of the Indo-European languages and their descendants up to the present day constitute a distinctive race or...
man, and, by the same token, the victory of creative work, which always has been and always will be anti-Semitic".
Runic letters
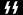

Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
and the modern Armanen runes
Armanen runes
The Armanen runes, or Armanen 'Futharkh' as Guido von List referred to them, are a row of 18 runes that are closely based in shape on the Younger Futhark...
have been used by Nazism
Nazism
Nazism, the common short form name of National Socialism was the ideology and practice of the Nazi Party and of Nazi Germany...
and neo-Nazi groups that associate themselves with Germanic traditions, mainly the Sigel
Sigel
Sigel may refer to:* Siȝel, the Old English for "Sun", see Sól ** the Old English name of the s-rune, see Sowilo rune-Surname:*Franz Sigel , Union general in the American Civil War...
, Eihwaz
Eihwaz
Eiwaz or Eihaz was a Proto-Germanic word for "yew", and the reconstructed name of the rune ....
, Tyr (c.f. Odal
Odal rune
The Elder Futhark Odal rune represents the o sound. Its reconstructed Proto-Germanic name is *ôþalan. The corresponding Gothic letter is o, called oþal. Variations of the name include Othila and Othala...
(see Odalism) and Algiz
Algiz
The Algiz is part of the ancient Nordic and Anglo-Saxon runic alphabet, often equated to the modern day z, however was traditionally pronounced yr. The letter has come to symbolize many neo-pagan religions and is often worn as a pendant...
runes.
The fascination that runes seem to have exerted on the Nazis can be traced to the occult
Occult
The word occult comes from the Latin word occultus , referring to "knowledge of the hidden". In the medical sense it is used to refer to a structure or process that is hidden, e.g...
and völkisch author Guido von List
Guido von List
Guido Karl Anton List, better known as Guido von List was an Austrian/German poet, journalist, writer, businessman and dealer of leather goods, mountaineer, hiker, dramatist, playwright, and rower, but was most notable as an occultist and völkisch author who is seen as one of the most important...
, one of the important figures in Germanic mysticism and runic revivalism in the late 19th and early 20th century. In 1908, List published in Das Geheimnis der Runen
Das Geheimnis der Runen
Das Geheimnis der Runen is a book by Austrian mystic Guido von List, in which he presents his "Armanen Futharkh".It appeared as a periodical article in 1906, and as a standalone publication in 1908.-Contents:...
("The Secret of the Runes") a set of 18 so-called "Armanen Runes
Armanen runes
The Armanen runes, or Armanen 'Futharkh' as Guido von List referred to them, are a row of 18 runes that are closely based in shape on the Younger Futhark...
", based on the Younger Futhark
Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
, which were allegedly revealed to him in a state of temporary blindness after a cataract operation on both eyes in 1902.
In Nazi contexts, the s-rune is referred to as "Sig" (after List, probably from Anglo-Saxon Sigel). The "Wolfsangel
Wolfsangel
The Wolfsangel is a symbol. It is also known as the Wolf's Hook or Doppelhaken. The upright variant is also known as "thunderbolt" and the horizontal variant as "werewolf"....
", while not a rune historically, has the shape of List's "Gibor" rune.
Continued use by neo-Nazi groups
Many symbols used by the Nazis have further been appropriated by neo-NaziNeo-Nazism
Neo-Nazism consists of post-World War II social or political movements seeking to revive Nazism or some variant thereof.The term neo-Nazism can also refer to the ideology of these movements....
groups, including a number of runes. Neo-Nazis also employ various number symbols such as:
- 1818 (number)18 is the natural number following 17 and preceding 19.In speech, the numbers 18 and 80 are sometimes confused. When carefully enunciated, they differ in which syllable is stressed: 18 vs 80 . However, in dates such as 1864, or when contrasting numbers in the teens, such as 17, 18, 19, the stress...
, code for Adolf HitlerAdolf HitlerAdolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
. The number comes from the position of the letters in the alphabet: AAA is the first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is similar to the Ancient Greek letter Alpha, from which it derives.- Origins :...
= 1, HHH .) is the eighth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The Semitic letter ⟨ח⟩ most likely represented the voiceless pharyngeal fricative . The form of the letter probably stood for a fence or posts....
= 8. - 8888 (number)88 is the natural number following 87 and preceding 89.- In mathematics :Eighty-Eight is a refactorable number, a primitive semiperfect number and an untouchable number...
, code for Heil HitlerNazi saluteThe Nazi salute, or Hitler salute , was a gesture of greeting in Nazi Germany usually accompanied by saying, Heil Hitler! ["Hail Hitler!"], Heil, mein Führer ["Hail, my leader!"], or Sieg Heil! ["Hail victory!"]...
. Again the number comes from the position of the letter H in the Latin alphabet. - 1414 (number)14 is the natural number following 13 and preceding 15.In speech, the numbers 14 and 40 are often confused. When carefully enunciated, they differ in which syllable is stressed: 14 vs 40...
, from the Fourteen WordsFourteen WordsThe Fourteen Words is a phrase used predominantly by white nationalists. It most commonly refers to the 14-word slogan: "We must secure the existence of our people and a future for White Children", and it can also refer to another 14-word slogan: "Because the beauty of the White Aryan women must...
coined by David Lane: "We must secure the existence of our people and a future for White children.
14 and 88 are sometimes combined with each other (i.e. 14/88, 8814, 1488).
See also
- Strafgesetzbuch section 86a
- Fascist symbolismFascist symbolismAs there were many different manifestations of fascism, especially during the interwar years, there were also many different symbols of Fascist movements...
- Uniforms and insignia of the SchutzstaffelUniforms and insignia of the SchutzstaffelThe uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel were paramilitary ranks and uniforms used by the SS between 1925 and 1945 to differentiate that organization from the regular German armed forces, the German state, and the Nazi Party....
- Nazi memorabiliaNazi memorabiliaNazi memorabilia are items of Nazi origin that are collected by museums and private individuals. Much of it comes from soldiers who collected small items as trophies during the Second World War....

