
Nuclear family
Encyclopedia
Nuclear family is a term used to define a family group consisting of a father and mother and their children. This is in contrast to the smaller single-parent family, and to the larger extended family
. Nuclear families typically center on a married couple, but not always; the nuclear family may have any number of children. There are differences in definition among observers; some definitions allow only biological children that are full-blood siblings, while others allow for a stepparent and any mix of dependent children including stepchildren and adopted children. Alternate definitions have included family units headed by same-sex parents, and perhaps additional adult relatives who take on a cohabiting parental role.
The concept of the nuclear family was first noticed in Western Europe in the 17th century. With the emergence of proto-industrialization
and early capitalism, the nuclear family became a financially viable social unit.
The concept that a narrowly defined nuclear family is central to stability in modern society has been promoted by modern social conservatives in the United States, and has been challenged as historically and sociologically inadequate to describe the complexity of actual family relations.
dates the term back to 1947, whilst the Oxford English Dictionary
has a reference to the term from 1924; thus it is relatively new, although nuclear family structures themselves date back thousands of years. The term nuclear is used in its general meaning referring to a central entity or "nucleus" around which others collect.
In its most common usage, the term nuclear family refers to a household consisting of a father
, a mother
and their child
ren all in one household dwelling. George Murdock
, an early and influential observer of families, describes the term in this way:
Many individuals are part of two nuclear families in their lives: the family of origin in which they are offspring, and the family of procreation in which they are a parent.
 Current information from United States Census Bureau
Current information from United States Census Bureau
shows that 70% of children in the US live in traditional two-parent families, with 66% of those living with parents who are married, and 60% living with their biological parents, and that "the figures suggest that the tumultuous shifts in family structure since the late 1960s have leveled off since 1990."
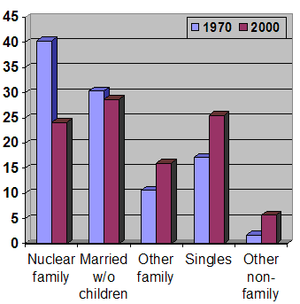
If considered separate from couples without children, single-parent families, or unmarried couples with children, in the United States traditional nuclear families appear to constitute a minority of households with rising prevalence of other family arrangements. As of 2000, nuclear families with the original biological parents constituted roughly 24.1% of American households, compared to 40.3% in 1970. Roughly two-thirds of all children in the United States will spend at least some time in a single-parent household.
In the UK, the number of nuclear families fell from 39% of all households in 1968 to 28% in 1992. The decrease accompanied an equal increase in the number of single-parent households and the number of adults living alone.
According to some sociologists, "[The nuclear family] no longer seems adequate to cover the wide diversity of household arrangements we see today." (Edwards 1991; Stacey 1996). A new term has been introduced, postmodern family, which is meant to describe the great variability in family forms, including single-parent families and child-free couples."
According to Professor Wolfgang Haak of Adelaide University
, the nuclear family is natural to Homo sapiens. A 2005 archeological dig in Elau, Germany, analyzed by Haak, revealed genetic evidence suggesting that the 13 individuals found in a grave were closely related. Haak said, "By establishing the genetic links between the two adults and two children buried together in one grave, we have established the presence of the classic nuclear family in a prehistoric context in Central Europe." However, even here the evidence suggests that the nuclear family was embedded with an extended family. The remains of three children (probably siblings based on DNA evidence) were found buried with a woman who was not their mother but may have been an "aunt or a step-mother."
Extended family
The term extended family has several distinct meanings. In modern Western cultures dominated by nuclear family constructs, it has come to be used generically to refer to grandparents, uncles, aunts, and cousins, whether they live together within the same household or not. However, it may also refer...
. Nuclear families typically center on a married couple, but not always; the nuclear family may have any number of children. There are differences in definition among observers; some definitions allow only biological children that are full-blood siblings, while others allow for a stepparent and any mix of dependent children including stepchildren and adopted children. Alternate definitions have included family units headed by same-sex parents, and perhaps additional adult relatives who take on a cohabiting parental role.
The concept of the nuclear family was first noticed in Western Europe in the 17th century. With the emergence of proto-industrialization
Proto-industrialization
Proto-industrialisation is a phase in the development of modern industrial economies that preceded, and created conditions for, the establishment of fully industrial societies...
and early capitalism, the nuclear family became a financially viable social unit.
The concept that a narrowly defined nuclear family is central to stability in modern society has been promoted by modern social conservatives in the United States, and has been challenged as historically and sociologically inadequate to describe the complexity of actual family relations.
Usage of the term
Merriam-WebsterMerriam-Webster
Merriam–Webster, which was originally the G. & C. Merriam Company of Springfield, Massachusetts, is an American company that publishes reference books, especially dictionaries that are descendants of Noah Webster’s An American Dictionary of the English Language .Merriam-Webster Inc. has been a...
dates the term back to 1947, whilst the Oxford English Dictionary
Oxford English Dictionary
The Oxford English Dictionary , published by the Oxford University Press, is the self-styled premier dictionary of the English language. Two fully bound print editions of the OED have been published under its current name, in 1928 and 1989. The first edition was published in twelve volumes , and...
has a reference to the term from 1924; thus it is relatively new, although nuclear family structures themselves date back thousands of years. The term nuclear is used in its general meaning referring to a central entity or "nucleus" around which others collect.
In its most common usage, the term nuclear family refers to a household consisting of a father
Father
A father, Pop, Dad, or Papa, is defined as a male parent of any type of offspring. The adjective "paternal" refers to father, parallel to "maternal" for mother...
, a mother
Mother
A mother, mum, mom, momma, or mama is a woman who has raised a child, given birth to a child, and/or supplied the ovum that grew into a child. Because of the complexity and differences of a mother's social, cultural, and religious definitions and roles, it is challenging to specify a universally...
and their child
Child
Biologically, a child is generally a human between the stages of birth and puberty. Some vernacular definitions of a child include the fetus, as being an unborn child. The legal definition of "child" generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger than the age of majority...
ren all in one household dwelling. George Murdock
George Murdock
George Peter Murdock was a notable American anthropologist. He is remembered for his empirical approach to ethnological studies and his landmark works on Old World populations.-Early life:...
, an early and influential observer of families, describes the term in this way:
Many individuals are part of two nuclear families in their lives: the family of origin in which they are offspring, and the family of procreation in which they are a parent.
Compared to extended family
An extended family group consists of non-nuclear (or "non-immediate") family members considered together with nuclear (or "immediate") family members.Changes to family formation
The popularity of the concept of the nuclear family in the West, as opposed to the traditional extended family living together, came about in the early 20th century, prompted in part by increased wages earned by the working class. This enabled more and more families to be economically independent, and thus to own their own home.
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau is the government agency that is responsible for the United States Census. It also gathers other national demographic and economic data...
shows that 70% of children in the US live in traditional two-parent families, with 66% of those living with parents who are married, and 60% living with their biological parents, and that "the figures suggest that the tumultuous shifts in family structure since the late 1960s have leveled off since 1990."
If considered separate from couples without children, single-parent families, or unmarried couples with children, in the United States traditional nuclear families appear to constitute a minority of households with rising prevalence of other family arrangements. As of 2000, nuclear families with the original biological parents constituted roughly 24.1% of American households, compared to 40.3% in 1970. Roughly two-thirds of all children in the United States will spend at least some time in a single-parent household.
In the UK, the number of nuclear families fell from 39% of all households in 1968 to 28% in 1992. The decrease accompanied an equal increase in the number of single-parent households and the number of adults living alone.
According to some sociologists, "[The nuclear family] no longer seems adequate to cover the wide diversity of household arrangements we see today." (Edwards 1991; Stacey 1996). A new term has been introduced, postmodern family, which is meant to describe the great variability in family forms, including single-parent families and child-free couples."
According to Professor Wolfgang Haak of Adelaide University
University of Adelaide
The University of Adelaide is a public university located in Adelaide, South Australia. Established in 1874, it is the third oldest university in Australia...
, the nuclear family is natural to Homo sapiens. A 2005 archeological dig in Elau, Germany, analyzed by Haak, revealed genetic evidence suggesting that the 13 individuals found in a grave were closely related. Haak said, "By establishing the genetic links between the two adults and two children buried together in one grave, we have established the presence of the classic nuclear family in a prehistoric context in Central Europe." However, even here the evidence suggests that the nuclear family was embedded with an extended family. The remains of three children (probably siblings based on DNA evidence) were found buried with a woman who was not their mother but may have been an "aunt or a step-mother."
American conservatism
In the United States, the idea that the nuclear family is traditional is an important aspect of conservatism.See also
- Astronaut familyAstronaut familyAstronaut family is a term that is used to describe a family unit where the members reside in different countries across the world. The term is in contrast to the "nuclear family"....
- Complex family
- Human bondingHuman bondingHuman bonding is the process of development of a close, interpersonal relationship. It most commonly takes place between family members or friends, but can also develop among groups such as sporting teams and whenever people spend time together...
- Intentional communityIntentional communityAn intentional community is a planned residential community designed to have a much higher degree of teamwork than other communities. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, religious, or spiritual vision and often follow an alternative lifestyle. They...
- Hindu joint familyHindu joint familyA Hindu Joint Family or Joint Family is an extended family arrangement prevalent among Hindus of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of many generations living under the same roof. All the male members are blood relatives and all the women are either mothers, wives, unmarried daughters, or widowed...
- Kibbutzim and families
- Sociology of the familySociology of the familyThe Sociology of the family examines the family, as an institution and a unit of socialisation, through various sociological perspectives, particularly with regard to the relationship between the nuclear family and industrial capitalism, and the distinct gender roles and concepts of childhood which...
- Structural functionalismStructural functionalismStructural functionalism is a broad perspective in sociology and anthropology which sets out to interpret society as a structure with interrelated parts. Functionalism addresses society as a whole in terms of the function of its constituent elements; namely norms, customs, traditions and institutions...
- Family relationships

