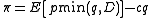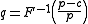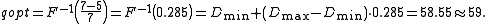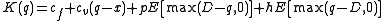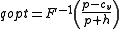Newsvendor
Encyclopedia
The newsvendor model is a mathematical model in operations management
and applied economics
used to determine optimal
inventory
levels. It is (typically) characterized by fixed prices and uncertain demand for a perishable product. If the inventory level is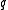 , each unit of demand above
, each unit of demand above 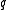 is lost. This model is also known as the Newsvendor Problem or Newsboy Problem by analogy with the situation faced by a newspaper vendor who must decide how many copies of the day's paper to stock in the face of uncertain demand and knowing that unsold copies will be worthless at the end of the day.
is lost. This model is also known as the Newsvendor Problem or Newsboy Problem by analogy with the situation faced by a newspaper vendor who must decide how many copies of the day's paper to stock in the face of uncertain demand and knowing that unsold copies will be worthless at the end of the day.
function is
where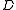 is a random variable
is a random variable
with probability distribution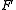 representing demand, each unit is sold for price
representing demand, each unit is sold for price 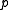 and purchased for price
and purchased for price  , and
, and 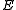 is the expectation operator. The solution to the optimal stocking quantity of the newsvendor which maximizes expected profit is:
is the expectation operator. The solution to the optimal stocking quantity of the newsvendor which maximizes expected profit is:
where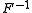 denotes the inverse
denotes the inverse
cumulative distribution function
of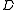 .
.
Intuitively, this ratio, referred to as the critical fractile, balances the cost of being understocked (a lost sale worth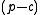 ) and the total costs of being either overstocked or understocked (where the cost of being overstocked is the inventory cost, or
) and the total costs of being either overstocked or understocked (where the cost of being overstocked is the inventory cost, or  so total cost is simply
so total cost is simply 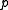 ).
).
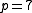 [$/unit] and purchase price is
[$/unit] and purchase price is 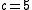 [$/unit]. Furthermore the
[$/unit]. Furthermore the  demand follows a uniform distribution (continuous)
demand follows a uniform distribution (continuous)
between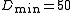 and
and 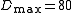 .
.
Therefore optimal inventory level is approximately 59 units.
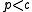 (i.e. the retail price is less than the purchase price), the numerator becomes negative. In this situation, it isn't worth keeping any item in the inventory.
(i.e. the retail price is less than the purchase price), the numerator becomes negative. In this situation, it isn't worth keeping any item in the inventory.
where the individual parameters are the following:
On the basis of the cost function the determination of the optimal inventory level is a minimization problem. So in the long run the amount of cost-optimal end-product can be calculated on the basis of the following relation:
Operations management
Operations management is an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and redesigning business operations in the production of goods and/or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as little resources as needed, and...
and applied economics
Applied economics
Applied economics is a term that refers to the application of economic theory and analysis. While not a field of economics, it is typically characterized by the application of economic theory and econometrics to address practical issues in a range of fields including labour economics, industrial...
used to determine optimal
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
inventory
Inventory
Inventory means a list compiled for some formal purpose, such as the details of an estate going to probate, or the contents of a house let furnished. This remains the prime meaning in British English...
levels. It is (typically) characterized by fixed prices and uncertain demand for a perishable product. If the inventory level is
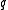 , each unit of demand above
, each unit of demand above 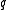 is lost. This model is also known as the Newsvendor Problem or Newsboy Problem by analogy with the situation faced by a newspaper vendor who must decide how many copies of the day's paper to stock in the face of uncertain demand and knowing that unsold copies will be worthless at the end of the day.
is lost. This model is also known as the Newsvendor Problem or Newsboy Problem by analogy with the situation faced by a newspaper vendor who must decide how many copies of the day's paper to stock in the face of uncertain demand and knowing that unsold copies will be worthless at the end of the day.Profit function
The standard newsvendor profitProfit (economics)
In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total opportunity costs of a venture to an entrepreneur or investor, whilst economic profit In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total...
function is
where
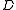 is a random variable
is a random variableRandom variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
with probability distribution
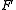 representing demand, each unit is sold for price
representing demand, each unit is sold for price 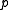 and purchased for price
and purchased for price  , and
, and 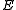 is the expectation operator. The solution to the optimal stocking quantity of the newsvendor which maximizes expected profit is:
is the expectation operator. The solution to the optimal stocking quantity of the newsvendor which maximizes expected profit is:where
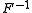 denotes the inverse
denotes the inverseInverse function
In mathematics, an inverse function is a function that undoes another function: If an input x into the function ƒ produces an output y, then putting y into the inverse function g produces the output x, and vice versa. i.e., ƒ=y, and g=x...
cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
of
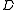 .
.Intuitively, this ratio, referred to as the critical fractile, balances the cost of being understocked (a lost sale worth
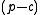 ) and the total costs of being either overstocked or understocked (where the cost of being overstocked is the inventory cost, or
) and the total costs of being either overstocked or understocked (where the cost of being overstocked is the inventory cost, or  so total cost is simply
so total cost is simply 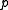 ).
).Numerical example
Assume that: retail price is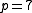 [$/unit] and purchase price is
[$/unit] and purchase price is 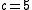 [$/unit]. Furthermore the
[$/unit]. Furthermore the 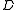 demand follows a uniform distribution (continuous)
demand follows a uniform distribution (continuous)Uniform distribution (continuous)
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
between
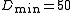 and
and 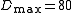 .
.Therefore optimal inventory level is approximately 59 units.
Extreme situation
If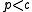 (i.e. the retail price is less than the purchase price), the numerator becomes negative. In this situation, it isn't worth keeping any item in the inventory.
(i.e. the retail price is less than the purchase price), the numerator becomes negative. In this situation, it isn't worth keeping any item in the inventory.Cost based optimization of inventory level
Assuming that the 'newsvendor' is in fact a small company who wants to produce goods to an uncertain market. In this more general situation the cost function of the newsvendor (company) can be formulated in the following manner:where the individual parameters are the following:
-
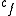 – fixed cost. This cost always exists when the production of a series is started. [$/production]
– fixed cost. This cost always exists when the production of a series is started. [$/production] -
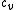 – variable cost. This cost type expresses the production cost of one product. [$/product]
– variable cost. This cost type expresses the production cost of one product. [$/product] -
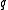 – The product quantity in the inventory. The decision of the inventory control policy concerns the product quantity in the inventory after the product decision. This parameter includes the initial inventory as well. If nothing is produced, then this quantity is equal to the initial quantity, i.e. concerning the existing inventory.
– The product quantity in the inventory. The decision of the inventory control policy concerns the product quantity in the inventory after the product decision. This parameter includes the initial inventory as well. If nothing is produced, then this quantity is equal to the initial quantity, i.e. concerning the existing inventory. -
 – Initial inventory level. We assume that the supplier possesses
– Initial inventory level. We assume that the supplier possesses  products in the inventory at the beginning of the demand of the delivery period.
products in the inventory at the beginning of the demand of the delivery period. -
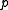 – penalty cost (or back order cost). If there is less raw material in the inventory than needed to satisfy the demands, this is the penalty cost of the unsatisfied orders. [$/product]
– penalty cost (or back order cost). If there is less raw material in the inventory than needed to satisfy the demands, this is the penalty cost of the unsatisfied orders. [$/product] -
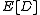 – Expected value of the
– Expected value of the 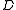 stochastic variable.
stochastic variable. -
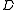 – This means the demand from the receiver for the product, which is an optional probability variable. [unit]
– This means the demand from the receiver for the product, which is an optional probability variable. [unit] -
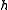 – inventory and stock holding cost. [$ / product]
– inventory and stock holding cost. [$ / product]
On the basis of the cost function the determination of the optimal inventory level is a minimization problem. So in the long run the amount of cost-optimal end-product can be calculated on the basis of the following relation:
See also
- Economic order quantityEconomic order quantityEconomic order quantity is the level of inventory that minimizes total inventory holding costs and ordering costs. It is one of the oldest classical production scheduling models. The framework used to determine this order quantity is also known as Wilson EOQ Model or Wilson Formula. The model was...
- Inventory control systemInventory control systemAn inventory control system is a process for managing and locating objects or materials. In common usage, the term may also refer to just the software components......
- Extended newsvendor model
Further reading
- Ayhan, Hayriye, Dai, Jim, Foley, R. D., Wu, Joe, 2004: Newsvendor Notes, ISyE 3232 Stochastic Manufacturing & Service Systems.