
Null corrector
Encyclopedia
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
, mirror
Mirror
A mirror is an object that reflects light or sound in a way that preserves much of its original quality prior to its contact with the mirror. Some mirrors also filter out some wavelengths, while preserving other wavelengths in the reflection...
s, beamsplitters, and converging lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
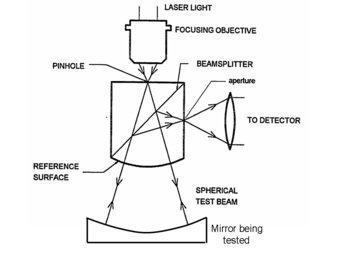
es. One method of doing this using a Shack cube is shown at the right, and many other setups are possible. An interferometer test such as this one generates a contour map of the deviation of the surface from a perfect sphere, with the contours in units of half the wavelength used. This is called a null test because when the mirror is perfect, the result is null (no contours at all). If the result is not null, then the mirror is not perfect, and the pattern tells where the optician should polish the mirror to improve it.
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
s or hyperbola
Hyperbola
In mathematics a hyperbola is a curve, specifically a smooth curve that lies in a plane, which can be defined either by its geometric properties or by the kinds of equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, which are mirror...
s, since these more complex shapes reduce optical aberrations and give a larger field of view
Field of view
The field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
. (See, for example, Ritchey-Chrétien telescope
Ritchey-Chrétien telescope
A Ritchey–Chrétien telescope is a specialized Cassegrain telescope designed to eliminate coma, thus providing a large field of view compared to a more conventional configuration. An RCT has a hyperbolic primary and a hyperbolic secondary mirror. It was invented in the early 1910s by American...
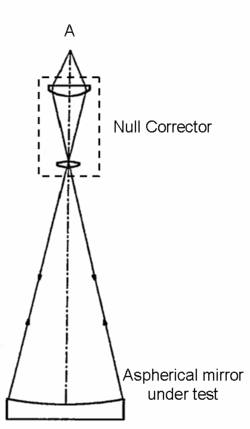
or LSST.) Non-spherical mirrors such as these will not give a null result when tested as above, and null results are strongly preferred (they are very clean tests that require little interpretation, and the results translate directly to polishing requirements). One solution is to introduce a null corrector, as shown in the second figure. This consists of one or more lenses and/or mirrors introduced into the optical path that makes the desired mirror look like a perfectly spherical mirror. Using this device, the measured contour map now shows difference from the desired shape instead of difference from a sphere. Now measurement and polishing can proceed just as in the spherical case. This method is used in the manufacture of almost all large mirrors for modern telescopes.
Since the mirror will be ground to what the null corrector thinks is the right prescription, it is critical that the null corrector be itself correct. An error in building the null corrector was in fact exactly the error that lead to the mirror in the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
being ground to the wrong shape. Less famously, this has happened in other cases as well, such as the New Technology Telescope
New Technology Telescope
The New Technology Telescope or NTT is an Alt-Az, 3.58-metre Richey-Chretien telescope part of the European Southern Observatory and began operations in 1989. It is located in Chile at the La Silla Observatory and was an early pioneer on the use of active optics...
. Originally, there was no easy way to test a null corrector, so mirror fabricators needed to take extra care that the lenses were correct and spaced correctly (this second part, spacing, was the source of the Hubble null corrector failure). With the advent of computer generated holograms
Computer generated holography
Computer Generated Holography is the method of digitally generating holographic interference patterns. A holographic image can be generated e.g...
, it is now possible to create a hologram with the phase response of an arbitrary mirror. Such a hologram can be made to analytically duplicate the phase response of the desired mirror, then tested with the null corrector just as the real mirror would be tested. If the combination looks like a spherical mirror to the interferometer, then both the null corrector and the hologram are shown to be correct. (In theory, they could each have errors that precisely cancel out, but this is highly unlikely since they are constructed independently by completely different procedures.)

