
Newborn transport
Encyclopedia

Premature birth
In humans preterm birth refers to the birth of a baby of less than 37 weeks gestational age. The cause for preterm birth is in many situations elusive and unknown; many factors appear to be associated with the development of preterm birth, making the reduction of preterm birth a challenging...
and other sick infants from hospital
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
s without specialist, intensive care facilities require for optimal care of the baby to hospitals with neonatal intensive care
Neonatal intensive care unit
A Neonatal Intensive Care Unit —also called a Special Care Nursery, newborn intensive care unit, intensive care nursery , and special care baby unit —is an intensive care unit specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants.The problem of premature and congenitally ill infants is not a...
and other specialist services. Neonatal transport services such as NETS utilise mobile intensive care incubators fitted with mechanical ventilators, infusion pumps and physiological monitors capable of being used in a mobile environment. These transport systems seek to emulate the environment of a neonatal intensive care and permit un-interrupted care to occur in a referring hospital and then during the journey by road or air ambulance
Ambulance
An ambulance is a vehicle for transportation of sick or injured people to, from or between places of treatment for an illness or injury, and in some instances will also provide out of hospital medical care to the patient...
. Power and medical gas supplies are carried within the system as well as making use of external supplies; as available. Infant transport systems commonly weigh over 100 kg and present a challenge to vehicle operators in terms of weight, manual handling, crash-worthiness and power consumption.
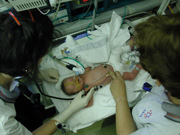
Typically, newborn transport teams spend some time stabilising a baby's condition prior to transport. Without adequate stabilisation, a clinical deterioration en route can be expected.
Wherever possible (and safe), in utero transfer is generally preferable to newborn transport. Transfer of the mother while still pregnant and with her infant unborn leads to improved survival and quality of survival for the baby.

