Noise gate
Encyclopedia
A Noise Gate or gate is an electronic device or software that is used to control the volume of an audio signal. In its most simple form, a noise gate allows a signal
to pass through only when it is above a set threshold: the gate is 'open'. If the signal falls below the threshold no signal is allowed to pass (or the signal is substantially attenuated): the gate is 'closed'. A noise gate is used when the level of the 'signal' is above the level of the 'noise
'. The threshold is set above the level of the 'noise' and so when there is no 'signal' the gate is closed. A noise gate does not remove noise from the signal. When the gate is open both the signal and the noise will pass through.
 They are commonly used in the recording studio
They are commonly used in the recording studio
and sound reinforcement. Rock musicians may also use small portable units to control unwanted noise from their amplification systems. Band-limited noise gates are also used to eliminate background noise from audio recordings by eliminating frequency
bands that contain only static
.
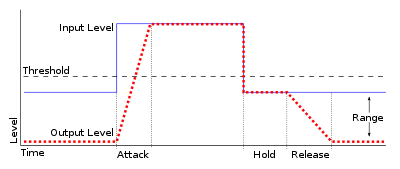
Noise Gates have a Threshold control to set the level at which the gate will open. More advanced noise gates have more features. The Release sets the amount of time for the gate to go from open to fully closed. A fast release abruptly cuts off the sound once it has fallen below the threshold, a slower release smoothly changes from open to closed, much like a slow fade out. If the release time is too short a click can be heard when the gate re-opens. Release is the most common control to find on a gate, after Threshold.
 The Attack control sets the time for the gate to change from closed to open, much like a fade-in. The Hold control allows you to define the amount of time the gate will stay open after the signal falls below the threshold. This is useful during short pauses between words or sentences in a speech signal.
The Attack control sets the time for the gate to change from closed to open, much like a fade-in. The Hold control allows you to define the amount of time the gate will stay open after the signal falls below the threshold. This is useful during short pauses between words or sentences in a speech signal.
The amount of attenuation
when the gate is closed can be set by the Range control. Often there will be complete attenuation, that is no signal will pass when the gate is closed. In some circumstances complete attenuation is not desired and the range can be changed.
Advanced gates have an external sidechain. This is an additional input that allows the gate to be triggered by another audio signal.
A variation of a sidechained noise gate used in electronic music
production is a trancegate or just simply gate, where the noise gate is not controlled by audio signal but a preprogrammed pattern resulting in a precisely controlled chopping of a sustained sound.
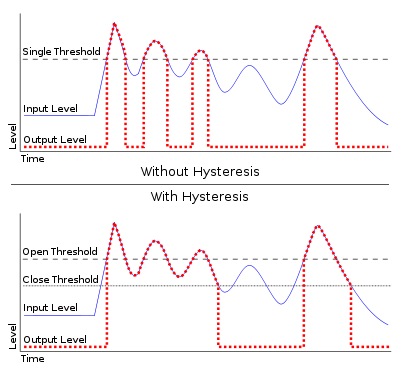
Noise gates often implement hysteresis
, that is, they have two thresholds. One to open the gate and another, set a few dB
below, to close the gate. This means that once a signal has dropped below the close threshold, it has to rise to the open threshold for the gate to open, so that a signal that crosses over the close threshold regularly does not open the gate and cause chattering. A longer hold time as described above also helps avoid chattering.
, noise gating reduces steady noise sources such as rumble
from LP record
s, hiss
from audio tape, static
from a radio
or amplifier
, and hum from a power system, without greatly affecting the source sound. An audio signal such as music
or speech is broken up into many frequency band
s by a collection of overlapping band-pass filter
s, and if the signal amplitude in any one band is lower than a preset threshold then that band is eliminated from the final sound. This greatly reduces perceptible background noise because only the frequency components of the noise that are within the gated passband
s survive.
The technique was implemented in real-time electronics in some audiophile
record players as early as the 1980s, and is now commonly used in audio production post-processing
, where software to Fourier transform
the audio signal can yield a very detailed spectrum
of the background noise. Common digital audio
editing software packages such as CoolEdit and Audacity
include easy-to-use digital noise gating code: the user selects a segment of audio that contains only static, and the amplitude levels in each frequency band are used to determine the threshold levels to be applied across the signal as a whole.
Noise gating works well when the static is steady and either narrowly confined in frequency (e.g. hum from AC power) or well below the main signal level (15 dB minimum is desirable). In cases where the signal merges with the background static (for example, the brushed drum sounds in the Sun King
track on the Beatles album Abbey Road) or is weak compared to the noise (as in very faint tape recordings), the noise gating can add artifacts
that are more distracting than the original static.
In the context of a multi-microphone recording session, noise gating is employed to reduce the leakage of sound into a microphone from sources other than the one the microphone was intended for. One example involves the mic-ing up of a drumkit. In most multi-mic drum recordings one microphone will be used to capture the snare drum
sound and another to capture the kick drum sound. The snare microphone will output a signal composed of a high level snare signal and a lower level kick drum signal (due to the further distance of the kick drum from the snare microphone). If the threshold level of the noise gate is set correctly a snare drum signal can be isolated. To fully isolate the snare drum signal the release rate has to be quite fast which can cause the tail end of the snare sound to be 'chopped off'. This can usually be remedied by the inclusion of one or more overhead microphone
, which can act as a general 'audio glue' for all the other gated sources.
For vocal applications on stage an optical microphone switch may be used. An infra-red sensor senses if somebody is in front of the microphone and switches on the microphone.
" effect heard on the drums on the Phil Collins
hit single "In the Air Tonight
", created by engineer-producer Hugh Padgham
, in which the powerful reverberation added to the drums is cut off by the noise gate after a few milliseconds, rather than being allowed to decay naturally. This can also be achieved by: sending the 'dry' snare signal to the reverb (or other process) unit, inserting a noise gate on the path of the reverb signal and connecting the snare sound to the side chain of the gate unit. With the gate unit set to 'external sidechain' (or 'external key') the gate will respond to the snare signal level and 'cut off' when that has decayed below the threshold, not the reverberated sound.
It is a common production trick to use spurious combinations of side chain inputs to control longer, more sustained sounds. For example, a hi-hat
signal can be used to control a sustained synthesized sound to produce a rhythmic melodic (or harmonic) signal which is perfectly in time with the hi-hat
signal. A good example of this use of the device can be found on the Godley & Creme
concept album
Consequences. The album's story required the creation of a number of special sound effects that would convey the impression of natural disasters. For the "Fire" sequence, Godley and Creme used a noise gate, triggered by the sound of multitracked voices, that created the 'voice' of a raging bushfire. During the recording of this segment, each time the voice signal began, it triggered the noise gate to open up another channel, which carried a pre-recorded loop of a crackling sound (created by overdubbing the sound of Bubble Wrap
being popped in front of a microphone). The combined voices and crackling created an eerie and quite convincing 'talking fire' effect.
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
to pass through only when it is above a set threshold: the gate is 'open'. If the signal falls below the threshold no signal is allowed to pass (or the signal is substantially attenuated): the gate is 'closed'. A noise gate is used when the level of the 'signal' is above the level of the 'noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
'. The threshold is set above the level of the 'noise' and so when there is no 'signal' the gate is closed. A noise gate does not remove noise from the signal. When the gate is open both the signal and the noise will pass through.

Recording studio
A recording studio is a facility for sound recording and mixing. Ideally both the recording and monitoring spaces are specially designed by an acoustician to achieve optimum acoustic properties...
and sound reinforcement. Rock musicians may also use small portable units to control unwanted noise from their amplification systems. Band-limited noise gates are also used to eliminate background noise from audio recordings by eliminating frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
bands that contain only static
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
.
Noise Gates have a Threshold control to set the level at which the gate will open. More advanced noise gates have more features. The Release sets the amount of time for the gate to go from open to fully closed. A fast release abruptly cuts off the sound once it has fallen below the threshold, a slower release smoothly changes from open to closed, much like a slow fade out. If the release time is too short a click can be heard when the gate re-opens. Release is the most common control to find on a gate, after Threshold.

The amount of attenuation
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
when the gate is closed can be set by the Range control. Often there will be complete attenuation, that is no signal will pass when the gate is closed. In some circumstances complete attenuation is not desired and the range can be changed.
Advanced gates have an external sidechain. This is an additional input that allows the gate to be triggered by another audio signal.
A variation of a sidechained noise gate used in electronic music
Electronic music
Electronic music is music that employs electronic musical instruments and electronic music technology in its production. In general a distinction can be made between sound produced using electromechanical means and that produced using electronic technology. Examples of electromechanical sound...
production is a trancegate or just simply gate, where the noise gate is not controlled by audio signal but a preprogrammed pattern resulting in a precisely controlled chopping of a sustained sound.
Noise gates often implement hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
, that is, they have two thresholds. One to open the gate and another, set a few dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
below, to close the gate. This means that once a signal has dropped below the close threshold, it has to rise to the open threshold for the gate to open, so that a signal that crosses over the close threshold regularly does not open the gate and cause chattering. A longer hold time as described above also helps avoid chattering.
Audio noise reduction
In audio post-processingPost-processing
Post-processing may refer to:* Differential GPS post-processing* Video post-processing, methods used in video processing and 3D graphics* Finite element model data post-processing...
, noise gating reduces steady noise sources such as rumble
Rumble (noise)
A rumble is a form of low-frequency noise created by a random sound wave existing between certain limitation points. In audio rumble refers to a low frequency sound from the bearings inside a turntable. This is most noticeable in low quality turntables with ball bearings...
from LP record
Gramophone record
A gramophone record, commonly known as a phonograph record , vinyl record , or colloquially, a record, is an analog sound storage medium consisting of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove...
s, hiss
Hiss
Hiss may refer to: a noise made by angry or frustrated animals, such as cats, birds, snakes, etc.-People:* Alger Hiss , U.S. State Department employee and a Soviet spy* Donald Hiss , younger brother of Alger Hiss...
from audio tape, static
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
from a radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
or amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
, and hum from a power system, without greatly affecting the source sound. An audio signal such as music
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
or speech is broken up into many frequency band
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
s by a collection of overlapping band-pass filter
Band-pass filter
A band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
s, and if the signal amplitude in any one band is lower than a preset threshold then that band is eliminated from the final sound. This greatly reduces perceptible background noise because only the frequency components of the noise that are within the gated passband
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
s survive.
The technique was implemented in real-time electronics in some audiophile
Audiophile
An audiophile is a person who enjoys listening to recorded music, usually in a home. Some audiophiles are more interested in collecting and listening to music, while others are more interested in collecting and listening to audio components, whose "sound quality" they consider as important as the...
record players as early as the 1980s, and is now commonly used in audio production post-processing
Post-processing
Post-processing may refer to:* Differential GPS post-processing* Video post-processing, methods used in video processing and 3D graphics* Finite element model data post-processing...
, where software to Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
the audio signal can yield a very detailed spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of the background noise. Common digital audio
Digital audio
Digital audio is sound reproduction using pulse-code modulation and digital signals. Digital audio systems include analog-to-digital conversion , digital-to-analog conversion , digital storage, processing and transmission components...
editing software packages such as CoolEdit and Audacity
Audacity
Audacity is a free software, cross-platform digital audio editor and recording application. It is available for Windows, Mac OS X, Linux and BSD.Audacity was created by Dominic Mazzoni while he was a graduate student at Carnegie Mellon University...
include easy-to-use digital noise gating code: the user selects a segment of audio that contains only static, and the amplitude levels in each frequency band are used to determine the threshold levels to be applied across the signal as a whole.
Noise gating works well when the static is steady and either narrowly confined in frequency (e.g. hum from AC power) or well below the main signal level (15 dB minimum is desirable). In cases where the signal merges with the background static (for example, the brushed drum sounds in the Sun King
Sun King (song)
"Sun King" is a song written primarily by John Lennon, but credited to Lennon–McCartney and recorded by The Beatles for their 1969 album, Abbey Road. It is the second song of the B-side's climactic medley.-History:...
track on the Beatles album Abbey Road) or is weak compared to the noise (as in very faint tape recordings), the noise gating can add artifacts
Sonic artifact
In sound and music production, sonic artifact, or simply artifact, refers to sonic material that is accidental or unwanted, resulting from the editing or manipulation of a sound....
that are more distracting than the original static.
In the context of a multi-microphone recording session, noise gating is employed to reduce the leakage of sound into a microphone from sources other than the one the microphone was intended for. One example involves the mic-ing up of a drumkit. In most multi-mic drum recordings one microphone will be used to capture the snare drum
Snare drum
The snare drum or side drum is a melodic percussion instrument with strands of snares made of curled metal wire, metal cable, plastic cable, or gut cords stretched across the drumhead, typically the bottom. Pipe and tabor and some military snare drums often have a second set of snares on the bottom...
sound and another to capture the kick drum sound. The snare microphone will output a signal composed of a high level snare signal and a lower level kick drum signal (due to the further distance of the kick drum from the snare microphone). If the threshold level of the noise gate is set correctly a snare drum signal can be isolated. To fully isolate the snare drum signal the release rate has to be quite fast which can cause the tail end of the snare sound to be 'chopped off'. This can usually be remedied by the inclusion of one or more overhead microphone
Overhead microphone
Overhead microphones are those used in sound recording and live sound reproduction to pick up ambient sounds, transients and the overall blend of instruments...
, which can act as a general 'audio glue' for all the other gated sources.
For vocal applications on stage an optical microphone switch may be used. An infra-red sensor senses if somebody is in front of the microphone and switches on the microphone.
Recording usages
A good example of time-controlled noise gating is the well-known "gated reverbGated reverb
Gated reverb is an audio processing technique that is applied to recordings of drums to make the drums sound powerful and "punchy," while keeping the overall mix clean and transparent-sounding...
" effect heard on the drums on the Phil Collins
Phil Collins
Philip David Charles "Phil" Collins, LVO is an English singer-songwriter, drummer, pianist and actor best known as a drummer and vocalist for British progressive rock group Genesis and as a solo artist....
hit single "In the Air Tonight
In the Air Tonight
"In the Air Tonight" is a song by Phil Collins that first appeared on his 1981 album Face Value. It was recorded in 1979 and was the first single of Collins' solo career, and remains one of his best-known hits. The music video, directed by Stuart Orme, was released in 1981.-The song/recording:The...
", created by engineer-producer Hugh Padgham
Hugh Padgham
Hugh Padgham is a British record producer. He has won many awards, including four Grammys, with Producer of the Year and Engineer of the Year. A 1992 poll in Mix magazine voted him one of the world's Top Ten Most Influential Producers....
, in which the powerful reverberation added to the drums is cut off by the noise gate after a few milliseconds, rather than being allowed to decay naturally. This can also be achieved by: sending the 'dry' snare signal to the reverb (or other process) unit, inserting a noise gate on the path of the reverb signal and connecting the snare sound to the side chain of the gate unit. With the gate unit set to 'external sidechain' (or 'external key') the gate will respond to the snare signal level and 'cut off' when that has decayed below the threshold, not the reverberated sound.
It is a common production trick to use spurious combinations of side chain inputs to control longer, more sustained sounds. For example, a hi-hat
Hi-hat
A hi-hat, or hihat, is a type of cymbal and stand used as a typical part of a drum kit by percussionists in R&B, hip-hop, disco, jazz, rock and roll, house, reggae and other forms of contemporary popular music.- Operation :...
signal can be used to control a sustained synthesized sound to produce a rhythmic melodic (or harmonic) signal which is perfectly in time with the hi-hat
Hi-hat
A hi-hat, or hihat, is a type of cymbal and stand used as a typical part of a drum kit by percussionists in R&B, hip-hop, disco, jazz, rock and roll, house, reggae and other forms of contemporary popular music.- Operation :...
signal. A good example of this use of the device can be found on the Godley & Creme
Godley & Creme
Godley & Creme were an English pop music duo composed of Kevin Godley and Lol Creme. The pair began releasing albums as a duo after splitting from the pop band 10cc. In 1979 they directed their first music video for their own single "An Englishman in New York"...
concept album
Concept album
In music, a concept album is an album that is "unified by a theme, which can be instrumental, compositional, narrative, or lyrical." Commonly, concept albums tend to incorporate preconceived musical or lyrical ideas rather than being improvised or composed in the studio, with all songs contributing...
Consequences. The album's story required the creation of a number of special sound effects that would convey the impression of natural disasters. For the "Fire" sequence, Godley and Creme used a noise gate, triggered by the sound of multitracked voices, that created the 'voice' of a raging bushfire. During the recording of this segment, each time the voice signal began, it triggered the noise gate to open up another channel, which carried a pre-recorded loop of a crackling sound (created by overdubbing the sound of Bubble Wrap
Bubble Wrap
Bubble wrap is a pliable transparent plastic material commonly used for packing fragile items. Regularly spaced, protruding air-filled hemispheres provide cushioning for fragile items....
being popped in front of a microphone). The combined voices and crackling created an eerie and quite convincing 'talking fire' effect.

