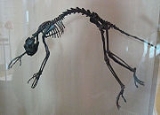
Notharctinae
Encyclopedia
Notharctinae is an extinct subfamily of primates that were common in North America
during the early and middle Eocene
(55-34 million years ago). The six genera that make up the group (Cantius
, Pelycodus
, Copelemur, Hesperolemur
, Notharctus
, and Smilodectes
) contain species that are among the most primitive of the adapiform group, which is one of the most primitive groups of primates. The evolutionary history of this subfamily has been comparatively well documented and has been used to argue for evolutionary gradualism. Though it is generally accepted that adapiforms gave rise to modern day lemur
s and loris
es, it is not currently known which branch of Adapiformes these living species are most closely related to. Notharctines went extinct in the middle Eocene, most likely because of a combination of factors including climatic change and competition with other North American primates.
, of the Notharctidae
family, which is a member of the infraorder Adapiformes along with Adapidae and Sivaladapidae. Compared to other subfamilies, the notharctines were not terribly diverse with only two or three species occurring synchronously. However, notharctines are some of the most common species found in early and middle Eocene deposits. Each genus has between 1 (Hesperolemur) and 11 (Cantius) species for a total of 25 species making up the subfamily. Body size ranges from 1100 grams in early species of Cantius to 6900 grams in late occurring Notharctus with an overall trend of increasing body size.
Overall, each genus was restricted to a small geographic region. Cantius was a northern (Wyoming
) early Eocene genus, while the other two early Eocene genera, Pelycodus and Copelemur, occupied more southern habitats (New Mexico
). Middle Eocene taxa, Notharctus and Smilodectes. were again found in Wyoming, while Hesperolemur is known only from southern California
. This move to the north may be associated with climatic warming between the early and the middle Eocene.
within the orbit, and, except for Notharctus, an unfused mandible. All have small orbits which indicate a diurnal
lifestyle and there is some evidence of the reduction of the sense of smell in favor of the sense of sight. One of the diagnostic features of this subfamily is that later species acquired a hypocone
, or an extra cusp on the upper molars
, from the postprotocingulum, instead of the lingual cingulum
(a shelf on the margin of the tooth at the side of the tongue) as in cercamoniines. Many later species show increasing adaptation for folivory
including increased body size, the loss of the paraconids, and the fusion of the mandible. Hesperolemur is unique among notharctines in having the tympanic ring partially fused to the auditory bulla
.
Postcranial remains of Notharctus have linked notharctine locomotion with that of living lemurs. There is also evidence of canine sexual dimorphism
in Notharctus which may indicate the presence of social groups.
diet to a folivorous one.
Some have suggested that there were two separate immigrations of Cantius, one which gave rise to the larger Pelycodus and one which gave rise to the smaller lineages of Copelemur, Smilodectes and Notharctus. Others have suggested that a single lineage of Cantius split, with one branch leading to Copelemur, one to Pelycodus, and one gradually acquiring a fused mandible, one of the few diagnostic features between Cantius and Notharctus. Smilodectes either derived from the lineage that became Notharctus or from the more southern Copelemur lineage. Hesperolemur, a middle Eocene taxa, has only recently been described and is currently thought to be an immigrant species.
Though some scientists believe that members of the adapiform radiation gave rise to simian
s because of the long list of dental and cranial similarities including a fused mandible, loss of paraconids, and large, sexually dimorphic canines, normally the European cercamoniines are the specific subfamily cited. It is more widely agreed upon that adapiforms are closely related to modern lemurs and lorises, although there much speculation as to which taxa are more closely related.
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
during the early and middle Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
(55-34 million years ago). The six genera that make up the group (Cantius
Cantius
Cantius was a genus of adapiformes primate that lived in the Eocene....
, Pelycodus
Pelycodus
Pelycodus is an extinct Adapiform primate that lived during the early Eocene period in North America, specifically Wyoming and New Mexico. It is very closely related to Cantius and may even be its subgenus. It may also have given rise to the Middle Eocene Uintan primate Hesperolemur, although...
, Copelemur, Hesperolemur
Hesperolemur
Hesperolemur actius is an extinct primate that lived in the middle Eocene of southern California. It is an immigrant taxa which appears to be most closely related to the earlier European forms of Cantius...
, Notharctus
Notharctus
Notharctus was an early primate that inhabited Europe and North America 50 million years ago. Modern lemurs evolved from primates similar to this genus....
, and Smilodectes
Smilodectes
Smilodectes is an extinct genus of primate that lived in Wyoming. It possesses a post-orbital bar and grasping thumbs and toes. Smilodectes has a small cranium size and the foramen magnum was located at the back of the skull, on the occipatal bone....
) contain species that are among the most primitive of the adapiform group, which is one of the most primitive groups of primates. The evolutionary history of this subfamily has been comparatively well documented and has been used to argue for evolutionary gradualism. Though it is generally accepted that adapiforms gave rise to modern day lemur
Lemur
Lemurs are a clade of strepsirrhine primates endemic to the island of Madagascar. They are named after the lemures of Roman mythology due to the ghostly vocalizations, reflective eyes, and the nocturnal habits of some species...
s and loris
Loris
Loris is the common name for the strepsirrhine primates of the subfamily Lorisinae in family Lorisidae. Loris is one genus in this subfamily and includes the slender lorises, while Nycticebus is the genus for the slow lorises....
es, it is not currently known which branch of Adapiformes these living species are most closely related to. Notharctines went extinct in the middle Eocene, most likely because of a combination of factors including climatic change and competition with other North American primates.
Taxonomic diversity
Notharctinae is one of the two subfamilies, along with CercamoniinaeCercamoniinae
Cercamoniinae is a subfamily within the extinct primate family Notharctidae.- Classification :*Family Notharctidae**Subfamily Cercamoniinae***Genus Anchomomys***Genus Buxella***Genus Darwinius***Genus Donrussellia...
, of the Notharctidae
Notharctidae
Notharctidae is an extinct family of primitive primates.- Classification :*Family Notharctidae**Subfamily Cercamoniinae***Genus Anchomomys***Genus Buxella***Genus Darwinius***Genus Donrussellia***Genus Europolemur...
family, which is a member of the infraorder Adapiformes along with Adapidae and Sivaladapidae. Compared to other subfamilies, the notharctines were not terribly diverse with only two or three species occurring synchronously. However, notharctines are some of the most common species found in early and middle Eocene deposits. Each genus has between 1 (Hesperolemur) and 11 (Cantius) species for a total of 25 species making up the subfamily. Body size ranges from 1100 grams in early species of Cantius to 6900 grams in late occurring Notharctus with an overall trend of increasing body size.
Overall, each genus was restricted to a small geographic region. Cantius was a northern (Wyoming
Wyoming
Wyoming is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States. The western two thirds of the state is covered mostly with the mountain ranges and rangelands in the foothills of the Eastern Rocky Mountains, while the eastern third of the state is high elevation prairie known as the High...
) early Eocene genus, while the other two early Eocene genera, Pelycodus and Copelemur, occupied more southern habitats (New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
). Middle Eocene taxa, Notharctus and Smilodectes. were again found in Wyoming, while Hesperolemur is known only from southern California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
. This move to the north may be associated with climatic warming between the early and the middle Eocene.
Morphology
Overall, the notharctines retain a very primitive primate morphology. They have long broad snouts, a dental formula of 2.1.4.3, a lacrimal boneLacrimal bone
The lacrimal bone, the smallest and most fragile bone of the face, is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders.-Lateral or orbital surface:...
within the orbit, and, except for Notharctus, an unfused mandible. All have small orbits which indicate a diurnal
Diurnal animal
Diurnality is a plant or animal behavior characterized by activity during the day and sleeping at night.-In animals:Animals that are not diurnal might be nocturnal or crepuscular . Many animal species are diurnal, including many mammals, insects, reptiles and birds...
lifestyle and there is some evidence of the reduction of the sense of smell in favor of the sense of sight. One of the diagnostic features of this subfamily is that later species acquired a hypocone
Hypocone
The hypocone is the name for a main cusp found on the molars of the upper dentition of hominids. It is found on the distal lingual side of the tooth. It fits into the grooves of the lower dentition and is an adaptation for the overall grinding and tearing of foods using the occlusal of the tooth...
, or an extra cusp on the upper molars
Molar (tooth)
Molars are the rearmost and most complicated kind of tooth in most mammals. In many mammals they grind food; hence the Latin name mola, "millstone"....
, from the postprotocingulum, instead of the lingual cingulum
Cingulum (tooth)
In dentistry, cingulum refers to an anatomical feature of the anterior teeth . It refers to the portion of the teeth, occurring on the lingual or palatal aspects, that forms a convex protuberance at the cervical third of the anatomic crown. It represents the lingual or palatal developmental lobe...
(a shelf on the margin of the tooth at the side of the tongue) as in cercamoniines. Many later species show increasing adaptation for folivory
Folivore
In zoology, a folivore is a herbivore that specializes in eating leaves. Mature leaves contain a high proportion of hard-to-digest cellulose, less energy than other types of foods, and often toxic compounds. For this reason folivorous animals tend to have long digestive tracts and slow metabolisms....
including increased body size, the loss of the paraconids, and the fusion of the mandible. Hesperolemur is unique among notharctines in having the tympanic ring partially fused to the auditory bulla
Auditory bulla
The auditory bulla is a hollow bony structure on the ventral, posterior portion of the skull of placental mammals that encloses parts of the middle and inner ear. In most species, it is formed by the tympanic part of the temporal bone.In extant primates, the structure is found in tarsiers,...
.
Postcranial remains of Notharctus have linked notharctine locomotion with that of living lemurs. There is also evidence of canine sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is a phenotypic difference between males and females of the same species. Examples of such differences include differences in morphology, ornamentation, and behavior.-Examples:-Ornamentation / coloration:...
in Notharctus which may indicate the presence of social groups.
Evolutionary history
The earliest widely accepted adapiform was the European cercamoniine Donrussellia, though recent finds of additional species may soon show otherwise. Donrussellia is closely related to the earlier and more primitive European notharctine species of Cantius. After surviving the Atlantic crossing, more advanced species of Cantius gradually got bigger and developed larger mesostyles and hypocones, which go along with the switch from a primarily frugivorousFrugivore
A frugivore is a fruit eater. It can be any type of herbivore or omnivore where fruit is a preferred food type. Because approximately 20% of all mammalian herbivores also eat fruit, frugivory is considered to be common among mammals. Since frugivores eat a lot of fruit they are highly dependent...
diet to a folivorous one.
Some have suggested that there were two separate immigrations of Cantius, one which gave rise to the larger Pelycodus and one which gave rise to the smaller lineages of Copelemur, Smilodectes and Notharctus. Others have suggested that a single lineage of Cantius split, with one branch leading to Copelemur, one to Pelycodus, and one gradually acquiring a fused mandible, one of the few diagnostic features between Cantius and Notharctus. Smilodectes either derived from the lineage that became Notharctus or from the more southern Copelemur lineage. Hesperolemur, a middle Eocene taxa, has only recently been described and is currently thought to be an immigrant species.
Though some scientists believe that members of the adapiform radiation gave rise to simian
Simian
The simians are the "higher primates" familiar to most people: the Old World monkeys and apes, including humans, , and the New World monkeys or platyrrhines. Simians tend to be larger than the "lower primates" or prosimians.- Classification and evolution :The simians are split into three groups...
s because of the long list of dental and cranial similarities including a fused mandible, loss of paraconids, and large, sexually dimorphic canines, normally the European cercamoniines are the specific subfamily cited. It is more widely agreed upon that adapiforms are closely related to modern lemurs and lorises, although there much speculation as to which taxa are more closely related.

