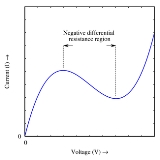
Negative resistance
Encyclopedia
Negative resistance is a property of some electric circuit
s where an increase in the current
entering a port results in a decreased voltage
across the same port. This is in contrast to a simple ohmic resistor
, which exhibits an increase in voltage under the same conditions. Negative resistors are theoretical and do not exist as a discrete component. However, some types of diode
s (e.g., tunnel diode
s) can be built that exhibit negative resistance in some part of their operating range. Such a differential negative resistance is illustrated in Figure 1 with a resonant-tunneling diode. Similarly, some chalcogenide
glasses, organic semiconductors, and conductive polymers exhibit a similar region of negative resistance as a bulk property.
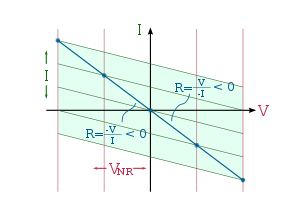 Figure 2 shows a graph of a negative resistor, showing the negative slope. In contrast to this, a resistor will have a positive slope. Tunnel diode
Figure 2 shows a graph of a negative resistor, showing the negative slope. In contrast to this, a resistor will have a positive slope. Tunnel diode
s and Gunn diode
s exhibit a negative resistance region in their IV (current – voltage) curve. They have two terminals like a resistor; but are not linear devices. Unijunction transistor
s also have negative resistance properties when a circuit is built using other components.
For negative resistance to be present there must be active components in the circuit providing a source of energy. This is because current through a negative resistance implies a source of energy just as current through positive resistance implies that energy is being dissipated.
A resistor produces voltage that is proportional to the current through it according to Ohm's law
. The IV curve of a true negative resistor has a negative slope and passes through the origin of the coordinate system (the curve can only enter the 2nd and 4th quadrants if energy is being supplied). This is to be compared with devices such as the tunnel diode where the negative slope portion of the curve does not pass through the origin. Clearly, there is no source of energy in a two terminal diode.
devices such as the dynatron
exhibit negative differential resistance effects. Practical and economic devices only became available with solid state technology
. The typical true negative impedance circuit—the negative impedance converter
– is due to John G. Linvill
(1953) and the popular element with negative differential resistance—the tunnel diode
– is due to Leo Esaki
(1958).
s are heavily doped semiconductor junctions that have an "N" shaped transfer curve. A vacuum tube
can also be made to exhibit negative resistance. Other negative resistance diodes have been built that have an "S" shaped transfer curve. When biased so that the operating point is in the negative resistance region, these devices can be used as an Amplifier
. These devices can also be biased so that they will switch between two states very quickly, as the applied voltage changes.
 , the input resistance (for an ideal opamp) is given by;
, the input resistance (for an ideal opamp) is given by;
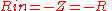
The input port of the circuit can be connected into another network as if it were a negative resistance component.
In the general case can be selected to produce negative capacitances or negative inductances.
can be selected to produce negative capacitances or negative inductances.
, Colpitts oscillator
, Hartley oscillator
, Wien bridge oscillator
, and some types of relaxation oscillator
s. If the feedback loop is broken and the input impedance examined it will be found to include negative resistance. Negative resistance characteristics of Gunn diode
s are often used in microwave
frequencies as well.
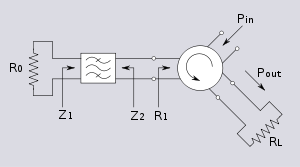 A device exhibiting negative resistance can be used to amplify a signal and this is an especially useful technique at microwave
A device exhibiting negative resistance can be used to amplify a signal and this is an especially useful technique at microwave
frequencies. Such devices do not present as pure negative resistance at these frequencies (in the case of the tunnel diode a large parallel capacitance is also present) and a matching filter is usually required. The reactive components of the device's equivalent circuit can be absorbed into the filter design so the circuit can be represented as a pure resistance followed by a bandpass filter. The output of this arrangement is fed into one port
of a three-port circulator
. The other two ports constitute the input and output of the amplifier with the direction of circulation as shown in the diagram. Treating R0 as being positive, the reflection coefficient
s at the two ends of the filter are given by;
 and,
and, 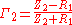
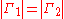
Since the filter has no resistive elements, there is no dissipation and the magnitudes of the two reflection coefficients must be equal,
The input power entering the cirulator is directed at the matching filter, is reflected at both the input and output of the filter and a portion finally arrives at the load. This portion is given by;
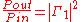
For a well matched filter, the reflection coefficients will be very small in the passband and very little power will reach the load. On the other hand if R0 is replaced by a negative resistance such that,
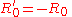 then,
then,
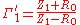 and,
and,
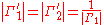
Now the reflection coefficients are very large and more power is reaching the load than was injected in the input port. The net result of terminating one port in a negative resistance is amplification between the remaining two ports.
This property is used in telephony line repeaters and in circuits such as the Howland current source, Deboo integrator and load cancellers.
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
s where an increase in the current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
entering a port results in a decreased voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
across the same port. This is in contrast to a simple ohmic resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
, which exhibits an increase in voltage under the same conditions. Negative resistors are theoretical and do not exist as a discrete component. However, some types of diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s (e.g., tunnel diode
Tunnel diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is capable of very fast operation, well into the microwave frequency region, by using quantum mechanical effects....
s) can be built that exhibit negative resistance in some part of their operating range. Such a differential negative resistance is illustrated in Figure 1 with a resonant-tunneling diode. Similarly, some chalcogenide
Chalcogenide
A chalcogenide is a chemical compound consisting of at least one chalcogen ion and at least one more electropositive element. Although all group 16 elements of the periodic table are defined as chalcogens, the term is more commonly reserved for sulfides, selenides, and tellurides, rather than...
glasses, organic semiconductors, and conductive polymers exhibit a similar region of negative resistance as a bulk property.
Properties

Tunnel diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is capable of very fast operation, well into the microwave frequency region, by using quantum mechanical effects....
s and Gunn diode
Gunn diode
A Gunn diode, also known as a transferred electron device , is a form of diode used in high-frequency electronics. It is somewhat unusual in that it consists only of N-doped semiconductor material, whereas most diodes consist of both P and N-doped regions...
s exhibit a negative resistance region in their IV (current – voltage) curve. They have two terminals like a resistor; but are not linear devices. Unijunction transistor
Unijunction transistor
A unijunction transistor is an electronic semiconductor device that has only one junction. The UJT has three terminals: an emitter and two bases . The base is formed by lightly doped n-type bar of silicon. Two ohmic contacts B1 and B2 are attached at its ends. The emitter is of p-type and it is...
s also have negative resistance properties when a circuit is built using other components.
For negative resistance to be present there must be active components in the circuit providing a source of energy. This is because current through a negative resistance implies a source of energy just as current through positive resistance implies that energy is being dissipated.
A resistor produces voltage that is proportional to the current through it according to Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
. The IV curve of a true negative resistor has a negative slope and passes through the origin of the coordinate system (the curve can only enter the 2nd and 4th quadrants if energy is being supplied). This is to be compared with devices such as the tunnel diode where the negative slope portion of the curve does not pass through the origin. Clearly, there is no source of energy in a two terminal diode.
History
In early research it was noticed that arc discharge devices and some vacuum tubeVacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
devices such as the dynatron
Dynatron
For the brand, see Dynatron Radio LtdThe dedicated dynatron vacuum tube was invented by Albert Hull in 1918. It has three electrodes: a thermionic cathode, a perforated anode, and a supplementary anode or plate, and its characteristic curves have a region exhibiting negative resistance, which is...
exhibit negative differential resistance effects. Practical and economic devices only became available with solid state technology
Solid state (electronics)
Solid-state electronics are those circuits or devices built entirely from solid materials and in which the electrons, or other charge carriers, are confined entirely within the solid material...
. The typical true negative impedance circuit—the negative impedance converter
Negative impedance converter
The negative impedance converter is a one-port op-amp circuit acting as a negative load which injects energy into circuits in contrast to an ordinary load that consumes energy from them. This is achieved by adding or subtracting excessive varying voltage in series to the voltage drop across an...
– is due to John G. Linvill
John G. Linvill
John G. Linvill was an American professor of Electrical engineering at Stanford University, known for his pioneering work in higher education, integrated circuits and semiconductors, and for development of the Optacon reading machine for the blind.-Early life and education:He received his A.B...
(1953) and the popular element with negative differential resistance—the tunnel diode
Tunnel diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is capable of very fast operation, well into the microwave frequency region, by using quantum mechanical effects....
– is due to Leo Esaki
Leo Esaki
Reona Esaki also known as Leo Esaki is a Japanese physicist who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1973 with Ivar Giaever and Brian David Josephson for his discovery of the phenomenon of electron tunneling. He is known for his invention of the Esaki diode, which exploited that phenomenon...
(1958).
Implementations

Diodes
Tunnel diodeTunnel diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode which is capable of very fast operation, well into the microwave frequency region, by using quantum mechanical effects....
s are heavily doped semiconductor junctions that have an "N" shaped transfer curve. A vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
can also be made to exhibit negative resistance. Other negative resistance diodes have been built that have an "S" shaped transfer curve. When biased so that the operating point is in the negative resistance region, these devices can be used as an Amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
. These devices can also be biased so that they will switch between two states very quickly, as the applied voltage changes.
Operational amplifiers
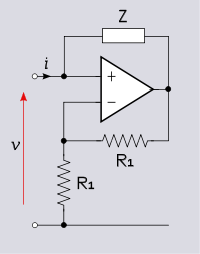
The negative resistance circuit shown in Figure 3 is an opamp implementation of the negative impedance converter (see below). The two resistors R1 and the op amp constitute a negative feedback non-inverting amplifier with gain A = 2. In the case , the input resistance (for an ideal opamp) is given by;
, the input resistance (for an ideal opamp) is given by;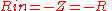
The input port of the circuit can be connected into another network as if it were a negative resistance component.
In the general case
 can be selected to produce negative capacitances or negative inductances.
can be selected to produce negative capacitances or negative inductances.Oscillators
All feedback oscillators imply the presence of negative resistance. There are many such topologies, including the dynatron oscillatorDynatron oscillator
A dynatron oscillator is an electronic circuit that uses negative resistance to keep an LC tank circuit oscillating.In theory, if an ideal capacitor is connected in parallel with an ideal inductor, they form a resonant circuit that, once it begins oscillating, will oscillate forever as the energy...
, Colpitts oscillator
Colpitts oscillator
A Colpitts oscillator, invented in 1920 by American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts, is one of a number of designs for electronic oscillator circuits using the combination of an inductance with a capacitor for frequency determination, thus also called LC oscillator...
, Hartley oscillator
Hartley oscillator
The Hartley oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses an inductor and a capacitor in parallel to determine the frequency. Invented in 1915 by American engineer Ralph Hartley, the distinguishing feature of the Hartley circuit is that the feedback needed for oscillation is taken from...
, Wien bridge oscillator
Wien bridge oscillator
A Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It can generate a large range of frequencies. The oscillator is based on a bridge circuit originally developed by Max Wien in 1891....
, and some types of relaxation oscillator
Relaxation oscillator
A relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system's return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy...
s. If the feedback loop is broken and the input impedance examined it will be found to include negative resistance. Negative resistance characteristics of Gunn diode
Gunn diode
A Gunn diode, also known as a transferred electron device , is a form of diode used in high-frequency electronics. It is somewhat unusual in that it consists only of N-doped semiconductor material, whereas most diodes consist of both P and N-doped regions...
s are often used in microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
frequencies as well.
Amplifiers

Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
frequencies. Such devices do not present as pure negative resistance at these frequencies (in the case of the tunnel diode a large parallel capacitance is also present) and a matching filter is usually required. The reactive components of the device's equivalent circuit can be absorbed into the filter design so the circuit can be represented as a pure resistance followed by a bandpass filter. The output of this arrangement is fed into one port
Two-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
of a three-port circulator
Circulator
A circulator is a passive non-reciprocal three- or four-port device, in which microwave or radio frequency power entering any port is transmitted to the next port in rotation...
. The other two ports constitute the input and output of the amplifier with the direction of circulation as shown in the diagram. Treating R0 as being positive, the reflection coefficient
Reflection coefficient
The reflection coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude or the intensity of a reflected wave relative to an incident wave...
s at the two ends of the filter are given by;
 and,
and, 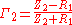
Since the filter has no resistive elements, there is no dissipation and the magnitudes of the two reflection coefficients must be equal,

The input power entering the cirulator is directed at the matching filter, is reflected at both the input and output of the filter and a portion finally arrives at the load. This portion is given by;
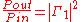
For a well matched filter, the reflection coefficients will be very small in the passband and very little power will reach the load. On the other hand if R0 is replaced by a negative resistance such that,
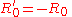 then,
then,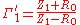 and,
and,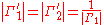
Now the reflection coefficients are very large and more power is reaching the load than was injected in the input port. The net result of terminating one port in a negative resistance is amplification between the remaining two ports.
Mixers and frequency converters
The highly non-linear characteristics of tunnel diodes makes them useful as frequency mixers. The conversion gain of a tunnel diode mixer can be as high as 20 dB if it is biased to operate in the negative resistance region.Antenna design
Another concept of negative resistance exists in the domain of radio frequency antenna design. This is also known as negative impedance. It is not uncommon for an antenna containing multiple driven elements to exhibit apparent negative impedance in one or more of the driven elements.Impedance cancellation
Negative impedances can be used to cancel the effects of positive impedances, for example, by eliminating the internal resistance of a voltage source or making the internal resistance of a current source infinite.This property is used in telephony line repeaters and in circuits such as the Howland current source, Deboo integrator and load cancellers.
Further reading
- Negatron yields real natural frequency, Aleksandr Belousov, USA, EDN, 08/1993 (practical application of the equivalent Negatron circuit related to Instrumentation and Measurement knowledge domain)
- E.W. Herold, "Negative Resistance and Devices for Obtaining It," Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers, Volume 23, Number 10, October 1935.
External links
- Negative Resistance Revived – condensed version of article originally published in Amateur Radio, November 1995
- Negative-resistance circuits – nice material from Answers.com
- Handbook Of Operational Amplifier Active RC Networks – a formal but well-written electronic book
- Negatrons enrich filter, oscillator designs, Aleksandr Belousov, USA, EDN, July 21, 1994
- Negative resistance as it applies to microwave oscillators
- Negative resistance oscillators using Zinc plated steel
- Oscillations and Regenerative Amplification using Negative Resistance Devices
- Resonant Tunneling Diode Simulation Tool on NanohubNanohubnanoHUB.org is science cyberinfrastructure comprising community-contributed resources and geared toward educational applications, professional networking, and interactive simulation tools for nanotechnology...
enables the simulation of resonant tunneling diodes under realistic bias conditions for realistically extended devices.

